Types of Shear Tests
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Shear Strength
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we're going to explore shear strength in soils. Who can tell me why shear strength is important in engineering?

I think it determines how much load the soil can support.

Exactly! The shear strength indicates the soil's ability to resist sliding or shearing forces. Today, we'll look into specific tests.

What types of tests do we use?

Good question! We have the Direct Shear Test, Triaxial Shear Tests and Unconfined Compression Test. Let's start with the Direct Shear Test!
Direct Shear Test
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The Direct Shear Test allows us to measure the shear strength by applying a horizontal shear force. Can anyone tell me what parameters we determine during this test?

We determine cohesion and the angle of internal friction, right?

Yes! Those underlie the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion. Why is it beneficial to know these properties?

It helps us predict how the soil will behave under loads.

Exactly. Let’s not forget, the test is relatively simple and gives us quick results.
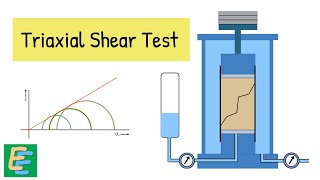
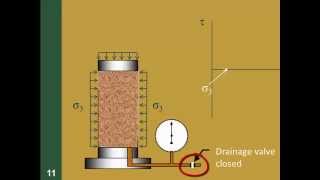
Triaxial Shear Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next up is the Triaxial Shear Test, which comes in three forms—UU, CU, and CD. What distinguishes them?

The drainage conditions during the test?

Right! Can someone summarize each type?

UU doesn't allow drainage, CU allows drainage before shearing, and CD allows drainage throughout the test.

Perfect! Each test can simulate different real-world conditions. Why might we choose one over the others?

It depends on the soil type and its anticipated behavior under load.

Exactly! Each test provides insights based on specific scenarios.
Unconfined Compression Test
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, we have the Unconfined Compression Test. Who can explain how this one works?

It tests cohesive soils without any confining pressure, measuring their unconfined compressive strength.

Exactly! What's advantageous about this test?

It's quick and straightforward to perform.

Right! While it doesn’t provide as comprehensive data as the Triaxial Test, it’s useful for initial assessments. In summary, shear tests are crucial for evaluating soil behavior!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, students will learn about the different types of shear tests used to determine the shear strength of soils, including the Direct Shear Test, Triaxial Shear Test (UU, CU, CD), and Unconfined Compression Test. Understanding these tests is essential for assessing the load support capacities of soils in transportation engineering.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In the field of geotechnical engineering, understanding the shear strength of soils is pivotal, particularly when designing and constructing different types of pavements. This section categorizes the shear tests into three main types:
- Direct Shear Test: This test measures the shear strength of a soil sample under controlled conditions by applying a shearing stress. It allows for the direct measurement of the failure plane in the soil and helps to find the effective stress parameters.
- Triaxial Shear Test: This is a more complex test where a cylindrical soil sample is subjected to all-around confining pressure, allowing for a precise measurement of soil strength under different drainage conditions:
- Unconsolidated Undrained (UU): No drainage occurs during the test, generally used for undisturbed clay samples.
- Consolidated Undrained (CU): The sample is allowed to consolidate before the shearing occurs.
- Consolidated Drained (CD): The sample is drained during shearing, making it suitable for cohesionless soils.
- Unconfined Compression Test (UCT): Primarily for cohesive soils, this test determines the unconfined compressive strength of soil without any confining pressure. It is simpler and quicker than the triaxial shear test.
Understanding these tests and their results provide engineers with vital information for assessing soil behavior under loads and designing pavements accordingly.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Direct Shear Test
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Direct Shear Test
Detailed Explanation
The Direct Shear Test measures the shear strength of soil by applying a normal load and a shear load until failure occurs. It divides the soil sample into two halves and shears them apart along a predetermined plane. This test helps to determine the soil's cohesion and angle of internal friction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Direct Shear Test like trying to pull a book from a stack of books. If you apply a strong enough force, the book will slide out. The strength required to pull it out is similar to the shear strength of soils.
Triaxial Shear Test
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Triaxial Shear Test (UU, CU, CD)
Detailed Explanation
The Triaxial Shear Test evaluates soil strength under different conditions of confining pressure. There are three types: Unconsolidated Undrained (UU), Consolidated Undrained (CU), and Consolidated Drained (CD). Each test varies based on the drainage conditions. This allows engineers to understand how soil will behave in different scenarios when subjected to stress.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how a sponge behaves when you squeeze it underwater (UU), release it (CU), or let it dry first (CD). The sponge reacts differently based on the pressure and moisture, similar to how soil behaves in each type of triaxial test.
Unconfined Compression Test
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Unconfined Compression Test (for cohesive soils)
Detailed Explanation
The Unconfined Compression Test assesses the compressive strength of cohesive soils without any lateral confinement. A cylindrical soil sample is subjected to axial loading until it fails. This test is particularly useful for cohesive soils, which tend to deform and lose strength when the moisture content changes.
Examples & Analogies
Picture squeezing a soft piece of dough in your hands. Initially, it deforms easily under pressure because there’s no outside support. This can represent the way cohesive soils act when force is suddenly applied.
Key Concepts
-
Direct Shear Test: A test to determine the shear strength of soil by applying horizontal forces.
-
Triaxial Shear Test: A method for determining shear strength under different conditions of drainage and pressure.
-
Unconfined Compression Test: A straightforward test for assessing the compressive strength of cohesive soils without confinement.
Examples & Applications
An engineer conducts a Direct Shear Test to obtain soil strength data needed for a roadway project.
In a city with clayey subgrades, a Triaxial Shear Test is performed to evaluate how the soil will respond to the stresses from traffic loads.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Shear strength tests must be done, to see how soil holds together, one in a box, one in a press, and one simply unconfined, oh yes!
Stories
Once upon a time, a civil engineer had a tricky site with clayey soil. To understand its strength, he performed tests – first pulling it apart with the Direct Shear Test, then squeezing with the Unconfined Test, and finally holding it in pressure with the Triaxial Test. He understood how the soil would behave and crafted the perfect pavement.
Memory Tools
Remember the types of shear tests with 'DUT': Direct, Unconfined compression, and Triaxial.
Acronyms
Use ‘SUTT’ for Shear tests
for Shear strength
for Unconfined Compression
for Triaxial
for Tests.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Shear Strength
The ability of a soil to resist shear stress, influencing its load-bearing capacity.
- Direct Shear Test
A test that measures the shear strength of soil by applying a horizontal force to it.
- Triaxial Shear Test
A test that measures shear strength under varying confining pressures and drainage conditions.
- Unconfined Compression Test (UCT)
A test that determines the unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soils.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
