Deque Interface
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll delve into the Deque interface, which adds flexibility to our data structures. What does a double-ended queue mean to you?

Does it mean we can add and remove elements from both ends?

Exactly! You can think of it as a train where you can get on and off from either end. This allows for both FIFO and LIFO operations!

Can you give us an example of when we’d use a Deque instead of just a regular Queue?

Absolutely! A great example is a task scheduler where you want to add urgent tasks to the front but regular tasks can go to the back.

So, using a Deque helps manage tasks more efficiently!

Exactly! Let's remember that using Deque can optimize our data flow.
Key Methods of Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into the main methods of the Deque interface. Who can list them for us?

I think they include addFirst and addLast?

Correct! Those methods allow you to add elements to both ends. Can anyone explain what removeFirst does?

It should remove the first element in the Deque.

Perfect! And the removeLast method does the same for the last element. Can anyone think of a scenario where these would be useful?

If we’re managing a to-do list, we could add tasks at the start when they are prioritized.

Great example! Remember these methods well as they are foundational for many applications!
Implementations of Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the implementations of the Deque interface. Can anyone name one?

I heard about ArrayDeque, which is resizable?

Exactly! ArrayDeque is an efficient array-based implementation. What about another implementation?

Isn't there a LinkedList implementation as well?

Yes! LinkedList allows efficient insertions and deletions but has a bit of overhead. When might you choose one over the other?

I think if we're looking for performance in frequent additions and removals, LinkedList might be better, right?

That's right! Performance considerations are key when deciding what to use.
Practical Applications of Deque
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone suggest real-world applications for using a Deque?

Maybe for undo functions in a text editor where you can go back and forth between actions?

Great thought! That's a classic example. It allows users to navigate actions seamlessly. What else?

It could be used in a browser's back-forward navigation. You can add pages to both ends.

Exactly! Always think about how data flows. Deque is perfect when flexibility is paramount. How will you remember its features?

I could create a rhyme to remember the methods!

Great idea! Creative memory aids enhance recall and understanding.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Deque interface is a part of the Java Collections Framework that implements a double-ended queue. It facilitates both FIFO (first-in-first-out) and LIFO (last-in-first-out) operations through its key methods, including addFirst, addLast, removeFirst, and removeLast. Understanding these operations is essential for effectively managing collections in Java.
Detailed
Deque Interface in Java
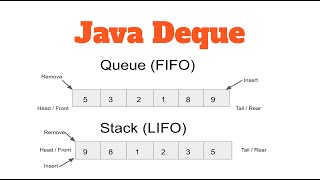
The Deque (Double-Ended Queue) interface in Java is a versatile collection that enables the addition, removal, and access of elements from both ends. This directly supports both FIFO (First-In-First-Out) and LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) operations. Unlike a standard Queue, which restricts operations to one end, Deque allows for greater flexibility in management.
Key Methods:
- addFirst(E e): Inserts the specified element at the front of the deque.
- addLast(E e): Inserts the specified element at the end of the deque.
- removeFirst(): Removes and returns the first element of the deque.
- removeLast(): Removes and returns the last element of the deque.
This interface is crucial for applications requiring dynamic data structure manipulation, such as task scheduling, palindromic checks, or undo mechanisms in applications. Familiarity with these operations allows developers to implement efficient data processing algorithms in Java.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Deque
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Deque Interface
Double-ended queue allowing FIFO and LIFO.
Detailed Explanation
The Deque interface in Java represents a double-ended queue. This means that you can add and remove elements from both ends of the queue. FIFO, or 'First In, First Out', means that elements added first will be the first to be removed, similar to waiting in line. LIFO, or 'Last In, First Out', means that the last element added will be the first one to be removed, much like stacking plates.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a deque as a line at a concert. If you are at the front (the first in line), you get to enter the concert first (FIFO). But if there are a stack of tickets in your hand, and you can only pass forward the last ticket you picked up to enter, that's like LIFO.
Deque Operations
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• addFirst(), addLast(), removeFirst(), removeLast()
Detailed Explanation
The Deque interface provides several key methods that allow you to manipulate the elements it contains. 'addFirst()' adds an element to the front of the deque, while 'addLast()' adds an element to the end. Similarly, 'removeFirst()' removes and returns the element at the front, and 'removeLast()' removes and returns the element at the back. These operations make it flexible for handling data where you might need to access either end more frequently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a parking garage where you can park cars in two directions: you can park cars from the front or from the back. 'addFirst()' would be like parking a car at the entrance, while 'addLast()' is parking at the exit. When retrieving cars, 'removeFirst()' allows you to take the car parked at the entrance first, and 'removeLast()' lets you take the last car parked at the exit.
Key Concepts
-
Deque Interface: Allows addition and removal of elements from both ends, enabling FIFO and LIFO operations.
-
addFirst and addLast: Methods for adding elements to the front and back of the Deque respectively.
-
removeFirst and removeLast: Methods to remove and retrieve elements from the front and back of the Deque respectively.
-
Implementations: Common implementations include ArrayDeque and LinkedList, each with unique performance characteristics.
Examples & Applications
Using a Deque to implement a browser's history where users can navigate back and forth between pages.
Creating an undo feature in a text editor where actions can be undone or redone using both ends of a Deque.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a Deque we find, items unwind, from both ends they fly, first or last, oh my!
Stories
Imagine a bustling train station where passengers can get on and off trains at both ends, seamlessly choosing their route.
Memory Tools
A D.E.Q.U.E can Add First, Add Last, Remove First and Remove Last - remember: 'A-F, A-L, R-F, R-L'.
Acronyms
D.E.Q. (Double-ended Queue) - Double life
adding/removing
enriching data approaches!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Deque (DoubleEnded Queue)
A linear collection that allows addition or removal of elements from both ends.
- FIFO
First-In-First-Out, a method where the first element added is the first to be removed.
- LIFO
Last-In-First-Out, a method where the last element added is the first to be removed.
- addFirst()
Method to insert an element at the front of the deque.
- addLast()
Method to insert an element at the end of the deque.
- removeFirst()
Method to remove and return the first element from the deque.
- removeLast()
Method to remove and return the last element from the deque.
- ArrayDeque
An array-based resizable implementation of the Deque interface.
- LinkedList
A linked list implementation of the Deque interface that allows for efficient insertions and deletions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
