Photocatalytic Cement
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Photocatalytic Cement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing photocatalytic cement. Can anyone tell me what they think this could be?

Is it some kind of cement that can clean air?

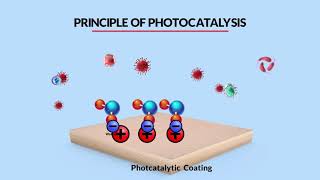
Exactly! Photocatalytic cement contains titanium dioxide, which, when exposed to sunlight, breaks down pollutants. This makes it quite unique.

How does it do that?

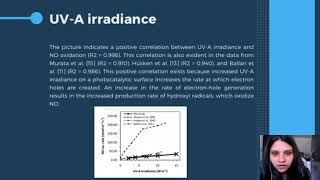
Good question! The TiO₂ interacts with light to produce reactive species that decompose harmful substances in the air, like nitrogen oxides.

So, it helps improve air quality?

Yes! By using photocatalytic cement in construction, we can have buildings that actively work to clean the surrounding air.

Yes, it's typically applied in urban areas, especially on building facades and pavements.

Perfect! Let's summarize what we've learned. Photocatalytic cement uses TiO₂ to purify air when exposed to sunlight.
Mechanism and Benefits of Photocatalytic Cement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into how photocatalytic cement works. Does anyone remember the role of sunlight in this process?

It activates the titanium dioxide, right?

Correct! Once activated, TiO₂ generates reactive species. Can anyone give me an example of pollutants it breaks down?

Nitrogen oxides and maybe VOCs?

Spot on! These pollutants can cause significant health and environmental issues. How do you think using such cement can impact urban development?

It would make cities healthier with better air quality.

Exactly! In summary, photocatalytic cement not only contributes to cleaner air but also enhances the sustainability of urban infrastructure.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the unique properties and applications of photocatalytic cement, which incorporates titanium dioxide (TiO₂). This material is designed to purify air by breaking down pollutants and is particularly useful in urban environments where air quality is a concern.
Detailed
Photocatalytic Cement
Photocatalytic cement is a groundbreaking innovation in the field of civil engineering, incorporating titanium dioxide (TiO₂) to create surfaces that can purify air. When exposed to sunlight, this type of cement can break down harmful pollutants, making it an excellent choice for facades and pavements in urban areas.
Key Aspects of Photocatalytic Cement
- Mechanism of Action: When titanium dioxide is illuminated by UV light (from sunlight), it generates reactive species that can decompose organic pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Applications: Primarily used in the construction of building facades, pavements, and other outdoor structures where air quality improvement is needed.
- Environmental Impact: The use of photocatalytic cement can significantly help mitigate urban pollution, providing a more sustainable approach to construction.
Incorporating photocatalytic technology into cement not only improves the longevity and maintenance of structures but also contributes positively to the environment by promoting cleaner air.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Photocatalytic Cement
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Photocatalytic Cement
- Contains titanium dioxide (TiO₂) which breaks down pollutants when exposed to sunlight (used in facades and pavements).
Detailed Explanation
Photocatalytic cement is a special type of cement that contains titanium dioxide (TiO₂). When this cement is exposed to sunlight, it has the ability to break down pollutants in the environment. This function is particularly useful for maintaining cleaner buildings and surfaces, as it helps reduce the levels of harmful substances in the air.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a solar-powered device that cleans your windows whenever the sun shines on it. Similar to this device, photocatalytic cement uses sunlight to activate its pollution-fighting properties, acting like a filter for the air, especially on building exteriors.
Uses of Photocatalytic Cement
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used in facades and pavements.
Detailed Explanation
Photocatalytic cement is primarily used in building facades and pavements. In facades, this cement not only provides structural integrity but also helps in keeping the building's surface cleaner by degrading dirt and pollutants, which can lead to a longer-lasting and more visually appealing structure. For pavements, the same properties contribute to reducing the buildup of grime, thereby enhancing public cleaner walking surfaces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of photocatalytic cement as a self-cleaning paint on a wall or floor. Just as self-cleaning glass can break down dirt and grime with light exposure, photocatalytic cement works to keep itself and the surfaces around it clean, making public spaces or buildings more attractive and reducing maintenance costs.
Key Concepts
-
Photocatalytic Cement: Uses TiO₂ to improve air quality.
-
Mechanism: Activated by sunlight to decompose pollutants.
-
Environmental Benefits: Enhances urban infrastructure sustainability.
Examples & Applications
Photocatalytic cement can be used in constructing building facades to reduce the accumulation of pollutants.
Pavements made with this cement help decrease nitrogen oxides levels in urban centers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cement that can break down dirt, under sunlight it does its work.
Stories
Once there was a cement which upon seeing the sun turned into a superhero that battled pollution, freeing the air of dangerous substances.
Memory Tools
TiO₂ - Think of it as 'Titanium's Office of Oxidation' for breaking down pollutants.
Acronyms
PAVE
Photocatalytic Air-Value Enhancer
helping to clean our environment.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photocatalytic Cement
A type of cement containing titanium dioxide which helps break down air pollutants under sunlight.
- Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂)
A chemical compound used in photocatalytic cement that activates under UV light to decompose harmful pollutants.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Air pollutants that can cause respiratory problems and contribute to smog.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
A group of organic chemicals that can lead to air quality issues and health problems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
