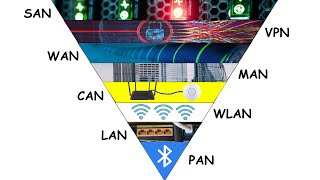
Types of Networks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding LAN
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about Local Area Networks or LANs. Why do you think we need LANs?

To connect computers in a small area, like a home or office, right?

Exactly! LANs are great for high-speed communication within a limited area. Can you think of some devices typically found on a LAN?

Maybe printers and personal computers?

Yes, printers, desktops, and laptops. Remember, LANs usually have a higher data transfer rate compared to wider networks. Can anyone name a popular LAN technology?

Isn't Ethernet commonly used for LANs?

That's right! So, to remember, think "LAN = Local + High-Speed Networking"!
Exploring WAN
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move to Wide Area Networks, or WANs. Who can define what a WAN is?

Is it a network that covers a large area, like multiple cities?

Exactly! WANs connect large geographical areas. Important examples include our own Internet. What kind of technology does a WAN typically use?

It uses leased lines, doesn’t it?

Correct again! WANs are essential for businesses operating in multiple locations. A way to remember: "WAN means Wide Area Needs Networking!"
Understanding MAN
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about Metropolitan Area Networks. Who can explain what a MAN is?

It’s a network that interconnects users in a city or town, right?

Exactly! MANs serve as a midpoint between LANs and WANs. What advantages do they offer?

They provide faster connection speeds compared to WANs because they cover a smaller area.

Correct! Think of a MAN as the bridge between local networks and wider areas, or: "MAN is Metropolitan Area Network!"
Exploring PAN
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's dive into Personal Area Networks, or PANs. What do you think a PAN connects?

It connects personal devices like smartphones and tablets within a very close range.

Exactly! PANs are used for devices in close proximity and are typically facilitated by Bluetooth technology. Can anyone think of a use case for a PAN?

Connecting my phone to my Bluetooth speaker?

Yes! So, always remember: PAN = Personal Devices Networking!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore four primary types of networks: Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), and Personal Area Network (PAN). Each offers distinct characteristics that cater to various connectivity needs in different settings.
Detailed
Types of Networks
In this section, we discuss the four main types of computer networks:
-
LAN (Local Area Network):
A LAN is designed to connect computers within a limited geographical area, such as a single building or campus. It provides high-speed communication and is typically used in homes, schools, and office buildings. -
WAN (Wide Area Network):
WANs cover a large geographical area, often connecting multiple cities or countries. These networks utilize leased telecommunication lines to facilitate long-distance communication, such as the Internet. -
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, designed to connect users in a specific metropolitan region. It is commonly used by businesses to interconnect multiple offices in a city. -
PAN (Personal Area Network):
A PAN is a small network, typically covering personal devices in close proximity (e.g., smartphones, tablets, and computers). Technologies like Bluetooth often facilitate these networks.
Understanding these types of networks is essential for selecting the appropriate network design for a given situation, influencing both hardware choices and communication capabilities.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Local Area Network (LAN)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• LAN (Local Area Network)
Detailed Explanation
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or campus. It allows for high-speed data transfer and sharing of resources like printers and files among the connected devices. LANs typically use wired connections (like Ethernet) or wireless connections (Wi-Fi). Due to their limited range, they are ideal for small groups of computers that need to communicate frequently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a LAN as a small neighborhood where houses (devices) are connected by streets (cables or Wi-Fi). Neighbors can easily visit each other and share resources like gardens or tools. In an office, all computers and printers might belong to the same LAN, making it easy for employees to share documents and access the printer.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• WAN (Wide Area Network)
Detailed Explanation
A Wide Area Network (WAN) spans a large geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs across cities, countries, or even continents. WANs are used by businesses and organizations to facilitate communication and data exchange between remote offices. They typically rely on leased telecommunication lines and can include technologies such as satellites or fiber optics for long-distance communication. WANs are generally slower than LANs due to their expansive reach and complexity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a WAN as a major highway system that connects cities (different LANs) across the country. While it can transport vehicles (data) over long distances, it may take longer compared to driving on local streets (LANs) due to traffic and road conditions. Businesses might use a WAN to connect their offices in New York, London, and Tokyo, allowing them to work together despite the large distances.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
Detailed Explanation
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a larger geographic area than a LAN but is typically smaller than a WAN. It connects multiple LANs within a specific city or metropolitan area. MANs are often used by schools, universities, and government entities to share resources and information with various locations in the region. They offer high-speed connectivity and are designed for efficient communication among localized networks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a MAN like a city's public transportation system. Just as buses and trains connect different neighborhoods (LANs) within a city, a MAN links several local networks, facilitating efficient communication and resource sharing among them. For example, a university campus might connect its various buildings and research facilities through a MAN, allowing students and staff to access shared digital resources seamlessly.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• PAN (Personal Area Network)
Detailed Explanation
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a small network, typically within a range of a few meters, that connects personal devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. PANs use wireless technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to allow these devices to communicate and share data seamlessly. They are often used for activities such as connecting wireless keyboards, mice, and printers to a computer or smartphone.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a PAN as a personal gadget party in your living room. At this party, your smartphone, laptop, and tablet can all communicate with each other as long as they are close together. For instance, you might use your smartphone to control music playing on a Bluetooth speaker or send a photo to a printer in the same room. The devices easily share information without needing any physical connections.
Key Concepts
-
LAN: A network connecting devices in a small geographic area, providing high-speed connections.
-
WAN: A network connecting devices across large geographic distances, useful for internet connectivity.
-
MAN: A network connecting users in a specific metropolitan area, interconnecting various LANs.
-
PAN: A network connecting personal devices within close proximity, often using Bluetooth.
Examples & Applications
A LAN can be set up in a home office to connect computers and printers.
A WAN might connect branch offices of a multinational company across different countries.
A MAN could connect several offices of a city-based enterprise to facilitate communication.
A PAN can connect a smartphone to a wireless headset or smartwatch.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
LAN is close and fast, do your work with a blast! WAN stretches wide, letting many devices abide!
Stories
Imagine a city with multiple shops connected by a fast path, this path symbolizes a MAN, while a Bluetooth connection is like a friend sharing music, representing a PAN.
Memory Tools
L-W-M-P: Remember Local, Wide, Metropolitan, and Personal for types of networks.
Acronyms
Think of the acronym 'LAN-WAN-MAN-PAN' to recall the sequence of network types.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- LAN
Local Area Network, a network that connects computers within a limited geographical area.
- WAN
Wide Area Network, a network that covers a large geographical area, often connecting multiple cities.
- MAN
Metropolitan Area Network, a network that connects users in a specific metropolitan region.
- PAN
Personal Area Network, a small network for personal devices in close proximity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
