Java Socket Classes
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
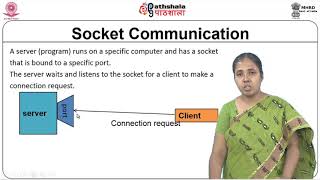
Understanding Sockets
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about sockets, which are crucial for network communication. Can anyone tell me what they think a socket is?

I think it's some kind of tool we use in programming to connect to other devices.

That's correct! A socket represents one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs. Remember, a socket consists of an IP address and a port number, often simplified as 'Socket = IP + Port.'

What kind of communication do we use sockets for?

We utilize sockets for both TCP, which is reliable and connection-oriented, and UDP, which is faster but less reliable. This distinction is essential for choosing the right protocol.

So we can use sockets in both client-server and peer-to-peer communication?

Exactly! And by the end of this section, you will understand how to implement these concepts using Java.

To summarize, a socket is a means of communication defined by an IP address and port number, serving as an endpoint for data exchange.
Client-Side Socket: java.net.Socket
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore `java.net.Socket`, the client-side class in Java. Who can tell me what we use this class for?

Isn't it used to connect to a server?

Correct! When you create a `Socket` using a server's IP address and port number, you establish a connection to that server. This class allows you to send and receive data from the server.

Is it similar to making a phone call?

That's a great analogy! Just like a phone call connects two people, a socket connects two applications. You also need the server to be ready to receive your call, which is where `ServerSocket` comes in.

Can you show us how to implement it?

Certainly! I'll walk you through a simple example of a TCP client that connects to a server on localhost. Remember to keep notes!

In summary, `java.net.Socket` is used for establishing a connection to a server, enabling data exchange.
Server-Side Socket: java.net.ServerSocket
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about the server side with `java.net.ServerSocket`. This class listens for incoming connections. Who can explain why we need a server socket?

To accept requests from clients, right?

Exactly! When a server socket is created, it binds to a port and waits for client requests. When a request is received, the server socket establishes a dedicated socket for that client.

Is it similar to a receptionist welcoming guests at a hotel?

Great analogy! The server socket is like the receptionist who accepts guests and provides them rooms (sockets) to stay. Remember, after listening for a request, the server uses the `accept()` method to handle it.

What happens if the server is not running?

If the server is offline, the client cannot connect, resulting in an error. So, always ensure your server is operational!

To recap, `java.net.ServerSocket` listens for incoming client connections and establishes communication when a request is accepted.
UDP Communication: java.net.DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's explore UDP communication through `java.net.DatagramSocket` and `java.net.DatagramPacket`. Who remembers the difference between TCP and UDP?

UDP is faster but less reliable than TCP.

Correct! The `DatagramSocket` class allows us to send and receive messages without establishing a connection. And the `DatagramPacket` is used to encapsulate the data being sent or received.

Why use UDP then?

Well, UDP is great for applications like video streaming or gaming where speed is more critical than reliability. It's a trade-off!

Can you summarize these classes?

Absolutely! `java.net.DatagramSocket` is for sending and receiving UDP packets, while `DatagramPacket` holds the actual data. Understanding these concepts is vital for network programming.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Java socket classes form the core of network programming in Java, enabling developers to create applications that communicate over the network. The section covers the essential classes, including java.net.Socket for clients, java.net.ServerSocket for servers, and java.net.DatagramSocket and java.net.DatagramPacket for UDP communication, highlighting their roles and how they are utilized.
Detailed
Java Socket Classes
In network programming with Java, the socket classes are critical for establishing connections and facilitating data exchange between applications. This section focuses on four fundamental socket classes:
-
java.net.Socket: This class represents the client side of a TCP connection. It facilitates the communication between the client and server by providing methods for sending and receiving data. When an instance of
Socketis created, it connects to a specified server at a given port. -
java.net.ServerSocket: This class serves as the server side of a TCP connection. It listens for incoming client connection requests on a specified port. When a connection request is made, it accepts the connection and creates a
Socketinstance for the specific client. - java.net.DatagramSocket: Used for sending and receiving UDP packets. Unlike TCP sockets, which provide a reliable, connection-oriented communication model, UDP is more suited for applications requiring low-latency communication with potentially lost packets, such as voice over IP or gaming.
-
java.net.DatagramPacket: This class is used in conjunction with
DatagramSocketto encapsulate the data being sent or received over UDP. It contains information about the data packet, such as the data length and address of the destination.
Understanding these socket classes is essential for effective network programming in Java and lays the foundation for developing both client and server applications.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Client-Side Socket Class
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• java.net.Socket – client side (TCP)
Detailed Explanation
The java.net.Socket class is used on the client-side to create a TCP socket connection. It essentially represents a connection between the client and the server. When a client wants to communicate with a server, it creates an instance of this class and attempts to connect to the server using its IP address and port number.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a telephone. The java.net.Socket class is like the receiver or mobile phone that dials a specific number (the server's IP and port) to connect with another person (the server) to start a conversation (data communication).
Server-Side Socket Class
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• java.net.ServerSocket – server side (TCP)
Detailed Explanation
The java.net.ServerSocket class is used on the server side to create a socket that listens for incoming client connections. It binds to a specified port number, allowing it to wait for requests from clients. When a client connects, the server can accept that connection and open a separate socket for communication.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a restaurant owner (the server) who waits for customers (clients) to arrive. The ServerSocket is like the owner at the entrance waiting to receive guests. Once a customer arrives, the owner escorts them to their table, starting their dining experience (the communication session).
Datagram Socket Class
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• java.net.DatagramSocket, java.net.DatagramPacket – for UDP
Detailed Explanation
The java.net.DatagramSocket class is part of Java's implementation for User Datagram Protocol (UDP). It allows applications to send and receive datagrams (packets of data) without establishing a connection first. The DatagramPacket class represents the data packet that is sent or received via the DatagramSocket. This method of communication is faster and is used for applications where speed is crucial and occasional packet loss is acceptable.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine sending postcards (UDP packets). You write a message and send it without expecting a formal reply. Sometimes, a postcard may get lost, but it’s generally quick and easy to send them out, similar to how the DatagramSocket method works where messages are sent quickly without the need for establishing and maintaining a connection.
Key Concepts
-
Socket: An endpoint for network communication, consisting of an IP address and port number.
-
java.net.Socket: The class used for client-side communication in a TCP connection.
-
java.net.ServerSocket: The class that listens for client connections on the server side.
-
java.net.DatagramSocket: The class for creating sockets for UDP communication.
-
java.net.DatagramPacket: A class for encapsulating data packets in UDP.
Examples & Applications
Creating a client using java.net.Socket to connect to a server and sending data.
Using java.net.ServerSocket to listen for client connections and responding to them.
Using java.net.DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket for sending and receiving messages without a connection.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sockets connect, ports align, data flows in perfect time.
Stories
Imagine a hotel receptionist (ServerSocket) welcoming guests (clients). Each guest gets a room (Socket) to communicate with friends downstairs.
Memory Tools
TCP stands for Trusty Communication Protocol, while UDP is Unpredictable Data Packet.
Acronyms
S.O.C.K.E.T
Sockets Offer Communication
Keeping Every Transmission.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Socket
An endpoint for sending or receiving data across a network.
- java.net.Socket
The class representing the client side of a TCP connection in Java.
- java.net.ServerSocket
The class representing the server side of a TCP connection that listens for incoming client connections.
- java.net.DatagramSocket
The class used to create a socket for sending and receiving UDP packets.
- java.net.DatagramPacket
The class representing a packet of data for transmission over UDP.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
