Queue Interface
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Queue Interface
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the Queue interface in Java. Can anyone tell me what FIFO stands for?

It stands for First-In-First-Out!

Exactly! This means that the first element added to the queue will be the first to be removed. It's like a line of customers waiting to be served. Now, can someone explain why this might be important in programming?

It helps manage tasks that need to be processed in the order they were received!

Great point! Using FIFO in applications like printer queues or task scheduling ensures fairness and efficiency. Let's move on to the methods we use with the Queue interface.
Key Methods in Queue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The Queue interface includes several important methods. Who can name one method used to add an element to the queue?

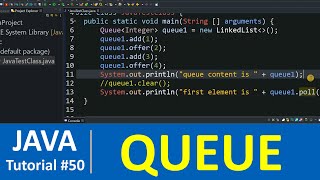
The `add()` method!

Correct! The `add()` method inserts a new element into the queue. What about a method that retrieves the head of the queue without removing it?

That would be the `peek()` method!

Well done! The `peek()` method allows us to check the next item to be processed without actually removing it from the queue. Can anyone tell me how the `poll()` method differs from `remove()`?

The `poll()` method returns null if the queue is empty, while `remove()` throws an exception!

Exactly! Understanding these differences helps in writing more robust applications. Remembering the acronym 'APPR' for Add, Peek, Poll, Remove can help you recall these methods easily.
Applications of Queue
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about the Queue interface's methods, let's talk about where we can apply it. Can someone give an example where we might use a Queue in real life?

In a printer queue where documents are printed in the order they were sent!

Exactly! In print spooling, documents are processed one at a time based on when they were submitted. Any other examples?

How about web servers handling requests? They can use queues to manage incoming requests in the order they arrive.

Spot on! Queues are crucial in managing user requests efficiently, ensuring that the oldest requests are processed first. Let's summarize today's key points.

We learned that the Queue interface utilizes FIFO, its main methods like `add()`, `peek()`, and `poll()`, and various applications like print queues and web servers!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In the Queue interface, elements are added at one end and removed from the other, facilitating FIFO operations essential for handling tasks and processes in programming. Key methods include add(), remove(), peek(), and poll(), which provide functionalities for inserting and accessing data.
Detailed
Queue Interface
The Queue interface in Java is a part of the Java Collections Framework that supports FIFO (First-In-First-Out) data structures. This means that the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed, making it particularly useful in scenarios such as task scheduling, where order of processing is crucial.
Key Features:
- Basic Operations: The main methods associated with the Queue interface include:
add(E e): Inserts the specified element into the queue.remove(): Retrieves and removes the head of the queue, throwing an exception if the queue is empty.peek(): Retrieves the head of the queue without removing it, returning null if the queue is empty.poll(): Retrieves and removes the head of the queue, returning null if the queue is empty.
Significance:
Understanding the Queue interface and its methods is crucial for managing tasks where order and timing matter. It is widely used in applications ranging from print spooling to handling requests in web servers.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
FIFO Operations Overview
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used for FIFO operations.
Detailed Explanation
FIFO stands for 'First In, First Out', which is a method for organizing and manipulating a data buffer where the oldest entry, or the first one added, is the first to be removed. This principle is similar to a queue at a grocery store—customers are served in the order they arrive.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're standing in line at a bakery. The first person who arrives is the first to buy bread and leave. Similarly, in programming, a queue processes items in the order they were added, ensuring that tasks are completed in their arrival order.
Key Methods of the Queue Interface
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• add()
• remove()
• peek()
• poll()
Detailed Explanation
The Queue interface provides several essential methods to manipulate the queue:
- add(): Adds an element to the back of the queue. If the queue is full, it may throw an exception.
- remove(): Removes the element at the front of the queue and returns it. If the queue is empty, it may throw an exception.
- peek(): Looks at the front element of the queue without removing it. If the queue is empty, it returns null or throws an exception based on the implementation.
- poll(): Similar to remove, but instead of throwing an exception when the queue is empty, it returns null.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a line of students waiting to enter a classroom. When a student at the front of the line is called (the remove() operation), they leave the queue to take their seat (another queue operation is happening at the same time). If a teacher just wants to see who is next without calling them in (the peek() operation), they simply glance at the front. If the line is empty and someone tries to go in (a poll() operation), they might just be told there’s no one left to see.
Key Concepts
-
Queue Interface: A component in Java Collections that manages elements in FIFO order.
-
add() Method: Adds an element to the end of the queue.
-
remove() Method: Removes and returns the head of the queue.
-
peek() Method: Retrieves the head of the queue without removing it.
-
poll() Method: Removes the head of the queue and returns it, or returns null if empty.
Examples & Applications
Example of a printer queue where documents are printed in the order submitted.
Example of task scheduling in a web server that processes user requests based on arrival time.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the queue, the first to stand, is the first to leave, understand!
Stories
Imagine a bakery where customers are served in the order they arrive, just like a queue takes items in FIFO!
Memory Tools
Remember 'A P P R' for Queue methods: Add, Peek, Poll, Remove!
Acronyms
F.I.F.O - First In First Out!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- FIFO
First-In-First-Out; a method of processing where the first item added is the first one to be removed.
- Queue
A collection that holds elements in a specific order, allowing insertion at one end and removal from the other.
- add()
A method that adds an element to the queue.
- remove()
A method that removes and returns the head of the queue, throwing an exception if empty.
- peek()
A method that retrieves the head of the queue without removing it; returns null if empty.
- poll()
A method that retrieves and removes the head of the queue, returning null if empty.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
