Covalent Bond
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Covalent Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today, we will delve into covalent bonds. A covalent bond forms when two atoms share electrons. Can anyone tell me why atoms might want to share electrons?

To fill their outer electron shell and become stable!

Exactly! This is why we often talk about the 'octet rule.' To help you remember, think of the octet rule as the '8 is great' principle. Now, how can we represent these shared electrons visually?

Using Lewis dot structures!

Spot on! Lewis dot structures allow us to visualize how the electrons are shared. Let's sketch the structure for H2 together. Who wants to draw it?

I can do it! We just put one H atom with one dot and the other H with another dot, and connect them.

Great job! That shows the single covalent bond. Remember: single bonds are denoted by sharing a pair of electrons!

To summarize, covalent bonds form by electron sharing, achieving stability through the octet rule. Let's move to types of covalent bonds!
Types of Covalent Bonds
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we covered single covalent bonds, what happens when two atoms share more than one pair of electrons?

They form double or triple bonds!

That's right! For instance, in carbon dioxide (CO2), we have double bonds. Can anyone sketch that structure?

There would be one carbon in the middle and two oxygens at the ends, with two pairs of electrons between each pair.

Perfect! And what about nitrogen? What bond does nitrogen form in N2?

That would be a triple bond, right?

Exactly! So to summarize, one atom sharing one pair of electrons forms a single bond, while sharing two or three pairs forms double or triple bonds. Let’s practice with some Lewis structures!
Molecular Geometry and Bonding
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how does knowing about covalent bonds help us predict molecular geometry?

It helps us understand the shape based on how the bonding and lone pairs around the central atom repel each other.

Correct! This is known as the VSEPR theory. Does anyone remember the order of repulsion strengths?

It's lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair!

Awesome! So it affects the angles in those shapes too. Let's now attempt to predict the shape of water using the VSEPR model.

Since water has two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, it should have a bent shape.

Exactly! And as a recap, covalent bonds not only determine how atoms connect but also how those connections shape the entire molecule.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the concept of covalent bonding as articulated by Lewis and Langmuir, explaining how atoms achieve stable electron configurations through electron sharing. It delves into the formation of single, double, and triple bonds, and introduces Lewis dot structures as a way to visualize these bonds.
Detailed
Covalent Bond
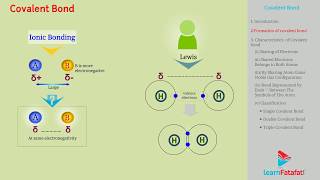
Covalent bonds are created when atoms share electrons, allowing them to achieve a full valence shell and connect in stable configurations. Langmuir refined Lewis's original postulation, explaining covalent bonds as the result of electron sharing. The sharing involves two atoms contributing at least one electron to form a pair that constitutes a bond. This section introduces Lewis dot structures, allowing for the representation of molecules.
Key Types of Covalent Bonds:
1. Single Covalent Bond: Formed when two atoms share one electron pair, exemplified by H2.
2. Double Covalent Bond: Involves sharing two pairs of electrons, as seen in CO2.
3. Triple Covalent Bond: Results from sharing three pairs of electrons, illustrated by N2.
In addition to introducing these concepts, the section emphasizes the need for understanding molecular geometry, which can be predicted based on the number of bonding and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom. The knowledge of such bonding types lays the groundwork for further explorations into molecular structure, stability, and reactivity.
Youtube Videos
![Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure [Complete] in Just 30 Minutes](https://img.youtube.com/vi/H1-COuLbvzI/mqdefault.jpg)


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Covalent Bond
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
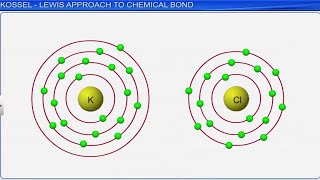
Langmuir (1919) refined the Lewis postulations by abandoning the idea of the stationary cubical arrangement of the octet, and by introducing the term covalent bond.
Detailed Explanation
In 1919, Langmuir improved upon earlier theories of chemical bonding by moving away from the concept that atoms arranged themselves in a fixed cube shape to achieve stability through an octet of electrons. Instead, he focused on the idea of covalent bonds, which are formed when two atoms share pairs of electrons. This concept allowed for a more flexible understanding of how atoms can bond together in different shapes and arrangements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of forming a team for a project; each team member brings their own skills (electrons) to the group. When team members share their skills with each other (similar to sharing electrons), they create a stronger, more effective team (covalent bond) rather than each person working in isolation.
Example of Covalent Bonding: Formation of Cl2
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Lewis-Langmuir theory can be understood by considering the formation of the chlorine molecule, Cl2. The Cl atom with electronic configuration, [Ne]3s2 3p5, is one electron short of the argon configuration. The formation of the Cl2 molecule can be understood in terms of the sharing of a pair of electrons between the two chlorine atoms, each chlorine atom contributing one electron to the shared pair.
Detailed Explanation
In a Cl2 molecule, two chlorine atoms come together and share their outermost electrons. Each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons (from its configuration of [Ne]3s2 3p5) and needs one more to achieve the stable configuration of 8 electrons (octet). By sharing one electron, they form a stable covalent bond. This sharing allows both atoms to fill their outer electron shell, resulting in a secure bond between them.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine two friends each having one half of a puzzle piece. When they share their pieces by putting them together, they complete the whole puzzle. Similarly, when two chlorine atoms share their electrons, they complete their 'puzzle' of having a full outer shell of electrons.
Lewis Dot Structures and Covalent Bonds
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The dots represent electrons. Such structures are referred to as Lewis dot structures. The important conditions are that each bond is formed as a result of sharing an electron pair between the atoms. Each combining atom contributes at least one electron to the shared pair.
Detailed Explanation
Lewis dot structures are visual representations that show how atoms share electrons through dots around their elemental symbols. In the context of covalent bonding, these representations help illustrate the pairs of electrons that are shared between atoms, creating bonds. Each bond is typically represented by a line connecting the two atomic symbols, indicating that a pair of electrons is being shared to stabilize both atoms' electron configurations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the idea of a partnership; if two people each contribute a piece of information (an electron), they can complete a project together. In Lewis dot structures, this partnership is visually represented by dots around each person's name (the atomic symbols), showing exactly how they come together to form a bond.
Types of Covalent Bonds: Single, Double, Triple Bonds
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When two atoms share one electron pair, they are said to be joined by a single covalent bond. In many compounds, we have multiple bonds between atoms. The formation of multiple bonds envisions sharing of more than one electron pair between two atoms.
Detailed Explanation
Covalent bonds can be classified into single, double, and triple bonds based on the number of electron pairs shared between two atoms. A single bond involves sharing one pair of electrons (like in H2), while a double bond involves sharing two pairs (like in O2), and a triple bond involves sharing three pairs (like in N2). The more pairs of electrons shared, the stronger the bond becomes, resulting in shorter bond lengths.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine stacking books to build a stronger tower. One book might represent a single bond, while two books stacked together can be seen as a double bond, and three books can represent a triple bond. The more books you stack (the more electrons you share), the more stable your tower (the bond) becomes.
Key Concepts
-
Covalent Bond: A bond formed by the sharing of electrons.
-
Lewis Dot Structure: Visual representation of atomic bonding.
-
Octet Rule: The principle of achieving eight valence electrons for stability.
-
Single Bond: Sharing one pair of electrons.
-
Double Bond: Sharing two pairs of electrons.
Examples & Applications
H2 molecule forms a single bond by sharing one pair of electrons.
CO2 showcases double bonds where one carbon atom shares two pairs of electrons with each oxygen atom.
N2 exemplifies a triple bond with each nitrogen sharing three pairs of electrons.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a bond that’s covalent, electrons share, rounding each soul with love and care.
Stories
Imagine two best friends sharing their toys to make a bigger one; that’s like atoms sharing electrons to form a bond.
Memory Tools
Remember: O for Octet with Eight, bonds are great - Single, Double, Triple, electrons create!
Acronyms
BOND
"B"onded
"O"xygen
"N"itrogen
"D"ouble for sharing!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Covalent Bond
A chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
- Lewis Dot Structure
A diagram that shows the valence electrons in an atom as dots and illustrates how they are shared in bonds.
- Octet Rule
The observation that atoms tend to bond in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell.
- Single Bond
A covalent bond involving one pair of shared electrons.
- Double Bond
A covalent bond involving two pairs of shared electrons.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
