Subgrade and Sub-base Conditions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Subgrade Conditions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll dive into how subgrade conditions influence concrete pavements. Can anyone tell me why the subgrade is important?

Is it because it supports the pavement structure?

Exactly! The subgrade is the foundation for our pavement. Its strength and stiffness directly affect how the pavement performs.

What if the subgrade is weak?

Good question! If the subgrade is weak, it can lead to deformation and cracking in the pavement. That's why we assess it carefully.

How do we evaluate its strength?

We typically use soil tests to determine its bearing capacity. This helps in designing a suitable concrete mix.

To summarize, a strong and stiff subgrade ensures longevity in our pavements. It prevents distress and maximizes durability.
Role of Drainage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about drainage quality. Does anyone know why it matters?

I think it prevents water from weakening the subgrade?

Precisely! Good drainage helps keep the subgrade dry, which is vital for maintaining its strength.

What happens if we have poor drainage?

Poor drainage can lead to water pooling, which then weakens the subgrade and causes premature pavement failure. Any thoughts on how we might improve drainage?

Using proper grading or installing drainage systems?

Right! We can implement various techniques to ensure drainage is effective. A solid drainage plan is crucial for our pavement design.

So remember, effective drainage protects both the subgrade and the pavement, enhancing overall durability.
Evaluating Sub-base Conditions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s discuss sub-bases. How do they differ from subgrades?

Isn't the sub-base the layer that is laid on top of the subgrade?

Exactly! The sub-base provides additional support and helps distribute loads. What kind of materials do you think we might use for sub-bases?

Could we use crushed stone or gravel?

Good suggestions! Materials like crushed stone are commonly used because they enhance drainage and increase stiffness. Choosing the right materials can significantly influence pavement performance.

So we must consider both layers' conditions when designing a concrete mix?

Absolutely! Both the subgrade and sub-base contribute to the stability of the pavement, and we need to account for them in our designs. This holistic approach helps in creating durable and long-lasting pavements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The strength and stiffness of the underlying layers, along with good drainage quality, are critical factors affecting pavement performance. These conditions must be carefully evaluated during the concrete mix design process to ensure longevity and effectiveness of pavements.
Detailed
In any pavement design, the role of subgrade and sub-base conditions is paramount. The underlying layers' strength and stiffness determine how well the pavement will perform under traffic loads and environmental conditions. Proper drainage quality is essential, as water intrusion can lead to weakening of the subgrade, resulting in premature pavement failure. Engineers must assess these factors thoroughly when designing concrete mixes to ensure they withstand stressors such as heavy loads, freeze-thaw cycles, and other environmental challenges. Understanding the interaction between the pavement and its underlying support system is crucial in achieving durable, long-lasting concrete pavements.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Strength and Stiffness of Underlying Layers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Strength and stiffness of underlying layers.
Detailed Explanation
The strength and stiffness of the subgrade and sub-base layers are critical because they determine how well the pavement will perform under load. A strong and stiff subgrade can support heavier loads without deforming. If these layers are too weak, they may not provide adequate support, which could lead to cracks or failure in the pavement surface.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a concrete slab as a table. If the table is placed on a strong, solid floor, it remains stable. However, if it's placed on a soft, unstable carpet, the table may wobble and even fall over. Similarly, strong subgrade layers keep the pavement intact.
Drainage Quality
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Drainage quality.
Detailed Explanation
Good drainage is essential for pavement longevity because excess water can weaken the subgrade and cause soil erosion. Poor drainage leads to water accumulation, which can saturate the soil, reducing its strength and increasing the risk of pavement cracking and heaving. Therefore, proper drainage systems like ditches, pipes, and graded surfaces must be designed into the pavement structure.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge that has been soaked in water. It becomes weak and can’t support anything placed on top of it. Similarly, if the soil beneath a pavement retains too much water, it loses strength and can’t support the pavement effectively.
Key Concepts
-
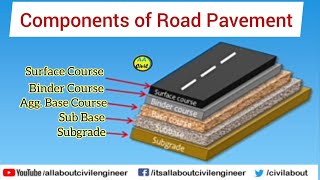
Subgrade Conditions: Underlying layer supporting the pavement; its strength and stiffness are crucial.
-
Sub-base Conditions: Provides an extra layer of support, influencing load distribution.
-
Drainage Quality: Essential for maintaining the integrity of the subgrade by preventing water accumulation.
Examples & Applications
In a case where a highway is constructed on loose soil, reinforcing the subgrade with additional layers of gravel may improve stress distribution and durability.
A pavement designed with well-draining sub-base materials can significantly extend its lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Subgrade strong, pavement lasts long; Drainage keep clear, fill with cheer.
Stories
Imagine a castle built on sand; without strong stones beneath, it's bound to fall. The subgrade is like the castle's foundation, holding everything steady!
Memory Tools
DSS - Drainage, Subgrade, Sub-base: Three keys to a strong pavement.
Acronyms
SDSC - Sturdy subgrade, durable sub-base, stable conditions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Subgrade
The layer of soil or material that supports the pavement structure.
- Subbase
The layer placed above the subgrade to provide additional support and load distribution.
- Drainage
The process of removing excess water to maintain the strength and integrity of the subgrade.
- Stiffness
The resistance of a material to deformation under load; a crucial property for pavement components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
