Parameterized Tests
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Parameterized Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we're going to explore Parameterized Tests in JUnit. Can anyone tell me what they think parameterized means in this context?

Does it mean testing a function with different values?

Exactly! Parameterized Tests allow us to run the same test multiple times with different inputs. This makes our tests more robust. Remember the acronym R.E.A.D. – **R**un, **E**valuate, **A**djust, **D**ocument. It helps us to recall the testing cycle while using Parameterized Tests.

So how do we set this up in JUnit?

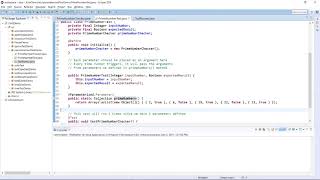
Great question! We use the `@ParameterizedTest` annotation followed by the parameter value source, like `@ValueSource(ints = {1, 2, 3})`. It will pass these values into our test method.
Example of Using Parameterized Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at an example. If we wanted to test if certain numbers are even, we can create a test method like this: `@ParameterizedTest @ValueSource(ints = {1, 2, 3})`. What do we expect here?

We expect the test to check each number if it's even or not.

Correct! The assertion would look like `assertTrue(number % 2 == 0);`. What is the significance of this approach?

It helps us avoid writing separate test cases for each number!

Exactly! It keeps our test class clean and efficient. Always think of ways to optimize your tests.
Benefits of Parameterized Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone mention some benefits of using Parameterized Tests rather than individual test cases?

It reduces duplication in tests!

Exactly! Reducing code duplication is crucial. Also, it makes maintaining tests easier. Let's remember the saying: 'Less code, fewer bugs.' What else?

It can lead to discovering edge cases more easily because you can test a range of inputs!

Great point! You can easily validate how your code behaves under various conditions with a single test method.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces Parameterized Tests in JUnit, explaining how to run the same test repeatedly with different parameters. It highlights the use of the @ParameterizedTest annotation and provides an example of testing even numbers using various integer inputs.
Detailed
Parameterized Tests in JUnit
Parameterized Tests allow JUnit to run the same test method with different input values, simplifying the process of testing functions that have similar logic but varying inputs. By using the annotation @ParameterizedTest, developers can test methods with a range of parameters provided through various sources such as @ValueSource, @MethodSource, or @CsvSource. This approach leads to cleaner and more maintainable test code while ensuring comprehensive testing coverage of edge cases and varying scenarios. For example, testing whether numbers are even can be efficiently done by providing an array of integers to verify against expectations with simple assertions.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Parameterized Tests
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
JUnit allows testing a method with multiple sets of parameters.
Detailed Explanation
Parameterized tests in JUnit enable a single test method to be executed multiple times with different inputs. This helps in eliminating redundant test code while still allowing thorough testing of a method's logic under various conditions. Instead of writing separate test methods for each input scenario, you define the method once and specify the varied inputs it should test against. This is particularly useful when the same logic is validated with several sets of data, making your tests easier to manage and understand.
Examples & Analogies
Think of parameterized tests like a recipe that can be made with different ingredients. For example, if you're testing a cake recipe that can have chocolate, vanilla, or lemon flavors, instead of writing separate instructions for each flavor, you can create a single set of instructions (the test) and just change the ingredient (the parameter) for each one. This makes it easier to see how the recipe holds up no matter which flavor you choose.
Example of a Parameterized Test
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
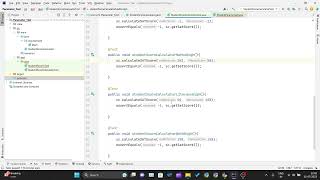
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(ints = {1, 2, 3})
void testEvenNumbers(int number) {
assertTrue(number % 2 != 0);
}
Detailed Explanation
In this example, we use the @ParameterizedTest annotation to define a test method, testEvenNumbers, that will be run three times—once for each value in the array {1, 2, 3}. The @ValueSource(ints = {1, 2, 3}) annotation is used to provide the different integer parameters to the test. Inside the test, we assert that the number is odd using assertTrue(number % 2 != 0), which means the test will pass if the number is indeed odd. However, since 1 and 3 are odd while 2 is even, this test will fail for the input 2. This highlights how parameterized tests can help confirm logic over a range of input values efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a health screening process that checks if a person's blood pressure reading is within normal limits. Instead of running separate tests for various readings, a parameterized test could use a range of sample data (like different blood pressure readings). The nurse could apply the same logic to check if each reading is 'normal' or 'high' without having to write separate tests for each reading.
Key Concepts
-
Parameterized Tests: Tests that allow multiple sets of parameters to be passed, enhancing testing flexibility.
-
@ParameterizedTest: Annotation indicating that the test runs with multiple sets of parameters.
-
ValueSource: Annotation that specifies a source of values to be used in parameterized tests.
Examples & Applications
Using @ParameterizedTest with @ValueSource for testing even numbers: @ParameterizedTest @ValueSource(ints = {2, 4, 6}) void testEvenNumbers(int number) { assertTrue(number % 2 == 0); }.
Running a parameterized test for checking odd numbers could look like: @ParameterizedTest @ValueSource(ints = {1, 3, 5}) void testOddNumbers(int number) { assertTrue(number % 2 != 0); }.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Run the test many times, spread the values wide, Parameterized testing shows results with pride.
Stories
Imagine a chef testing different recipes with multiple ingredients to find the best flavor. Each test represents a parameterized input, just like testing different values in JUnit.
Memory Tools
P.A.V.S: Parameterized Annotations like ValueSource Simplify testing!
Acronyms
R.E.A.D. = **R**un, **E**valuate, **A**djust, **D**ocument the testing process!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Parameterized Test
A test that is run multiple times with different parameters to validate the method's behavior under varying conditions.
- @ParameterizedTest
An annotation in JUnit that indicates the method is a parameterized test case.
- @ValueSource
An annotation that provides a single array of values to a parameterized test method.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
