Generic Class
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Generic Classes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll delve into the concept of generic classes in Java. A generic class allows us to define classes with type parameters. Can anyone explain why we might want to use generics?

I think it helps with type safety by preventing type casting errors!

Exactly, Student_1! This way, you're less likely to encounter runtime errors due to incorrect type casting. Does anyone know how we define a generic class?

Is it with angle brackets, like `class Box<T>`?

Correct, Student_2! The 'T' can be any identifier like T, E, or K, depending on the context. It's a placeholder for the actual type we will use.

To recap, generic classes enhance type safety and reusability. They're defined with type parameters in angle brackets.
Implementation of a Generic Class
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at how we can implement a generic class. Here's a simple example: `class Box<T> { private T value; public void set(T value) { this.value = value; } public T get() { return value; }}`. What does this class do?

It can hold any type of value and allows us to set and retrieve that value.

Right again, Student_3! This class can hold any type specified when creating an instance of `Box`, making it extremely flexible. Why do you think it's beneficial to have a method like `get()`?

It allows us to retrieve the value without knowing its type beforehand!

Exactly! This ability to operate on a variety of types while maintaining type safety is what makes generics powerful. Now, can anyone articulate the overall benefits of using a generic class?

It promotes code reusability and safety, which leads to fewer errors!

Great summary, Student_1! To conclude, generic classes enable safer and reusable code while allowing flexibility in data types.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
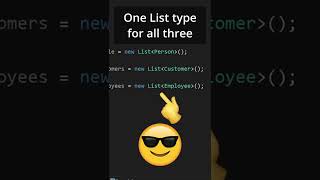
A generic class is a class that is defined with a type parameter, allowing the same class to work with different data types. This design enhances code reusability and type safety, reducing the need for casting and leading to cleaner, more maintainable code.
Detailed
In Java programming, a generic class is defined with a type parameter, represented typically by angle brackets (e.g., Box<T> can hold any type of object, and type parameters provide flexibility with minimal runtime overhead. By employing generics, programmers can write code that is more reusable and easier to maintain, reducing errors related to type mismatches. Understanding generic classes is crucial as they enable the construction of systems that are both robust and efficient.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of a Generic Class
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
class Box
private T value;
public void set(T value) { this.value = value; }
public T get() { return value; }
}
Detailed Explanation
A generic class is a class that can operate on objects of various types while providing compile-time type safety. In this example, 'BoxBox where T is a placeholder for the type of object that will be contained in the Box. The set method allows you to store an object of type T, and the get method allows you to retrieve that object. This way, Box can be reused for any type of object without losing type safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a generic class like a storage box you can use to keep anything safe—be it toys, books, or clothes. You can specify what goes inside (just like T specifies the type), and every time you pick something from the box, you know exactly what it is, ensuring it's not something unexpected.
Purpose and Benefits of Generic Classes
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Generic classes allow for code reusability and type safety.
Detailed Explanation
The main purpose of generic classes is to allow developers to write more flexible and reusable code. By defining a class as generic, you can create instances of that class for different data types without rewriting the class for each type. This also helps to prevent type-related bugs since the Java compiler checks types at compile time, reducing runtime errors associated with type casting.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a universal remote control that can operate different brands and models of TVs. Instead of having a separate remote for each TV brand (which is like writing a different class for each type), you can have one universal remote that works with all. This is similar to how generic classes allow for versatility without compromising on safety.
How to Use a Generic Class
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To use a generic class, specify the type in angle brackets. For example, Box
Detailed Explanation
When using a generic class, you specify the actual data type in angle brackets when creating an object of that class. For instance, if you want to create a box specifically for storing Strings, you use Box<String> stringBox = new Box<>();. This tells the compiler that this box will hold String objects, ensuring any element you add must be a String, enhancing type safety.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine buying a bottle for storing liquid. If you label it as a 'water bottle,' you know exactly what type of liquid to put in it. Similarly, when you specify Box<String>, you ensure that only String values can be added to this box, just like only water goes into a water bottle.
Key Concepts
-
Generic Class: A class defined with a type parameter, allowing for greater flexibility and code reuse.
-
Type Parameter: A placeholder for the actual type supplied when the class is instantiated.
-
Type Safety: Reduces the chances of runtime errors by enforcing types at compile time.
Examples & Applications
A Box class that holds an Integer: Box<Integer> intBox = new Box<>(); intBox.set(5); Integer value = intBox.get();
A Box class that holds a String: Box<String> stringBox = new Box<>(); stringBox.set("Hello"); String text = stringBox.get();
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Generic classes are quite nifty, they help avoid errors that make us shifty.
Stories
Imagine a box that can hold anything – this is the magic of generics in Java, where type safety is king!
Memory Tools
Remember 'GREAT': Generics Reduce Errors and Add Type safety.
Acronyms
Think 'G.I.V.E.'
Generics Improve Variable Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Generic Class
A class that can work with any data type defined with a type parameter.
- Type Parameter
A placeholder in the generic class definition that specifies the type it will operate on.
- Type Safety
The assurance that the code will not produce run-time type errors due to incorrect type use.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
