Queue and Deque
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Queue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the Queue interface, which allows us to manage collections in a FIFO manner. Can anyone tell me what FIFO means?

I think it means First In, First Out.

Exactly! FIFO ensures that the first element added to the queue is the first one to be removed. Now, can anyone name a few methods associated with the Queue interface?

There's add() and remove()!

Good! Remember, add() will insert an element, while remove() will take the element from the front. Can anyone think of a real-world example of a queue?

A line at a store! The first person in line is the first to check out.

Perfect analogy! Just like in a store queue, the first person added is the first one to be served. Let's take this knowledge forward.
Understanding Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to the Deque, which stands for Double-ended Queue. Can someone explain how this is different from a standard queue?

I believe a deque allows insertion and removal from both ends?

Correct! This dual functionality allows for both FIFO and LIFO operations. For example, you can add elements to both the front and back. What are some methods we’ve learned about?

We have addFirst(), addLast(), removeFirst(), and removeLast().

Brilliant! It's important to understand that while both Queue and Deque manage collections, the Deque offers more versatility. Can you guys think of situations where you might use a deque instead of a queue?

Maybe when implementing an undo feature where you might need to retrieve the last action?

Exactly! That's a great application for a Deque. Remember, it provides flexibility in how you manage your data.
Implementations of Queue and Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the implementations of both Queue and Deque. What implementations can anyone name?

I think PriorityQueue and ArrayDeque are important ones.

Great job! A PriorityQueue helps to manage elements based on priority rather than just order. And ArrayDeque offers a resizable array implementation of Deque. Why do you think ArrayDeque is often preferred?

It’s more efficient in terms of memory and performance compared to other implementations like LinkedList.

Spot on! Efficiency is key in programming, especially regarding performance metrics. These concepts will greatly aid in your future development tasks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the Queue and Deque interfaces in the Java Collections Framework. It discusses the core operations for both FIFO (First In, First Out) and LIFO (Last In, First Out) functionalities, as well as their popular implementations like PriorityQueue and ArrayDeque.
Detailed
Queue and Deque in Java
In this section, we explore the Queue and Deque interfaces from the Java Collections Framework.
Queue Interface
The Queue is a collection used to hold elements prior to processing, specifically designed for FIFO (First In, First Out) operations. It primarily includes methods such as:
- add(): Inserts an element into the queue.
- remove(): Eliminates the head of the queue.
- peek(): Retrieves the head of the queue without removing it.
- poll(): Retrieves and removes the head of the queue or returns null if the queue is empty.
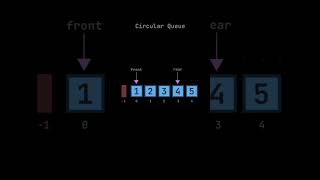
Deque Interface
The Deque (Double-ended queue) allows elements to be added or removed from both ends of the queue, accommodating both FIFO and LIFO (Last In, First Out) operations. Key methods include:
- addFirst(): Inserts an element at the front of the deque.
- addLast(): Inserts an element at the end of the deque.
- removeFirst(): Removes and returns the first element.
- removeLast(): Removes and returns the last element.
Implementations
Popular implementations include:
- PriorityQueue: Utilizes natural ordering or custom comparators for sorting.
- ArrayDeque: A highly efficient and resizable array-based deque implementation.
Understanding these interfaces allows developers to manage collections of data more flexibly, making them crucial for many algorithmic uses.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Queue Interface
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
15.4.1 Queue Interface
Used for FIFO operations.
• add(), remove(), peek(), poll()
Detailed Explanation
The Queue interface in Java is designed for FIFO (First-In-First-Out) operations, meaning that the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. This is similar to a line of people waiting at a store; the first person in line is the first to be served.
The Queue interface provides several key methods:
- add(): Adds an element to the end of the queue.
- remove(): Removes and returns the first element of the queue.
- peek(): Returns the first element without removing it.
- poll(): Removes and returns the first element, but returns null if the queue is empty, unlike remove(), which throws an exception.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a queue at a theme park. The first person who gets in line is the first one to get on the ride when it opens. If a new person arrives, they go to the end of the line. The methods of the Queue interface represent different actions you can take with this line; you can add a person (add()), let someone exit the line and get on the ride (remove()), see who’s first without letting them board (peek()), or let someone get on, with a possibility of the line being empty (poll()).
Deque Interface
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
15.4.2 Deque Interface
Double-ended queue allowing FIFO and LIFO.
• addFirst(), addLast(), removeFirst(), removeLast()
Detailed Explanation
The Deque (Double-Ended Queue) interface allows operations at both ends of the queue. This means you can add or remove elements from the front as well as the back, supporting both FIFO and LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) operations.
Key methods included in the Deque interface are:
- addFirst(): Adds an element to the front of the deque.
- addLast(): Adds an element to the end of the deque.
- removeFirst(): Removes and returns the first element from the deque.
- removeLast(): Removes and returns the last element from the deque.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a deque as a flexible line of people where not only can you queue up for a ride but you can also switch places with someone at either end of the line. For instance, if someone realizes they forgot a backpack at the entrance, they can dash back (removeLast()) or let a friend jump ahead (removeFirst()). You can also let newcomers join at the front (addFirst()) or the back (addLast()). This versatility makes deques useful in situations where you may want to add and remove items from both ends.
Implementations of Queue and Deque
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
15.4.3 Implementations
• PriorityQueue – for natural ordering or custom comparators.
• ArrayDeque – efficient resizable array-based implementation.
Detailed Explanation
Various implementations of the Queue and Deque interfaces cater to different use cases:
- PriorityQueue: This implementation orders its elements according to their natural ordering or allows for custom ordering using comparators. This means that instead of merely adhering to FIFO, it can prioritize certain elements based on predefined criteria.
- ArrayDeque: This is an efficient resizable array-based implementation of the deque that allows for quick access to elements and low memory overhead. It is often preferred when you want a stack or queue implementation with no size limitations.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a hospital emergency room where patients are treated based on the severity of their condition rather than the order they arrived in. A PriorityQueue would serve those patients first who need urgent care. Conversely, an ArrayDeque represents a supermarket checkout line where customers can enter and exit from either end, efficiently managing queues in a busy shopping environment.
Key Concepts
-
Queue: A data structure where the first element added is the first to be removed (FIFO).
-
Deque: A data structure that allows adding and removing elements from both ends.
-
FIFO: First In, First Out ordering of elements.
-
LIFO: Last In, First Out ordering of elements, similar to stack behavior.
-
PriorityQueue: A queue where elements are processed based on defined priority.
-
ArrayDeque: A flexible, resizable-array implementation of the Deque interface.
Examples & Applications
A queue can be represented by a printer queue where documents are printed in the order they are submitted.
A deque can be used in a browser history feature where you need to access both the most recent and the oldest pages visited.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a Queue, the first comes to view, while a Deque lets both ends shine true.
Stories
Imagine a customer service line; the first customer in is the first to be served. Meanwhile, a double-ended reel of film can be played from either side, illustrating how a Deque operates.
Memory Tools
For remembering FIFO, think 'First In, First Out' - keep your orders in line.
Acronyms
Deck Everything Accessibly = DEQUE (add/remove both ends)
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Queue
A collection that operates in a First In, First Out (FIFO) manner.
- Deque
A double-ended queue that allows insertion and removal from both ends.
- FIFO
An acronym for First In, First Out, describing a collection order.
- LIFO
An acronym for Last In, First Out, often referring to stack operations.
- PriorityQueue
A queue where elements are processed based on priority rather than insertion order.
- ArrayDeque
A resizable array implementation of the Deque interface.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
