Generic Interface
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Generic Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore something called a Generic Interface in Java. Can anyone tell me what they understand by the term 'generic'?

Isn't it related to using different data types without changing the code?

Exactly! Generics allow code to be more flexible and reusable by being able to work with any data type. For example, we can define an interface like 'DataStore<T>' which can operate with different types, substituting 'T' with whatever type we need.

So, how does that help in writing code?

Great question! By using generics, we can write methods that can accept a parameter of any type while ensuring type safety. This means fewer errors and more reusable code. Let's dig into that with some examples.
Example of a Generic Interface
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

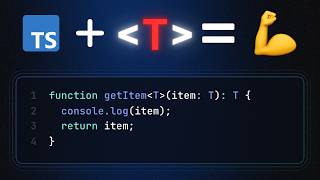
Let's look at a simple example of a generic interface. Here’s a snippet: 'interface DataStore<T> { void save(T item); }'. What do you think is happening here?

It looks like you're defining an interface that can save an item of any type, based on what 'T' is.

Exactly! When we implement this interface, we specify what 'T' will be, so we can store different types of items without changing our interface. Why do you think this is beneficial?

It avoids creating multiple interfaces just for different types, right?

That's right! This promotes a clean codebase and enhances maintainability. Let’s summarize what we’ve learned so far today.
Benefits of Using Generic Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, can anyone list some benefits of using generic interfaces?

It makes the code type-safe!

And it reduces code duplication.

Correct! Additionally, they make our code more understandable and manageable. By enabling a single interface for multiple types, we can write clearer and more concise code. Who can think of a real-world application for a generic interface?

Maybe something like a storage system that needs to handle various item types?

Excellent example! Let's remember that generic interfaces are key elements in crafting flexible and efficient Java applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains the concept of a Generic Interface in Java, providing the syntax and basic example of a Generic Interface called 'DataStore
Detailed
Detailed Overview of Generic Interface
What is a Generic Interface?
A Generic Interface in Java allows you to define an interface with a type parameter. This means that the methods in the interface can be defined to operate with any data type, promoting code reusability and type safety. This flexibility is pivotal in creating frameworks and libraries that are versatile and adaptable to various types.
Example of a Generic Interface
The syntax for defining a generic interface was illustrated with the following interface:
In this example, the DataStore interface has a type parameter T. The method save allows items of type T to be saved, meaning you can implement this interface with any data type.
Significance of Generic Interfaces
Generic interfaces improve the overall design of Java applications by allowing developers to create more generalized and reusable components, leading to cleaner and more maintainable code. They are an essential part of the Java Collections Framework, enabling collections to manage objects of various types safely and efficiently.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Generic Interface
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
interface DataStore
void save(T item);
}
Detailed Explanation
A Generic Interface in Java is defined using the interface keyword followed by the interface name and a type parameter. In this example, DataStore<T> is a generic interface that can work with any type T. The method save(T item) is specified within the interface, meaning any class that implements this interface must provide an implementation for this method that can accept an argument of type T.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a Generic Interface like a recipe that can be used to create various dishes (like cakes or cookies) depending on the ingredients you have. The DataStore<T> acts like a recipe book that lets you specify what type of item you want to store (your ingredients) without limiting you to a specific kind.
Flexibility of Generics
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The use of type parameters (like
Detailed Explanation
By using type parameters such as <T>, the DataStore interface can handle different data types in a type-safe manner. This means that when you implement the interface, you can define it with a specific type, such as DataStore<String> or DataStore<Integer>, which makes the interface applicable for various data management tasks without compromising on safety or performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine having a versatile toolbox. You can have a screwdriver, a wrench, or even a hammer, depending on what you need to fix. Similarly, the DataStore<T> interface serves as a toolbox that can be filled with different types of data, making it adaptable to various situations.
Implementation Example
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
class ObjectStore implements DataStore
Detailed Explanation
Next, we can see a class ObjectStore implementing the DataStore<Object>. It promises to provide functionality for the save method. By specifying <Object>, the class indicates that it will accept any type of item to be saved. This approach allows for a broad and generic implementation that can handle a variety of objects.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ObjectStore as a general storage box that can hold anything—tools, toys, or books. No matter what you put inside, it can handle diverse items efficiently because of the generic nature of the DataStore<Object> interface.
Key Concepts
-
Generic Interface: Allows defining interfaces with type parameters.
-
Type Safety: Ensured through the use of generics, preventing incompatible types.
-
Code Reusability: Generic interfaces promote the reuse of code for multiple data types.
Examples & Applications
The DataStore
An ArrayList can be defined as ArrayList
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Generics help keep types in line, no more casting all the time!
Stories
Imagine a toolbox that can adjust its tools based on what you need; that's a Generic Interface that adjusts to the type of data you work with!
Memory Tools
GREAT: Generics Reuse, Ensure All Types (for remembering benefits of generics!).
Acronyms
GI - Generic Interface
for Generalization
for Item Types.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Generic Interface
An interface in Java that allows for type parameters, enabling the interface to operate on different types.
- Type Parameter
A placeholder in a generic type or method that enables the use of different data types.
- Type Safety
The guarantee that a program cannot perform operations on incompatible types.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
