ArrayDeque
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ArrayDeque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the ArrayDeque. Can anyone tell me what a deque is?

Isn't it a double-ended queue where you can add or remove items from both ends?

Exactly! Now, ArrayDeque is Java's specific implementation of a deque. Who can explain how it manages its storage?

I think it uses a resizable array, so it grows when needed?

That's correct! The flexibility of resizing contributes to its efficiency compared to linked-list implementations.

How does it compare with ArrayList then?

Great question! While both use arrays, ArrayDeque does not allow null elements and is optimized for fast access at both ends. Remember: A for ArrayDeque is for Accessing both ends!
Common Operations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at some common operations in the ArrayDeque. Who can list a few methods?

There's addFirst, addLast, removeFirst, and removeLast!

Good job! These methods allow addition and removal of elements from both ends. Can anybody describe when you would use addFirst?

Maybe when implementing a stack, you'd want to add at the front?

Precisely! And that's the versatility of ArrayDeque. It can adapt to various data structures depending on how you utilize it.

So, it can function as both a queue and a stack!

Exactly! Remember: Deque = Double-ended versatility!
Comparative Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare ArrayDeque with LinkedList and Stack. When might you prefer ArrayDeque?

I guess if you want better performance in adding or removing elements?

Correct! ArrayDeque can outperform LinkedList due to lower memory overhead. When would you opt for LinkedList, then?

Maybe when you need a synchronized option, like for multithreading?

Exactly! Remember ArrayDeque is not synchronized. So, in scenarios requiring thread safety, you’d choose another option.

And Stack is synchronized too, right?

Yes! But ArrayDeque offers better overall performance in terms of capacity. Just remember: Use Stack for legacy support and synchronized needs!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
ArrayDeque is an implementation of the Deque interface in Java that allows the use of a resizable array to manage elements. It offers efficient methods for adding and removing elements from both the front and the back of the queue. This section details how ArrayDeque differs from other implementations, its common use cases, and the key methods available.
Detailed
ArrayDeque in Java
ArrayDeque is a part of Java's Collections Framework, specifically the Deque interface, which allows for a double-ended queue.
Key Features:
- Resizable Array: Unlike fixed-size arrays, ArrayDeque automatically adjusts its size.
- Efficiency: It provides O(1) time complexity for adding and removing elements from both ends, making it more efficient than linked-list based alternatives for certain operations.
- Versatile Usage: It can be used as a stack (LIFO) or a queue (FIFO), accommodating a variety of data handling needs.
Comparison:
- ArrayDeque does not have capacity restrictions like ArrayList; however, it is not synchronized, making it unsuitable for concurrent access unless externally synchronized.
Understanding ArrayDeque and its capabilities enhances a developer's ability to choose the appropriate collection for specific use cases in Java programming.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
ArrayDeque Overview
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• ArrayDeque – efficient resizable array-based implementation.
Detailed Explanation
ArrayDeque is a type of data structure in Java that implements a double-ended queue (deque) using a resizable array. This means you can efficiently add and remove elements from both ends of the deque. It grows as needed, which allows it to handle more elements without running out of space, unlike a fixed-size array.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ArrayDeque like a flexible rubber band. Just like a rubber band can stretch to hold more items when needed, an ArrayDeque can resize itself to hold more elements as you add them. If you want to remove an item, you can take it from either end of the rubber band, making it flexible and convenient.
Key Concepts
-
Resizable Array: ArrayDeque grows dynamically to accommodate more elements.
-
Efficiency: Fast access time for both ends, making it suitable for various applications.
-
Versatility: Functions as both a queue and a stack, allowing flexible data handling.
Examples & Applications
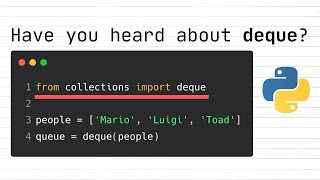
Creating an ArrayDeque: ArrayDeque
Adding elements: deque.addFirst(1); deque.addLast(2);
Removing elements: deque.removeFirst(); // returns 1, deque.removeLast(); // returns 2
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In ArrayDeque’s space we glide, add and remove from both sides wide!
Stories
Imagine a magic box where you can pull out objects from either end, that’s how ArrayDeque works, pulling treasures from both sides!
Memory Tools
D for Double-ended, A for Array, Q for Quick operations, E for Efficient using ArrayDeque!
Acronyms
D.A.Q.E = Deque.Able.Quick.Efficient, a reminder of how ArrayDeque operates.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ArrayDeque
A resizable array implementation of the Deque interface that allows adding and removing elements from both ends.
- Deque
A double-ended queue interface in Java that supports adding and removing elements from both ends.
- Capacity
The size limit of a data structure, which can be dynamic in the case of ArrayDeque.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
