Socket Programming
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Sockets
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Alright class, today we're diving into socket programming. To start, can anyone explain what a socket is?

I think a socket is used to connect programs over a network?

That's correct, Student_1! A socket is indeed the endpoint of a two-way communication link between programs. It can be considered as a combination of an IP address and a port number. Can anyone tell me the main types of sockets we work with?

Are there TCP sockets and UDP sockets?

Exactly! TCP sockets provide a reliable, connection-oriented communication, while UDP sockets allow quicker, connectionless transfers. Remember this: **'TCP is Trusty, while UDP is Unpredictably Fast'.** Any questions so far?

Why do we have two different types of sockets?

Great question! TCP is for applications where data reliability is paramount, while UDP is used when speed is crucial and lost packets can be tolerated. Let's move on to the available Java socket classes.
Java Socket Classes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Java provides several classes for socket programming. Who can name one of the socket classes Java offers?

There's `java.net.Socket` for clients!

Correct, Student_4! And what about the server-side implementation?

`java.net.ServerSocket` is used for that, right?

Right again! `ServerSocket` listens for incoming connections. Now, for those using UDP, we have `java.net.DatagramSocket` and `java.net.DatagramPacket`. It’s crucial to remember these classes when you're building networked applications. Can anyone tell me how we can visualize a socket connection?

I guess it would be like a phone call, where one party dials another and they communicate back and forth?

Exactly! You can think of a socket as a phone line connecting two parties for a conversation. Now, let's summarize this section.

To recap, sockets are essential endpoints for communication, and in Java, we utilize various classes for TCP and UDP communication. Keep these concepts in mind as they will be vital for practical applications!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines socket programming as a critical aspect of network communication, detailing the types of sockets, the Java socket classes used for TCP and UDP communication, and their significance in networking.
Detailed
Socket Programming in Depth
Socket programming is key to enabling communication between applications across networks. A socket is essentially one endpoint in a two-way communication link between programs, characterized by its combination of an IP address and a port number. Programmatically, Java provides several socket classes:
java.net.Socket: Used for client-side TCP sockets.java.net.ServerSocket: Facilitates server-side TCP operations.java.net.DatagramSocket&java.net.DatagramPacket: Enable UDP-based communication.
Understanding these components allows developers to implement various networked applications, from simple client-server systems to complex, distributed networks.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Socket?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
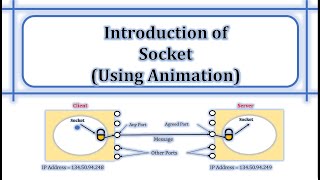
A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network.
- Socket = IP address + Port number
- Types: Stream (TCP), Datagram (UDP)
Detailed Explanation
A socket serves as a communication endpoint between two programs over a network. Each socket is defined by an IP address, which identifies a machine on the network, and a port number, which specifies a specific service or application on that machine. There are two primary types of sockets: stream sockets for TCP communications (which ensures reliable data transmission) and datagram sockets for UDP communications (which is faster but may not guarantee delivery).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a socket as a telephone in a house (the IP address being the home address and the port number being a specific extension). Just like making calls to different extensions for various departments, different sockets allow programs to communicate with each other over the network.
Java Socket Classes
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
java.net.Socket– client side (TCP)java.net.ServerSocket– server side (TCP)java.net.DatagramSocket, java.net.DatagramPacket– for UDP
Detailed Explanation
In Java, the java.net.Socket class is used for client-side socket programming, allowing clients to connect to a server. On the server side, the java.net.ServerSocket class listens for incoming client connections. For applications using UDP, the java.net.DatagramSocket class is utilized to send and receive datagrams, and java.net.DatagramPacket is used to encapsulate the data in those datagrams.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you own an office building (the server), and clients (the clients) are calling up to request services. The ServerSocket is like your receptionist who answers the main line and forwards calls to different departments (sockets for each client) while the individual Socket instances handle the specific conversations.
Key Concepts
-
Socket: Endpoints in network communication.
-
TCP Socket: Reliable connection-oriented communication.
-
UDP Socket: Fast, connectionless communication.
-
java.net.Socket: Client-side TCP socket.
-
java.net.ServerSocket: Server-side TCP socket.
-
java.net.DatagramSocket: Socket for UDP communication.
-
java.net.DatagramPacket: Represents UDP data packets.
Examples & Applications
A socket is established when a program on one computer connects to another via an IP address and port number.
The java.net.Socket class is used within a client application to open a connection to a server.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the connection game, sockets play a part, with TCP being reliable and UDP's quick heart.
Stories
Imagine two friends talking on the phone. If one friend hangs up without saying goodbye, it's like UDP; quick, but messages may not be received!
Memory Tools
For remembering types of sockets: 'TCP' - 'Trusty' and 'UDP' - 'Unpredictable' help recall their characteristics.
Acronyms
TCP = Trustworthy, Connection-oriented; UDP = Unreliable, Datagram.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Socket
An endpoint for communication between two programs over a network, identified by an IP address and a port number.
- TCP Socket
A type of socket that provides reliable, connection-oriented communication.
- UDP Socket
A type of socket that enables faster, connectionless communication.
- java.net.Socket
A Java class that represents the client-side socket for TCP connections.
- java.net.ServerSocket
A Java class that enables server-side socket operations for accepting TCP connections.
- java.net.DatagramSocket
A Java class used for sending and receiving UDP packets.
- java.net.DatagramPacket
A class representing a packet of data sent or received through a DatagramSocket.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
