Cement
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Types of Cement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the different types of cement used for concrete pavements. The most common type is Ordinary Portland Cement or OPC. Have any of you heard about the different grades of OPC?

I've heard of 43 and 53 grade cements. What's the difference between them?

Great question! The numbers indicate the compressive strength in MPa. So, 43 grade cement offers a compressive strength of 43 MPa, while the 53 grade provides 53 MPa. This means the 53 grade is typically used for high-load situations.

What about blended cements?

Blended cements, like PPC and PSC, include additional materials that enhance durability, especially against environmental conditions. PPC, for instance, includes pozzolana to improve workability.

Why is that important for pavements?

Because pavements face various stresses from traffic and environmental effects. Using the right cement can lead to longer-lasting pavements with fewer repairs.

To summarize, we primarily use OPC for pavements with specific grades for strength requirements, and blended cements improve durability.
Properties of Cement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the properties of cement. What do you think are some important characteristics we should consider when selecting cement for concrete pavements?

Maybe strength and how fast it sets?

Exactly! Strength development is crucial. Consistency and setting time also affect how easily we can work the mix. Fineness, which is the particle size, influences the reactivity of the cement.

How do these properties impact the overall concrete?

Good question! A finer cement can lead to a stronger mix by providing greater surface area for the chemical reactions. Faster setting times can improve project efficiency but may complicate handling.

What should engineers keep in mind when mixing?

Engineers must balance these properties to achieve a mix that offers adequate workability, strength, and durability for the specific conditions the pavement will face. In conclusion, understanding these properties helps in making informed material choices.
Impact of Cement on Pavement Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's consider how cement characteristics impact the pavement's performance. Why do you think this is important?

Because if the cement isn't good, the pavement won't last long.

Exactly! The choice of cement affects factors like compressive strength, resistance to environmental stress, and even maintenance needs. How does this relate to the lifecycle cost of the pavement?

If we use better cement, it might cost more initially, but it could save money later on.

Precisely! A smart investment in quality cement can lead to long-term savings due to reduced repairs and longer service life. To conclude, selecting the right type of cement based on its properties is essential for optimal pavement performance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Cement is a critical component in concrete pavements, primarily focusing on Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and blended types. Understanding its properties, including strength development and consistency, is essential for achieving optimal concrete mix design.
Detailed
Cement is a vital ingredient in concrete pavements, and its properties significantly impact the performance of the final product. In pavement construction, Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is commonly used, with specific grades such as 43 and 53 being most prevalent. Additionally, blended cements like PPC (Pozzolana Portland Cement) and PSC (Portland Slag Cement) may also be utilized for enhanced longevity and durability. The characteristics of cement include its consistency, setting time, fineness, and strength development potential. A thorough understanding of these properties is crucial for selecting the appropriate cement type, enabling engineers to design concrete mixes that exhibit the necessary strength, workability, and durability to meet the demands of pavement applications.
Youtube Videos









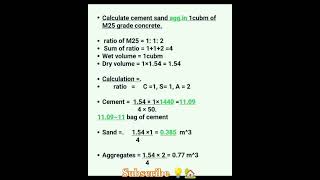
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Cement Types
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cement types include Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) – 43 or 53 grade, or blended cement like PPC or PSC.
Detailed Explanation
Cement is classified into different types based on its properties and usage. The Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) comes in grades of 43 and 53, indicating its compressive strength measured in megapascals (MPa). Blended cements, such as Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) and Portland Slag Cement (PSC), combine various materials to enhance characteristics like durability and workability. For pavement applications, selecting the appropriate type of cement is vital for ensuring durability and suitable performance under specified conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cement as the glue in concrete. Just like how a stronger glue is needed for heavier objects, different types of cement are used based on the load and exposure conditions of the pavement. Selecting the right grade ensures that the pavement endures various environmental challenges.
Cement Properties
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Properties of cement include consistency, setting time, fineness, and strength development.
Detailed Explanation
Cement must have specific properties to function effectively in concrete. Consistency refers to the uniformity of the cement, influencing its workability and mixing. The setting time determines how quickly the cement hardens, which is crucial for construction schedules. Fineness indicates how finely the cement is ground; finer cement can hydrate more rapidly, leading to faster strength gain. Strength development is essential, as it defines how quickly the cement reaches adequate strength for use.
Examples & Analogies
Consider baking a cake. The consistency of the batter impacts how it rises, much like how cement's consistency affects the workability of concrete. Similarly, the setting time ensures that the cake cooks properly without collapsing, just as optimized setting times allow concrete to harden effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC): The primary type of cement used in concrete pavements, notable for its significant compressive strength.
-
Blended Cements: These include materials like fly ash or slag to enhance concrete properties.
-
Cement Properties: Important characteristics include consistency, setting time, fineness, and strength development.
Examples & Applications
Using 53-grade OPC for high-load applications in expressways ensures higher durability.
Blended cements can be more sustainable options due to lower environmental impacts during production.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For a pavement to stand the test, OPC is what we need for the best.
Stories
Imagine a highway where sturdy OPC gets the job done, while blended cement is like a helper giving it strength against storms.
Memory Tools
Cement Properties: Strength, Setting Time, Fineness - recall as 'SSF'.
Acronyms
CEMENT
Compressive strength
Environmentally friendly
Mixing characteristics
Effective for pavements
Notable durability
Timing of hardening.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
A type of cement used in concrete that is classified based on its compressive strength, commonly available in 43 and 53 grades.
- Blended Cement
Cement that includes additional materials such as fly ash or slag to enhance durability and resist environmental stress.
- Consistency
A property of cement that refers to how thick or fluid the mix is, which affects mixing and application.
- Fineness
The particle size of the cement. Finer cement has a larger surface area that increases its reactivity.
- Setting Time
The time taken for cement to begin to harden after mixing with water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
