Soil Texture and Gradation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Soil Texture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will talk about soil texture and its importance in engineering! Can anyone here tell me what soil texture refers to?

Is it about how the soil feels, like gritty or smooth?

Good observation, Student_1! Soil texture more specifically deals with the distribution of different particle sizes in the soil. This affects drainage and compaction.

How does the particle size affect drainage?

Great question! Larger particles tend to drain better because there are more voids for water to pass through, whereas finer particles can hold water.

Can you give us an example of a soil type?

Certainly! Sandy soils are well-drained and can support construction well. Now, let's remember that soil texture is not just about feel but about size distribution!

To recap, what do we use to measure soil texture?

Sieve analysis!

Exactly! Well done, everyone!
Methods of Particle Size Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand soil texture, let's discuss how to measure the particle sizes. Who knows the methods we use?

We use sieve and hydrometer analysis, right?

Exactly! Sieve analysis is for particles larger than 75 µm, while hydrometer analysis focuses on smaller particles. Can anyone tell me what we can learn from these analyses?

We can find out the gradation of the soil!

Right again! The gradation will help us classify the soil as well-graded, poorly graded, or gap-graded. What differences do you think that makes in engineering?

Well-graded soils would have better compaction properties.

Exactly! Remember that well-graded soils tend to have a mix of particle sizes, leading to better compaction and support.

Let's summarize: What are the key analyses we perform for soil texture?

Sieve analysis and hydrometer analysis!

Right! Well done!
Types of Gradation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's wrap up our discussion by talking about the types of gradation in soil. Can anyone name the three types?

Well-graded, poorly-graded, and gap-graded!

That’s correct! Can someone explain what well-graded means?

It means there's a wide range of particle sizes!

Exactly! And how is that beneficial?

It compacts better, right?

Spot on! Now, what about poorly-graded soils?

They have mostly the same size of particles!

Yes, and those typically do not compact as well. Lastly, what about gap-graded?

They miss some intermediate sizes.

Exactly! These gradations can significantly impact how a soil behaves under load. Let’s summarize: what are the three types of gradation?

Well-graded, poorly-graded, and gap-graded!

Excellent! You all did great in understanding soil gradation.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Soil texture is defined by the distribution of different particle sizes within a soil sample, which greatly influences its engineering properties such as drainage, compaction, and load distribution. The section discusses methods like sieve and hydrometer analysis for determining particle size distribution, and it categorizes the types of gradation, including well-graded, poorly-graded, and gap-graded soils.
Detailed
Soil Texture and Gradation
Soil texture is crucial in civil engineering as it describes the distribution of soil particle sizes, affecting various engineering properties including drainage, compaction, and load support. Understanding soil texture helps engineers assess the suitability of soils for construction projects. The key points covered in this section include:
- Particle Size Distribution: This defines the proportions of different particle sizes in a soil sample, which is vital for determining its physical behavior.
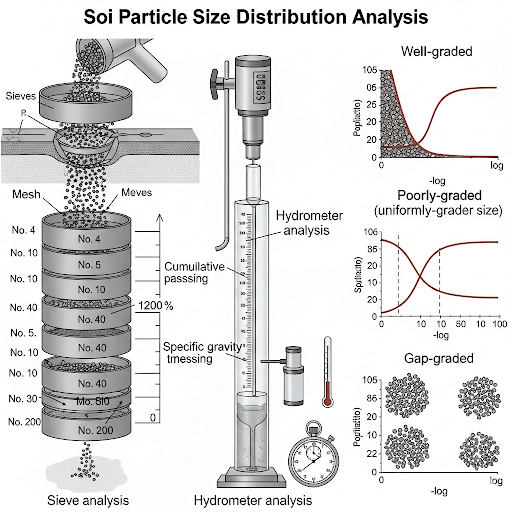
- Sieve Analysis: A method for assessing the distribution of soil particles larger than 75 µm using mechanical sieves. The results can be visualized on a gradation (or particle size) curve.
- Hydrometer Analysis: Used for particles smaller than 75 µm to evaluate fine soils such as silt and clay, utilizing Stokes' law of sedimentation.
- Types of Gradation: Includes well-graded (a wide range of particle sizes), poorly-graded (uniform particle size), and gap-graded (missing intermediary sizes) soils. These classifications directly influence soil behavior and compaction capabilities.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Particle Size Distribution
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Represents the range and proportion of particle sizes
- Important for understanding drainage, compaction, and load distribution
Detailed Explanation
Particle size distribution refers to the varying sizes of particles that make up the soil. This distribution is crucial because it affects how water drains through soil and how well the soil can be compacted. For example, finer particles like clay can hold water more than larger particles like sand. Understanding this distribution helps engineers predict how soil will behave under certain conditions, such as during heavy rainfall or certain weight applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of particle size distribution like a bag of mixed nuts. If you have a variety of sizes, the small ones can fill in the gaps between the larger ones, making for a dense and stable mix. However, if all the nuts are the same size, they won’t fit together well, leading to a less stable structure.
Sieve Analysis
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- For particles > 75 µm (mechanical sieving)
- Results plotted on a gradation curve
Detailed Explanation
Sieve analysis is a method used to determine the particle size distribution of coarse-grained soils. In this process, soil is passed through a series of sieves with different mesh sizes. Particles larger than 75 micrometers are retained on the sieves, allowing engineers to assess the proportion of different sizes in the soil sample. The results are usually graphed on a gradation curve, which visually represents how many particles fall into various size categories. This analysis is fundamental for understanding how well the soil can support structures.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making a fruit salad. If you have a mixture of large apples and small grapes, the sieve analysis would help you see how much of each fruit (size) you have in your mix. Just as a balanced fruit salad needs a good mix for taste and texture, a well-graded soil mix is important for stability and drainage.
Hydrometer Analysis
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- For particles < 75 µm (silt and clay)
- Based on sedimentation principles (Stokes’ law)
Detailed Explanation
Hydrometer analysis is used to determine the distribution of fine particles in soil, specifically those smaller than 75 micrometers, like silt and clay. This method utilizes Stokes' law, which states that the rate of sedimentation is proportional to the square of the particle diameter. By observing how quickly particles settle in a fluid, engineers can quantify the sizes and concentrations of the fine particles within a given soil sample. This information is critical for understanding the soil's behavior, especially in terms of drainage and load-bearing.
Examples & Analogies
Think of hydrometer analysis like observing how different types of sand and clay settle when mixed in water. Larger grains will sink quickly, while tiny clay particles will take longer to settle. Just like distinguishing how fast different types of sediment settle helps you understand the makeup of a riverbed, hydrometer analysis helps engineers understand soil composition.
Types of Gradation
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Well-graded: Wide range of sizes
- Poorly-graded (uniform): Mostly same-sized particles
- Gap-graded: Missing intermediate sizes
Detailed Explanation
Gradation refers to the distribution of particle sizes within a soil sample. There are three main types:
- Well-graded soils have a wide range of particle sizes, leading to better compaction and stability.
- Poorly-graded (or uniform) soils consist mostly of particles of the same size, which can result in poorer load distribution and higher susceptibility to erosion.
- Gap-graded soils lack particles of intermediate sizes, which can create voids and reduce stability. Each type has implications for engineering projects, especially in constructing pavements and foundations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine packing a suitcase. If you pack your shoes (large items), socks (small items), and clothes (medium items) well together, you'll be able to fit everything in tightly. That's like well-graded soil. If you only pack all socks, your suitcase would have lots of empty space (poorly-graded), and if you had only shoes and no socks or clothes, you’d find it awkward and unstable (gap-graded).
Key Concepts
-
Soil Texture: Describes the proportions of different particles in the soil which influence its properties.
-
Particle Size Distribution: The composition of various particle sizes within a soil sample, crucial for understanding soil behavior.
-
Sieve Analysis: A method to determine the gradation of soil particles larger than 75 µm.
-
Hydrometer Analysis: An analysis technique for particles smaller than 75 µm, especially in silt and clay.
Examples & Applications
Sandy soil has a high proportion of larger particles, resulting in excellent drainage.
Clay soil has very fine particles, which lead to poor drainage and high plasticity.
Well-graded gravels are ideal for subbase layers due to their ability to compact effectively.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sandy soil drains free, Clay holds water, can't you see?
Stories
Imagine a beach where grains of sand sit side by side, each size playing its role; some drain well, while others tightly hold moisture just like the gentle clay beside a pond.
Memory Tools
For particle sizes, think ‘S, H, G’ - Sieve, Hydrometer, Gap! (Sieve for bigger, Hydro for small, Gap for sizes that don't mingle at all.)
Acronyms
P-S-H
Particle Sizes Help! (Remember 'P' for Particle
'S' for Sizes
'H' for Help in analysis.)
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Soil Texture
The relative proportions of different particle sizes in soil, influencing its physical properties.
- Particle Size Distribution
The distribution of various particle sizes in a soil sample, impacting its behavior and engineering applications.
- Sieve Analysis
A technique used to determine the size distribution of soil particles larger than 75 µm using mechanical sieves.
- Hydrometer Analysis
A method for measuring the particle size distribution of fine soils through the use of sedimentation principles.
- WellGraded Soil
Soil with a wide range of particle sizes, resulting in good compaction and stability.
- PoorlyGraded Soil
Soil composed predominantly of one particle size, which usually leads to poor compaction.
- GapGraded Soil
Soil that is lacking certain intermediate sizes in its particle distribution, which affects its compaction and drainage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
