LinkedList
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to LinkedList
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to talk about the LinkedList class in Java. Can anyone tell me what they think a LinkedList is?

Isn't it a type of data structure that has linked elements?

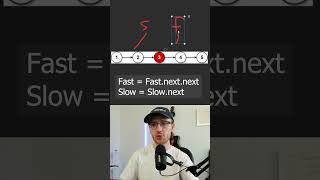
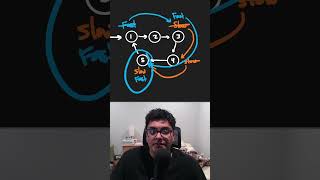
Exactly! A LinkedList consists of nodes, where each node points to the next one, and also the previous one! This is what we mean by a doubly-linked list. Now, why do you think this might be beneficial?

Maybe because we can easily add or remove items without having to shift everything around?

Correct! The efficiency in inserting and deleting nodes is a key advantage of using LinkedList over ArrayList. We can perform these operations very quickly.
Key Methods of LinkedList
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at some important methods provided by the LinkedList class. Who can name one?

What about 'add()' to insert items into the list?

That's right! The 'add()' method allows you to insert elements at various positions. What about removing?

There’s a method called 'remove()'? Does it work in the same way?

Yes! 'remove()' allows you to take elements out of the list by specifying the item or the index. These methods help maintain the dynamic capability of the list.
When to Use LinkedList
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When do you think it would be better to use LinkedList over other collections, like ArrayList?

If we are going to add and remove a lot of items frequently, right?

Yes, that's correct! LinkedList excels in scenarios where the frequency of insertion and deletion operations is high in a list. Given its structural design, it handles these changes seamlessly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The LinkedList class in Java is implemented as a doubly-linked list, providing advantages for operations involving modification such as adding or removing elements. Unlike ArrayList, it allows for efficient insertions and deletions in the list.
Detailed
LinkedList in Java
The LinkedList class in Java is a key implementation of the List interface that stores elements in the form of a doubly-linked structure. Each element, or 'node', contains references to both the previous and next nodes, enabling efficient dynamic adjustments to the size of the list. This makes the LinkedList particularly useful when frequent insertions and deletions are expected, as it can perform these operations in constant time, unlike ArrayList, which can incur significant overhead due to array copying. In this section, we will delve into its primary features, methods, and use cases, emphasizing its unique benefits in real-world applications.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
LinkedList Overview
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• LinkedList
o Doubly-linked list.
o Efficient insertions/deletions.
Detailed Explanation
The LinkedList is a specific implementation of the List interface in Java. It uses a doubly-linked list structure, which means each element, known as a node, contains a reference to both the next and the previous nodes in the sequence. This structure makes it easy to insert or remove elements from the LinkedList, especially when compared to other List implementations like ArrayList, which may need to shift elements around when changes are made.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a train, where each car is a node in a LinkedList. Each car can easily be added or removed from the train without having to rearrange the others. If you want to add or take away a car, you simply change the connections between the train cars, making trains very flexible.
Efficiency of Insertions and Deletions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Efficient insertions/deletions.
Detailed Explanation
The efficiency of insertions and deletions in a LinkedList comes from its design. When you want to add or remove an element, you only need to update the links between nodes instead of moving multiple elements, as is necessary with an ArrayList. As a result, the time complexity for these operations in a LinkedList is O(1) if you're already at the position you want to change, whereas in an ArrayList, it can be O(n) if elements need to be shifted.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a LinkedList like a group of friends standing in a circle. If one friend wants to leave the circle, they can step out, and the two friends on either side can just link arms with each other, making it a seamless change without the need for everyone else to move.
Key Concepts
-
Doubly-Linked List: A linked structure where each node points to both the next and previous nodes, allowing bi-directional traversal.
-
Node Structure: Consists of data and references to others in the list, critical for dynamic data organization.
-
Efficient Insertions/Deletions: LinkedList allows efficient addition and removal of elements without shifting other elements.
Examples & Applications
Example of using LinkedList to store customer orders allows for easy addition of new orders and removal of completed ones.
Use case in a playlist application where songs can be easily rearranged or removed.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
LinkedList, oh what a twist, nodes in a line that you can't resist.
Stories
Imagine a chain of train cars, each linked to the next, ready to add more cars or detach them, demonstrating the LinkedList's flexibility.
Memory Tools
For LinkedList: Nodes Link into Chains - 'Town's Links Change!'
Acronyms
Remember 'NODE' for LinkedList
'Next On Double Ended.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- LinkedList
A data structure that consists of nodes, where each node contains data and pointers to both the next and previous nodes, allowing double-linked traversal.
- Node
The basic unit of a LinkedList that stores the data and references to the next and previous nodes.
- DoublyLinked List
A type of linked list in which each node contains references to both the next and the previous node in the sequence.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
