Shear Strength of Soils
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, which is essential in understanding the shear strength of soils. Can anyone tell me the main components of this criterion?

Isn't it about cohesion and friction angle?

Exactly! The equation is τ = c + σ·tan(ϕ). Here, τ represents shear strength, c is cohesion, σ is normal stress, and ϕ is the angle of internal friction. Does anyone remember what cohesion and friction angle contribute to?

Cohesion helps with the bonding between particles, while the friction angle relates to how soils resist sliding.

That's correct! To remember this, think of 'Cohesion Provides Stability' and 'Friction Resists Sliding'. Let’s proceed to discuss shear tests.
Types of Shear Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore the different types of shear tests. First up is the Direct Shear Test. Why do we use this method?

To measure the shear strength directly, right?

Correct! In this test, soil samples are subjected to shear until failure occurs, providing vital strength information. Next, we have the Triaxial Shear Test. Can someone explain its significance?

It allows us to apply confining pressure, which helps simulate real-world conditions.

Great job! The Triaxial Test can further be categorized into UU, CU, and CD tests, depending on whether pore water pressure is drained or not. Lastly, we have the Unconfined Compression Test - who wants to explain its focus?

It’s primarily for cohesive soils and checks their strength without lateral support.

Good work! Remember, cohesive soils like clays behave quite differently in compression. Let's summarize what we learned today.
Role in Pavement Support
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How does shear strength affect pavement support?

Higher shear strength means better load support capacity!

Exactly! If we encounter soils with low shear strength, what might we need to do?

We might need to stabilize them, like with lime or cement.

Excellent point! Stabilization techniques can significantly improve weak soils for better pavement performance. Let's review today's key points: Mohr-Coulomb theory, types of shear tests, and their importance in pavement design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The shear strength of soils is critical in determining their load support capacity in engineering applications. This section introduces the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, various types of shear tests, and highlights how shear strength affects pavement design.
Detailed
Shear Strength of Soils
The shear strength of soils plays a crucial role in the stability and load-bearing capacity of pavement structures. It is governed by the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, which defines shear strength (τ) as a function of soil cohesion (c) and the normal stress (σ) at failure. The relationship is expressed mathematically as:
\[ τ = c + σ \cdot\tan(ϕ) \]
where ϕ is the angle of internal friction. This equation illustrates how both cohesion and friction angle contribute to a soil's ability to withstand shear stress.
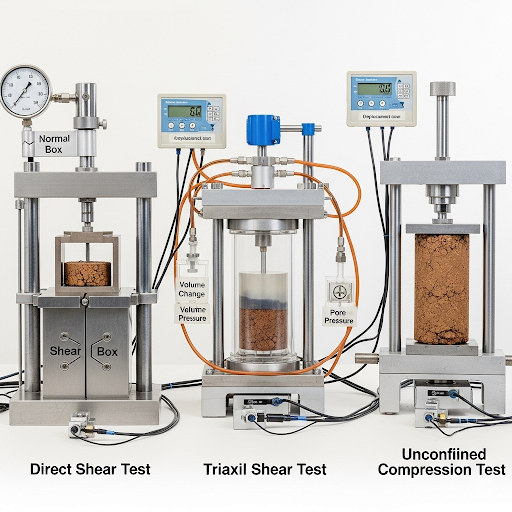
Many testing techniques have been developed to assess the shear strength of soils, the most common of which include:
- Direct Shear Test: Measures the shear strength by applying a shear force until failure occurs.
- Triaxial Shear Test: Provides insights into strength under varying confining pressures, with formats such as Unconsolidated Undrained (UU), Consolidated Undrained (CU), and Consolidated Drained (CD).
- Unconfined Compression Test: Primarily used for cohesive soils to determine their maximum load capacity without lateral confinement.
The shear strength of the soil directly influences the load support capacity of pavement. High shear strength soils are deemed suitable for providing adequate support under loads, while weaker soils may necessitate stabilization techniques to improve strength and performance in pavement applications. Thus, understanding shear strength is vital for successful transportation engineering and infrastructure stability.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
τ=c+σ⋅tan(ϕ)
- c: Cohesion
- φ: Angle of internal friction
Detailed Explanation
The Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion is a mathematical model that helps to determine when a soil will fail under shear stress. In the equation, τ represents the shear strength of the soil, c represents the cohesion (the inherent strength of the soil particles to stick together), and σ is the normal stress acting on the surface. The angle ϕ is the angle of internal friction, which indicates how much resistance the soil provides against sliding. When you apply stress to the soil, if the resulting shear stress exceeds the limit set by this equation, the soil will fail or slide.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a stack of books (soil layers) stacked on top of each other. The cohesion is like the sticky notes used to keep them together, while the angle of internal friction is how the rough surfaces of the book covers help prevent them from sliding off each other. If you push down with too much force (stress), the stack will collapse.
Types of Shear Tests
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Direct Shear Test
- Triaxial Shear Test (UU, CU, CD)
- Unconfined Compression Test (for cohesive soils)
Detailed Explanation
Shear tests are conducted to measure the shear strength of soil. The Direct Shear Test involves placing a soil sample in a device that allows it to be sheared under controlled pressure, providing direct measurements of shear strength. The Triaxial Shear Test is more complex and can control drainage conditions, testing different scenarios, including unconsolidated undrained (UU) and consolidated drained (CD) conditions. The Unconfined Compression Test is specific for cohesive soils and measures the compressive strength without any lateral confinement. This is particularly important for understanding how soils will behave under loads once constructed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the shear tests as different ways to test how a stack of cards behaves under pressure. The Direct Shear Test could be like pulling the cards sideways until they slip, while the Triaxial Test is like pushing from the sides while carefully lifting to see how much force they can take before falling apart. The Unconfined Compression Test is simply pressing down on the top of a stack of cards without any support, to see how much pressure they can handle before collapsing.
Role in Pavement Support
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- High shear strength → good load support capacity
- Low shear strength soils may require stabilization
Detailed Explanation
Shear strength is crucial in determining if the soil can support the weight of the infrastructure above it, such as roads and buildings. Soils with high shear strength can effectively support heavy loads without failing, making them ideal for pavement support. On the other hand, soils with low shear strength may not support such loads adequately, leading to potential pavement failure or deformation. To address this, stabilization methods can be employed to improve their strength.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a solid table can hold many books (high shear strength), while a stack of notebooks might buckle if too many are placed on it (low shear strength). When the notebooks are stacked, you could place a solid board underneath to support them better, just like how low shear strength soils can be stabilized to handle the weight of the pavement.
Key Concepts
-
Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion: A mathematical approach to compute shear strength based on cohesion and friction angle.
-
Shear Tests: Various testing methods (Direct Shear, Triaxial, Unconfined Compression) to determine soil shear strength.
-
Pavement Support: The relationship between shear strength and the load-bearing capacity of pavement structures.
Examples & Applications
In a Direct Shear Test, a soil sample is subjected to shear until failure, which allows engineers to determine the soil's shear strength.
Using the Triaxial Shear Test, engineers can simulate different pressures on a soil sample to analyze how it behaves under conditions analogous to those in the field.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cohesion sticks, Friction fends, Shear strength builds, the load it lends.
Stories
Imagine soil as a team, with Cohesion as the glue holding them together and Friction representing how they stand firm when challenged. When they work as a team, the soil is strong.
Memory Tools
To remember the shear strength equation, think of 'C-SF-ϕ' where C is Cohesion, S is Shear strength, and ϕ is the Friction angle.
Acronyms
Use the acronym C.A.S.T to remember
(Cohesion)
(Angle of internal friction)
(Shear strength)
(Type of test).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- MohrCoulomb Failure Criterion
A model that describes the shear strength of soils based on cohesion and internal friction.
- Cohesion
The tendency of soil particles to stick together, contributing to shear strength.
- Angle of Internal Friction (ϕ)
An angle that quantifies the shear resistance due to inter-particle friction.
- Direct Shear Test
A test that measures the shear strength of soil by applying a direct shear force.
- Triaxial Shear Test
A test that measures soil strength under controlled confining pressure.
- Unconfined Compression Test
A test used primarily for cohesive soils to measure their unconfined strength.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
