JUnit Assertions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to JUnit Assertions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to talk about JUnit Assertions, an essential tool for verifying our test results. Can anyone tell me what an assertion is in the context of testing?

I think it's a way to check if the expected outcome matches the actual outcome of a test.

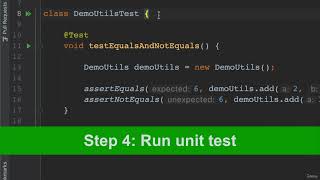
Exactly! Assertions help us determine whether our code works as intended. One popular assertion is `assertEquals(expected, actual)`, which checks if two values are equal.

So, if they are not equal, does that mean there's a bug in our code?

Yes! If the values don't match, it indicates that something isn't right. Remember the phrase 'Expect equals' to recall this.

Can we use other assertions for different situations?

Absolutely! Assertions like `assertTrue(condition)` and `assertNull(object)` are also available. These allow us to verify boolean expressions and check for null objects.

Can you give us an example?

Certainly! If we want to check if a user input is valid or not, we can assert that a certain condition holds true.

What if we expect an exception?

Great question! For that scenario, we use `assertThrows()` to verify that the expected exception occurs during execution.

In summary, JUnit Assertions provide various options for testing different conditions in our code, helping us ensure its correctness.
Common Assertion Methods
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've discussed the importance of assertions, let's dive into some common methods. First, who can remind me what `assertEquals()` does?

It checks if two values are equal!

Precisely! And why is that important in testing?

Because if they are not equal, our code might not be working correctly.

Exactly. Next, let's discuss `assertTrue(condition)`. When would we use this?

When we want to ensure a specific condition is true!

Correct! Similarly, we use `assertFalse(condition)` to confirm that a condition is false. Both methods are essentials for validating expected behaviors.

What about null checks?

For checking null or non-null conditions, we use `assertNull(object)` and `assertNotNull(object)`. These methods help ensure that our objects exist or do not exist as expected.

And what’s the benefit of using `assertThrows()`?

This method allows us to confirm that specific code throws the expected exceptions, which is vital in error handling and testing!

So, can someone summarize what we learned about the different assertions?

We learned that assertions are methods that validate different conditions, such as equality and null values!

Exactly! Remember, using the right assertion helps us create robust and reliable unit tests.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
JUnit Assertions provide various methods to check different conditions in unit tests, such as verifying equality, checking boolean conditions, and validating nullability. They are essential for ensuring that the code behaves as expected during testing.
Detailed
JUnit Assertions
JUnit Assertions are a crucial component of the JUnit testing framework. They allow developers to check that the actual outcome of code matches the expected outcome during unit tests. The most commonly used assertion methods include:
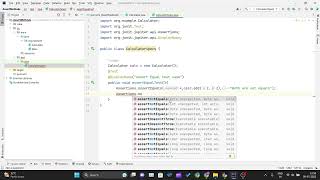
- assertEquals(expected, actual): Verifies if the expected and actual values are equal.
- assertTrue(condition): Checks if the specified condition evaluates to true.
- assertFalse(condition): Validates that a condition evaluates to false.
- assertNull(object): Assesses whether an object is null.
- assertNotNull(object): Confirms that an object is not null.
- assertThrows(): Checks if a specific exception is thrown during execution.
These assertion methods provide developers with the tools necessary to write effective unit tests, ensuring code reliability and correctness. By implementing various assertions, developers can identify issues early, making their code more maintainable and dependable.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Testing Exception Handling
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
assertThrows()Checks if exception is thrown
Detailed Explanation
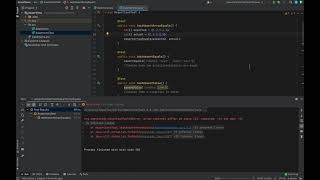
assertThrows() is an essential assertion method that allows you to test whether a specific exception is thrown in a given block of code. This is especially important for scenarios where you want to ensure that your code fails gracefully or handles errors correctly. You wrap the code that is expected to throw an exception in the assertThrows() method, which captures the exception type you anticipate, allowing you to confirm that your error handling works as intended.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an online payment system where users input their credit card information. If a user enters an invalid card number, the system should trigger an error notification. Testing whether this error handling functionality is working properly is akin to using assertThrows(). You are essentially confirming that your application responds correctly when faced with an expected problem, just like ensuring that an online system rejects invalid data and informs the user of the error.
Key Concepts
-
Assertion methods: Functions that validate expected outcomes in unit tests.
-
assertEquals: Method to check if two values are the same.
-
assertTrue: Method to verify that a provided condition is true.
-
assertThrows: Method to check if an exception is thrown.
Examples & Applications
Example of assertEquals: assertEquals(5, 3 + 2) checks if the calculation of '3 + 2' equals to '5'.
Example of assertThrows: assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> { throw new IllegalArgumentException(); }); checks if an IllegalArgumentException is thrown.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To check if it’s true, use assertTrue; if conditions are wrong, assertFalse all along.
Stories
Imagine a detective comparing clues, assertEquals checks all the views; and when in doubt about the state, assertNotNull decides the fate.
Memory Tools
Remember: ETV for Assertions: Equals, True, Value! It's essential for success!
Acronyms
AET for assertions
= assertEquals
= assertTrue
= assertThrows.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- assertEquals
A JUnit method that checks if two values are equal.
- assertTrue
A JUnit method that verifies if a specified condition is true.
- assertFalse
A JUnit method that verifies if a specified condition is false.
- assertNull
A JUnit method that checks if a given object is null.
- assertNotNull
A JUnit method that checks if a given object is not null.
- assertThrows
A JUnit method that verifies whether a specific exception is thrown.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
