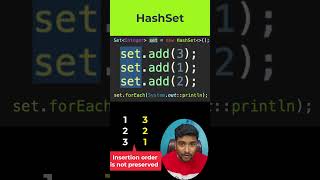
LinkedHashSet
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to LinkedHashSet
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the LinkedHashSet, a unique implementation of the Set interface. Can anyone tell me what a Set is?

A Set stores unique elements and doesn't allow duplicates.

Exactly! And the LinkedHashSet not only prevents duplicates but also maintains the order of elements. Why do you think maintaining order might be important?

It helps us retrieve data in the same sequence we added it!

Right! This is useful in many applications, like keeping the user’s actions in order. Remember: L for LinkedHashSet stands for 'Order Linked'.
Key Characteristics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Great! Now let’s talk about the characteristics of LinkedHashSet. Who can tell me how it combines features of both hash tables and linked lists?

It uses a hash table to ensure fast access and a linked list to remember the insertion order.

Exactly! This makes it efficient for operations like adding and removing elements! Can anyone share when they might prefer using a LinkedHashSet over a regular HashSet?

If I need to ensure the order of entries, I'd go for LinkedHashSet.

Precisely! That’s an important consideration in practical applications.
Performance of LinkedHashSet
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s touch on performance. Does anyone know the time complexity for basic operations like add, remove, and contains in a LinkedHashSet?

It's average constant time, O(1), right?

Spot on! And while it’s efficient, it does have a bit of overhead due to maintaining the linked list. What could be a downside?

It might use more memory than a HashSet because it has to keep track of the order.

Exactly! That’s a great point to consider when choosing which to use.
Practical Use Cases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s brainstorm some practical applications of LinkedHashSet. Can anyone think of a situation where maintaining insertion order is vital?

In a shopping cart, where we need to keep track of the order items were added!

Or a playlist, where the order of songs matters.

Fantastic examples! Both require unique entries and the order in which they were added. Always remember: LinkedHashSet = Unique + Order!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
LinkedHashSet allows for the storage of unique elements while preserving the order of insertion. It combines the advantages of a hash table with a linked list, enabling fast access and iteration while maintaining insertion order.
Detailed
LinkedHashSet
The LinkedHashSet class is part of the Java Collections Framework and implements the Set interface. It provides the main feature of maintaining insertion order while preventing duplicate elements. This is accomplished by using a combination of a hash table and a linked list, which means that it has characteristics of both:
- Prevention of Duplicates: Like other Set implementations, LinkedHashSet does not allow duplicate elements. If an attempt is made to add a duplicate element, the current entry remains unchanged.
- Maintaining Insertion Order: The order in which elements are added to LinkedHashSet is maintained, making it easier to iterate through the elements in the order they were inserted.
- Performance: Due to its structure, it offers average constant-time performance (O(1)) for basic operations like add, remove, and contains, with the added overhead of maintaining the linked list.
This makes LinkedHashSet a good choice when you require uniqueness alongside ordered iteration.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to LinkedHashSet
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• LinkedHashSet
o Maintains insertion order.
Detailed Explanation
A LinkedHashSet is a type of Set in Java that maintains the order in which elements are added. This means that when you iterate over the elements of a LinkedHashSet, they will be returned in the same sequence as they were inserted. This is particularly useful in scenarios where the order of items is important, such as when displaying a list of customer names in the order they were added.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a LinkedHashSet like a line of people waiting at a ticket counter. Each person stands in the order they arrive, and when the tickets are handed out, they are served in the exact order they lined up. Just like with the LinkedHashSet, the people (elements) can only be served once.
Key Characteristics of LinkedHashSet
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Maintains insertion order.
Detailed Explanation
One of the key characteristics of a LinkedHashSet is that it maintains the insertion order of its elements. Unlike a HashSet, which does not guarantee any specific order, a LinkedHashSet preserves the order in which the items are added. This is achieved through a combination of a hash table and a linked list, allowing for fast access and ordered iteration.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine compiling a list of your favorite songs in the order you heard them on the radio. If you were to write down each song on a notepad in the order they played, then that notepad would represent a LinkedHashSet. You could always look back and see which song you liked first, second, and so on, just like in a LinkedHashSet.
Use Cases for LinkedHashSet
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Useful when you want to maintain the order of elements while avoiding duplicates.
Detailed Explanation
A LinkedHashSet is particularly useful in scenarios where maintaining the order of insertion is crucial, and you want to avoid duplicates. For example, if you are tracking unique visitors to a website, you want to remember their order of arrival without recording the same person more than once. In this case, using a LinkedHashSet allows you to efficiently keep track of visitors while preserving the order.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a notebook where you jot down names of people who RSVP'd to a party. If someone changes their mind before the event, you want to make sure their name isn’t added again, but you also want to keep a record of the order in which they replied. A LinkedHashSet would keep your RSVP list unique and in order, just like that notebook.
Key Concepts
-
LinkedHashSet: A Set implementation that maintains insertion order and prevents duplicates.
-
Set Interface: Defines a collection that does not allow duplicate elements.
-
Hash Table: A data structure used to implement sets for efficient lookups.
-
Insertion Order: The sequence in which elements are added to a collection.
Examples & Applications
Creating a LinkedHashSet with initial elements: LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
Iterating through a LinkedHashSet to retrieve elements in the order they were added using an enhanced for-loop.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
LinkedHashSet keeps the order in sight,
Stories
Imagine a queue outside a popular cafe where customers are served in the order they arrive. No two customers can hold the same order ticket—this is like a LinkedHashSet preserving order and uniqueness.
Memory Tools
For LinkedHashSet remember: L = Linked (for order) and H = Hash (for fast access).
Acronyms
Predict 'LHS' = Linked Hash Set
for Linked order
for Hash efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- LinkedHashSet
A Set implementation in Java that maintains a doubly-linked list to preserve the order of elements as they are inserted.
- Set
An interface in Java that defines a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements.
- Hash Table
A data structure used by HashSet, providing efficient operations for storing and retrieving data using key-value pairs.
- Insertion Order
The sequence in which entries are added to a collection.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
