Best Practices in Testing and Debugging
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Testing Best Practices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're delving into the best practices for testing. Can anyone tell me why writing tests for both positive and negative cases is crucial?

It's important because we need to see how our code behaves under both expected and unexpected scenarios.

Yeah, if we only test one case, we might miss bugs that appear under different conditions.

Exactly! This approach ensures that our software can handle different user inputs effectively. Now, why should we keep test cases isolated and repeatable?

So that if one test fails, we can tell it's due to that specific case and not because of others interfering.

Correct! Clear isolation helps in pinpointing issues. Remember, meaningful test names improve readability—think clarity!

Right, it makes it easier to understand what each test does at a glance.

Great, let's recap! Writing tests for both positive and negative cases ensures thorough checking, and isolated test cases enhance accuracy in debugging.
Debugging Best Practices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, shifting gears, what’s one of the first things you should do when you encounter a bug?

We should try to reproduce the bug consistently to understand its conditions!

And we could use version control to see if any recent changes might have caused the issue.

Absolutely! Both techniques are essential. Logging important events also helps track down what's happening in the code—can someone share why logging is invaluable?

Logs show us what the application was doing leading up to an error, which can be crucial for troubleshooting.

Exactly. Lastly, how should we approach debugging mentally?

We shouldn’t panic! Taking a systematic approach helps us dissect the problem step-by-step.

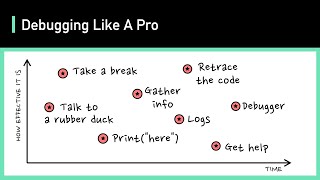
Well said! To sum up, effective debugging is about replication, monitoring, and remaining calm to solve issues systematically.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights critical methodologies for fostering robust testing and debugging processes, enabling developers to ensure code reliability and quality. It underscores the importance of conducting tests for both positive and negative scenarios, maintaining isolated test cases, and employing systematic debugging techniques.
Detailed
Best Practices in Testing and Debugging
This section emphasizes the significance of adhering to best practices in the realms of testing and debugging to facilitate reliable software development.
Testing Best Practices
- Write tests for both positive and negative cases: it is crucial to assess how code behaves under different scenarios, ensuring reliability and robustness.
- Keep test cases isolated and repeatable: tests should not depend on one another, fostering a reliable test environment where failures can be traced accurately.
- Use meaningful test names: descriptive naming conventions enhance readability and clarity, making it easier to understand what each test is intended to validate.
- Keep tests in a separate test directory: a well-organized structure facilitates better management and quick location of tests.
- Run tests in CI pipelines: integrating testing routines in continuous integration processes ensures that code changes are assessed and validated regularly.
Debugging Best Practices
- Reproduce bugs consistently: replicating bugs is crucial in understanding the conditions under which they manifest, aiding in effective troubleshooting.
- Use version control to compare changes: examining code revisions aids in identifying introduced issues since last successful builds.
- Log important events and exceptions: maintaining logs is invaluable in understanding the application's behavior during execution, especially when problems arise.
- Don't panic—be systematic: a methodical approach to debugging not only enhances effectiveness but also maintains composure during troubleshooting processes.
These practices contribute significantly towards achieving a high standard of code quality and reliability, which is especially important in large-scale and mission-critical applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Testing Best Practices
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Write tests for both positive and negative cases.
• Keep test cases isolated and repeatable.
• Use meaningful test names.
• Keep tests in a separate test directory.
• Run tests in CI pipelines.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines a series of key practices that help ensure effective testing of software. It emphasizes that tests should cover both successful scenarios (positive cases) and error scenarios (negative cases) to capture a comprehensive view of application performance. Furthermore, tests should be independent and reproducible; that means running one test shouldn’t affect others. Meaningful names help developers quickly identify what each test is verifying. Also, organizing tests in a separate directory helps maintain clarity within the project's code structure. Lastly, integrating testing into Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines ensures tests are executed automatically with every code change, which helps catch errors early.
Examples & Analogies
Think of testing like preparing for an exam. You would study both the potential easy questions (positive cases) and the trickier ones (negative cases). Each section of your study material should be independent, meaning understanding one chapter shouldn’t confuse another. Giving each topic a clear name (like 'Fractions' or 'Grammar') helps you know what to focus on quickly. By having organized study materials and regularly reviewing with past exams (CI pipelines), you increase your chances of passing the exam.
Debugging Best Practices
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Reproduce bugs consistently.
• Use version control to compare changes.
• Log important events and exceptions.
• Don't panic—be systematic.
Detailed Explanation
This part lists best practices for debugging effectively. Reproducing a bug consistently is crucial as it helps identify the root cause reliably. Utilizing version control allows developers to look at what changes might have caused a bug by comparing different versions of the code. Logging critical events and errors provides insight into how the application behaves in real situations and assists in diagnosing issues afterward. Finally, approaching debugging in a calm and systematic manner improves the chances of resolving the issue more efficiently rather than rushing into fixes that may not address the underlying problem.
Examples & Analogies
Consider debugging a software issue like troubleshooting a car that won’t start. First, you try to understand what leads to the problem consistently (reproduce the bug). Then, you check what previous repairs or modifications were made to see if they might have caused this issue (version control). Jotting down what you did each time, including failures, helps you pinpoint when things changed (logging events). Lastly, staying calm and methodical rather than panicking allows you to think clearly and work through potential issues, checking each one step by step until the problem is identified.
Key Concepts
-
Testing Best Practices: Crucial methodologies to ensure a robust testing process including scenarios that cover all cases.
-
Debugging Best Practices: Systematic methods to identify and resolve software issues efficiently.
Examples & Applications
Writing separate tests for user login: one for successful login, one for incorrect credentials to ensure both scenarios are covered.
Setting up logs to capture critical application errors to monitor the execution flow and quickly identify failures.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Test it twice, once wrong, once right, helps to catch bugs that may hide out of sight.
Stories
Imagine a detective in a town, testing all possible scenarios to catch a criminal—sometimes it’s not the one you expect!
Acronyms
R.A.C.E. - Reproduce, Analyze, Compare (changes), and Execute debugging methods.
S.A.F.E. - Systematic Approach For Efficient debugging.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Positive Case
A scenario where the code behaves as expected.
- Negative Case
A scenario that tests the code’s response to unexpected or invalid input.
- Isolated Test Case
A test case that is independent of others to avoid cascading failures.
- CI Pipeline
Continuous Integration pipelines where code is automatically tested upon changes.
- Version Control
A system that records changes to files over time, allowing comparisons and restorations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
