What is a Socket?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Sockets
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about sockets. Who can tell me what a socket is in the context of networking?

I think a socket is something that connects two computers?

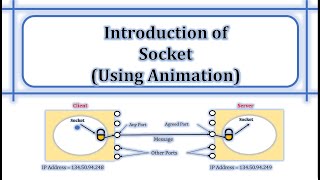
That's a good start! A socket is indeed a connection point, but it specifically refers to an endpoint of a two-way communication link between programs on a network. It’s essentially defined by an IP address and a port number.

So, is it like a mailbox where messages are sent and received?

Exactly! You can think of a socket as a mailbox for networked applications. The IP address is the address of the mailbox, while the port number tells us which mailbox we're using.

What types of sockets are there?

Great question! There are two main types: Stream Sockets, which use TCP for reliable communication, and Datagram Sockets, which use UDP for faster, connectionless communication.

What's the difference between TCP and UDP?

The main difference is reliability. TCP makes sure that data arrives in the same order it was sent, while UDP focuses on speed and is less reliable. Remember, TCP is like a postman delivering mail, ensuring you get every letter; UDP is more like sending postcards where some might get lost!

To wrap up, a socket is a fundamental concept in network programming, acting as a communication endpoint defined by an IP address and port number, with types including TCP for reliability and UDP for speed.
Understanding IP Address and Port Number
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what a socket is, let's break down its components: the IP address and the port number. Can anyone explain what an IP address is?

I think it's like a unique address for a computer on a network.

Correct! An IP address serves to uniquely identify a device on the network. It can be either IPv4 or IPv6. IPv4 addresses look like '192.168.1.1', while IPv6 addresses are longer to support more devices.

What about the port number?

Good question! The port number specifies which service or application on that device you want to communicate with. For instance, web servers commonly use port 80 for HTTP communication. The range is from 0 to 65535, with some ports being reserved for specific services.

So, if the IP is like the street address, the port is like the apartment number?

Exactly! The IP is the house on the street, and the port is the specific door you need to knock on to reach a particular service.

So, if I have two applications on my computer, they can use different ports for the same IP address?

Absolutely! This allows multiple services to run on the same machine simultaneously, thanks to the unique identification provided by port numbers.

In summary, every socket is defined by its IP address and port number, which allows for targeted communication between applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Sockets serve as critical components in network programming, representing one half of a two-way communication link. They can be categorized into stream (TCP) and datagram (UDP) types, with their structure involving an IP address and a port number.
Detailed
What is a Socket?
In the realm of network programming, a socket represents one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on a network. To establish a successful communication channel, each socket is defined by an IP address and a port number. This combination enables the identification of a specific service on a device within the network environment.
Types of Sockets
There are primarily two types of sockets you will encounter:
- Stream Sockets (TCP): These provide reliable, connection-oriented communication, ensuring that data is delivered in the same order it was sent.
- Datagram Sockets (UDP): These facilitate faster, connectionless communication where packet delivery is not guaranteed, thus allowing for lower latency in scenarios where speed is prioritized.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of sockets lays the groundwork for engaging in more complex networking tasks and enhances the communication capabilities of applications across various networks.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Socket
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network.
Detailed Explanation
A socket can be understood as a communication interface. When two programs need to exchange data over a network, they use sockets to establish a link. Each socket connects to the host machine and provides a way for the programs to send and receive data. This means that when you have a socket on your computer, it's like having a dedicated line where data can flow in both directions, allowing the two programs to communicate effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a socket like a telephone line. When two people want to talk, they each need a phone (socket) connected to a network (the telephone system). Once they pick up their phones, they can hear each other and exchange information back and forth, just as programs do over sockets.
Components of a Socket
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Socket = IP address + Port number
Detailed Explanation
Every socket is defined by two key components: the IP address and the port number. The IP address indicates which device on the network is communicating, while the port number specifies which application or service on that device the data should be sent to. This combination is essential because multiple applications can run on a single device, and the socket ensures that data reaches the correct application.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a mailing address where the street name is the IP address and the apartment number is the port number. The street name tells postal workers which building to go to, while the apartment number tells them exactly where in that building to deliver the package (the data).
Types of Sockets
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Types: Stream (TCP), Datagram (UDP)
Detailed Explanation
There are primarily two types of sockets: Stream sockets and Datagram sockets. Stream sockets use the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which is connection-oriented and ensures that data packets are delivered in order and without errors. On the other hand, Datagram sockets use the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which is connectionless and does not guarantee delivery or order, making it faster but less reliable. Understanding these types helps developers choose the appropriate socket based on the requirements of their application.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of TCP as a postal service that guarantees delivery. They ensure your mail arrives safely, even if it means taking longer to reach its destination. UDP is like leaving a message in someone’s mailbox: it’s faster, but there’s no confirmation if the message was delivered or if it got lost.
Key Concepts
-
Socket: An endpoint for network communication.
-
IP Address: Unique identifier for a device on a network.
-
Port Number: Identifier for a specific service on a device.
-
TCP: Reliable, connection-oriented protocol.
-
UDP: Fast, connectionless protocol.
Examples & Applications
A client application using a socket to send a message to a server application identified by a specific IP address and port.
A web browser utilizing TCP sockets to request a website from a server using port 80.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To reach your friend across the net, a socket's your best bet!
Stories
Imagine a post office where your IP address is the address of your home, and port numbers are the individual mailboxes everyone uses to send and receive messages.
Memory Tools
S-P-T! Sockets are defined by IP address (S) and Port number, with types: TCP and UDP.
Acronyms
SPP - Sockets, Port and Protocol, helps you remember how they connect!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Socket
An endpoint of communication between two programs on a network, defined by an IP address and a port number.
- IP Address
A unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
- Port Number
A numerical identifier in a networking context assigned to each service to distinguish multiple instances on the same IP address.
- TCP
Transmission Control Protocol, a connection-oriented protocol ensuring reliable communication.
- UDP
User Datagram Protocol, a connectionless protocol that allows faster transmission without guaranteeing delivery.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
