Setting Up JUnit
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Adding Dependency for JUnit
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn how to set up JUnit for testing in Java projects. Let's start by adding the necessary dependencies.

What do you mean by dependencies, and why are they important?

Great question! Dependencies are libraries or frameworks that your project requires to function correctly. In the case of JUnit, we need to tell our project to include the JUnit library so we can use its features for testing.

How do we add JUnit if we're using Maven?

If you're using Maven, you'll need to add the following code to your `pom.xml`: `<dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId> <version>5.10.0</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>`. This tells Maven to download JUnit version 5.10.0 from the repository.

What about Gradle? How do we add it there?

In Gradle, you would add this line to your `build.gradle` file: `testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.10.0'`. Remember, these dependencies are essential for your project’s testing functionalities.

Do we need to do anything else after adding the dependencies?

Yes! The next step is to ensure your IDE is properly configured to recognize and work with JUnit. This is key to executing your tests efficiently. Any questions on what we discussed?

Can you summarize the process of adding dependencies?

Sure! To summarize, you add the JUnit dependency in either the `pom.xml` for Maven or the `build.gradle` for Gradle, depending on your build tool.
Configuring Your IDE
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've added the dependencies, let’s talk about configuring your IDE. Most modern IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse support JUnit directly.

What settings do we need to check in IntelliJ IDEA?

In IntelliJ, you can simply create a new JUnit test class, and it should automatically recognize JUnit libraries if set up correctly. You can verify this by checking the project structure under Libraries.

And what about Eclipse, does it work the same way?

Yes! In Eclipse, ensure that JUnit is added as a library in your build path. This allows the IDE to run your JUnit tests without issues.

How important is it to have the IDE set up correctly?

Having the IDE set up correctly is critical as it streamlines your testing process, saving you time and avoiding confusion when running tests. Understanding both dependency management and IDE configuration is key to effective testing.

Can you recap the steps we discussed for configuring the IDE?

Absolutely! First, create a new test class, and the IDE should recognize JUnit. Check the project structure to confirm that JUnit libraries are included properly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Setting up JUnit involves adding the appropriate dependencies in your project using either Maven or Gradle and ensuring that your IDE is configured to support JUnit. This setup is crucial for leveraging JUnit's features effectively in unit testing.
Detailed
Setting Up JUnit
Setting up JUnit is a foundational step for conducting unit testing in Java applications. This section outlines two primary steps necessary for getting JUnit running:
Step 1: Add Dependency
- Maven: To use JUnit with Maven, you need to include the following dependency in your
pom.xmlfile:
- Gradle: For projects using Gradle, the same can be achieved by adding this line to your
build.gradlefile:
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.10.0'
Step 2: Configure IDE or Build Tool
Most modern Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse come with built-in support for JUnit, allowing you to execute your tests seamlessly. Ensuring that your IDE is properly configured is essential for an efficient testing workflow.
In this chapter, understanding how to set up JUnit correctly provides the groundwork for writing and executing unit tests, which ultimately enhances code quality through systematic testing.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
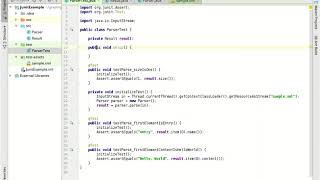
Step 1: Add Dependency
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Maven
Gradle
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.10.0'
Detailed Explanation
To use JUnit in your project, the first step is to add it as a dependency. If you are using Maven as your build tool, you will add a dependency block in your pom.xml file. This block specifies the JUnit library, indicating the group ID, artifact ID, and version. For Gradle, you will add the JUnit dependency in your build.gradle file using the testImplementation directive. This ensures that the JUnit library is included when you run your tests.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this step as adding an essential ingredient to a recipe. Just like you need flour to bake a cake, you need the JUnit library to write and run tests in your Java application.
Step 2: Configure IDE or Build Tool
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Most modern IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse support JUnit out of the box.
Detailed Explanation
After adding JUnit as a dependency, ensure that your development environment can recognize and use it. Most modern Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), such as IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse, have built-in support for JUnit, which means they can automatically detect the JUnit library. You may need to refresh or restart your IDE to fully integrate JUnit, allowing you to start writing your tests immediately.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you set up a new music system at home. After connecting all the cables, you would configure it with your smartphone to play your favorite songs. Just like that configuration allows you to enjoy music, this step sets up your IDE to work seamlessly with JUnit for testing.
Key Concepts
-
Dependencies: Required libraries or frameworks for a project.
-
JUnit Setup: How to configure your project to use JUnit with dependency managers like Maven or Gradle.
-
IDE Configuration: Ensuring your development environment is ready to recognize and run JUnit tests.
Examples & Applications
For Maven, add <dependency><groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId><artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId><version>5.10.0</version><scope>test</scope></dependency> to pom.xml.
For Gradle, add testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.10.0' to build.gradle.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Set up JUnit, don’t forget—pom and build together, your tests will be a hit!
Stories
Imagine a developer named Jack who wanted to test his code. He added JUnit through Maven and Gradle, like a magician preparing his tools for a show!
Memory Tools
To remember the steps for setting JUnit: DEP - Dependency, E - Easy configuration in IDE.
Acronyms
JEST - JUnit Easy Setup Tutorial.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- JUnit
A widely used open-source framework for writing and running tests in Java.
- Dependency
A library or framework that a program or project requires to function correctly.
- Maven
A build automation tool used primarily for Java projects that manages project builds and dependencies.
- Gradle
A powerful build automation tool that can handle projects in any language, including Java, often used for dependency management.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
