Admixtures
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Types of Admixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll be talking about admixtures, which are additives that can greatly improve the performance of concrete. Can anyone tell me why we might use an admixture?

Maybe to make the concrete set faster or slower?

Great point! We use different types of admixtures to modify specific aspects of concrete. For example, water-reducing agents help us reduce the water-cement ratio while keeping the mix workable. Has anyone heard of plasticizers?

I have! They make the concrete easier to work with, right?

Exactly! Now, let's remember this with the acronym P.A.S.R—Plasticizers, Air-entraining Agents, Superplasticizers, and Retarders. Can anyone explain how air-entraining agents help?

They help prevent damage from freeze-thaw cycles by adding tiny air bubbles.

Perfect! So, different admixtures adjust the properties of concrete to match our specific requirements.
Benefits of Using Admixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into the benefits of using admixtures, especially in pavement design. Why do you think it’s important to use superplasticizers?

They help make high-strength concrete without needing more water?

Exactly! It allows us to achieve high performance without compromising workability. Can anyone provide an example of a situation where we would use retarders?

During hot weather, right? To slow down the curing time.

That's correct! This ensures that the mix doesn't set too quickly and maintains workability. So, let's summarize: Retarders slow down the setting, superplasticizers enhance strength at low w/c, and air-entrainers improve durability against environmental stresses.
Selecting Admixtures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Choosing the right admixture is crucial. What factors should we consider when selecting admixtures for a particular project?

The environment, right? Like freeze-thaw cycles?

Absolutely! Environmental conditions significantly influence our choice. We also consider the type of pavement—whether it's JPCP or CRCP. Student_3, can you think of how heavy traffic might impact our mix design?

We might want admixtures that improve strength and durability to handle the loads better.

Spot on! So, when we consider traffic and environmental impacts, we can choose the best combination of admixtures to ensure optimal concrete performance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the various types of admixtures used in concrete for pavements, including water-reducing agents, superplasticizers, air-entraining agents, and retarders or accelerators. These admixtures play an essential role in modifying the properties of concrete to meet specific requirements in pavement applications.
Detailed
Admixtures in Concrete for Pavements
Admixtures are essential components in the design of concrete mixes, particularly for pavement applications. These chemical agents are added to alter the properties of concrete in various ways:
- Water-Reducing Agents (Plasticizers): These help in reducing the water-cement (w/c) ratio while maintaining workability, allowing for better strength development in the concrete.
- Superplasticizers: Used primarily when a high-strength mix is required. They enable a significant reduction in the w/c ratio without losing workability, essential for high-performance pavements.
- Air-Entraining Agents: Critical in regions with freeze-thaw cycles, these agents introduce tiny air bubbles into the concrete, enhancing its durability against harsh environmental conditions.
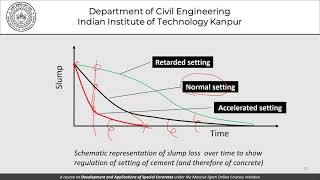
- Retarders and Accelerators: Depending on climatic conditions and project needs, retarders can delay the setting time of concrete, while accelerators can expedite it, allowing for adjustments based on environmental or scheduling requirements.
Incorporating these admixtures appropriately ensures that the concrete meets the necessary performance criteria for durability, workability, and economy, which are critical for pavement longevity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Water-Reducing Agents (Plasticizers)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Water-reducing agents (Plasticizers).
Detailed Explanation
Water-reducing agents, also known as plasticizers, are materials added to concrete to reduce the amount of water required for a given workability without compromising the strength of the concrete. This is particularly important because less water can lead to a denser and stronger concrete mix. By allowing less water, you achieve improved durability and strength of the finished concrete.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to bake a cake with too much water; the batter would be runny and wouldn’t hold its shape well. Similarly, in concrete, if we add too much water, it can weaken the structure. Water-reducing agents help maintain the right consistency without adding excess water.
Superplasticizers
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Superplasticizers for high strength or low w/c ratio.
Detailed Explanation
Superplasticizers are a type of high-range water-reducing agent that can greatly enhance the flowability of concrete at very low water-cement (w/c) ratios. This means you can create high-strength concrete mixes that are easier to work with. Superplasticizers allow for better mixing and placement of concrete, especially in complex forms or where high strength is needed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of superplasticizers like adding a little oil to a thick sauce to make it smoother and easier to pour. Just as the oil enhances the texture without changing the base, superplasticizers enhance the mix’s performance while keeping the essential combination of materials intact.
Air-Entraining Agents
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Air-entraining agents for freeze-thaw resistance.
Detailed Explanation
Air-entraining agents are additives that introduce tiny air bubbles into the concrete mix. These bubbles provide space for water to expand when it freezes, thus preventing cracking and damage to the concrete during repeated freeze-thaw cycles, which is especially important in colder climates. This helps improve the longevity of the pavement.
Examples & Analogies
Consider having a sponge that can expand slightly when you squeeze it; the sponge absorbs liquid without breaking. Similarly, the air bubbles in concrete allow it to expand and contract with temperature changes, protecting it from damage.
Retarders and Accelerators
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Retarders or accelerators depending on climatic conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Retarders are additives that slow down the setting time of concrete, which is beneficial in hot weather conditions where concrete may set too quickly. On the other hand, accelerators speed up the setting time, allowing for quicker completion of projects, which is useful in cold conditions. Adjusting the curing process with these admixtures ensures that the concrete reaches its desired properties effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of retarders like a traffic light that keeps you from moving too fast on the road, allowing smooth progress. Similarly, accelerators act like a green light, letting you move fast when conditions are right. Knowing when to use these agents helps manage how concrete sets.
Key Concepts
-
Admixtures: Chemical additives that modify concrete properties.
-
Water-Reducing Agents: Improves workability and reduces water content.
-
Superplasticizers: Reduces the water-cement ratio significantly for high-performance concrete.
-
Air-Entraining Agents: Enhances freeze-thaw resistance by introducing air bubbles.
-
Retarders and Accelerators: Modify the setting time of concrete to suit environmental conditions.
Examples & Applications
Using a superplasticizer in a concrete mix for a high-rise building to achieve the required compressive strength while keeping the mix workable.
Adding air-entraining agents for concrete intended for pavements in cold climates to enhance durability against freeze-thaw cycles.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Admixtures can keep concrete neat, with bubbles, strength, and pace that can't be beat.
Stories
Imagine a concrete mix like a cake. To ensure it's fluffy, we add air bubbles (air-entrainers) and adjust the wetness (plasticizers)—too much water would ruin the mix, but just the right amount gives a strong, lasting road for cars to fixate.
Memory Tools
Remember P.A.S.R for Admixtures—Plasticizers, Air-entrainers, Superplasticizers, Retarders.
Acronyms
P.A.S.R
Plasticizers
Air-entraining agents
Superplasticizers
Retarders.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Admixture
A chemical additive used in concrete to modify its properties.
- Plasticizer
An admixture used to reduce the water-cement ratio while maintaining workability.
- Superplasticizer
A high-range water reducer that allows significant reductions in water content.
- AirEntraining Agent
An admixture that adds air bubbles to the concrete mix, improving its resistance to freeze-thaw damage.
- Retarder
An admixture that slows the setting time of concrete.
- Accelerator
An admixture that speeds up the setting time of concrete.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
