Generic Classes and Interfaces
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Generic Classes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're learning about generic classes. Can anyone tell me what a generic class is?

Is it a class that can handle different data types?

Exactly! A generic class allows us to define classes with type parameters, making our code flexible and type-safe. For example, look at this `Box<T>` class.

What does the 'T' signify?

The 'T' is a type placeholder that can be replaced with any object type at runtime. So `Box<Integer>` and `Box<String>` are both valid instances of this class. Remember, this flexibility reduces type casting errors!

Can we create a Box for any type? What about custom classes?

Great question! Yes, you can create `Box<YourCustomClass>` as well. It allows for maximum reusability and type safety, which is crucial for maintaining code quality.

In summary, generic classes enhance our programming capabilities significantly by improving code reusability and minimizing runtime errors related to type casting.
Exploring Generic Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s move on to generic interfaces. Who can explain what a generic interface does?

Is it like a class, but for defining methods that can operate on types?

Exactly! A generic interface allows a method to operate on objects of different types while ensuring type safety. For instance, the `DataStore<T>` interface allows us to define a method like `save(T item)`, where 'T' can be any type.

How does that help in programming?

It promotes consistency and ensures that the data being processed fits the expected type. This is especially useful when implementing data storage solutions where type integrity is crucial.

So, if I implement `DataStore`, I can define what type I want to save, say, a `User` class?

Exactly! This example demonstrates how generics can be applied flexibly across different usages and implementations. Always remember: with great flexibility comes great responsibility regarding type management!

In conclusion, both generic classes and interfaces are foundational in Java, improving code maintainability and execution reliability.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Generic classes and interfaces allow developers to define classes and interfaces with placeholder types, enabling type-safe operations. This section introduces the syntax and implementation of generic classes like Box<T> and interfaces such as DataStore<T>, emphasizing their importance in modern Java programming.
Detailed
Generic Classes and Interfaces
In Java, generics enable classes and interfaces to operate on types specified by the user. This capability improves type safety and allows for code that is both flexible and reusable.
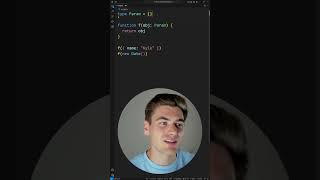
Generic Class
A generic class defines a class with type parameters. It allows the creation of objects with a specified type at runtime while maintaining type safety.
Example of a Generic Class:
In this example, Box<T> can hold any type, and methods set and get manage the contents safely without the need for casting.
Generic Interface
Similar to classes, interfaces can also be made generic. A generic interface defines methods with type parameters, enhancing the flexibility of data handling.
Example of a Generic Interface:
This allows any implementer of DataStore to work with a specific type, promoting type safety and reducing errors.
Understanding and utilizing generic classes and interfaces is integral to leveraging the full capabilities of Java's Collections Framework and ensuring high-quality, maintainable code.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Generic Class
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
class Box{ private T value; public void set(T value) { this.value = value; } public T get() { return value; } }
Detailed Explanation
A generic class in Java is defined using the class keyword followed by a name and a type parameter enclosed in angle brackets. In this case, Box<T> means that Box is a class that can hold a value of any type specified when creating an instance of it.
Within the class, there is a private variable value of type T, which can be set or retrieved using the methods set(T value) and get(). This approach allows for type safety, meaning the specific type of value this class can handle is determined when an instance of Box is created, which reduces the chances of runtime errors caused by type mismatches.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a generic class like a storage box that can hold anything you want—be it toys, books, or groceries. When you first get the box, you decide, 'I want this box to hold toys' (let's say, the type Toy). From that point on, you can only put toys in it. If you try to place a book in it, it wouldn’t fit, and that helps you avoid a mix-up of items.
Generic Interface
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
interface DataStore{ void save(T item); }
Detailed Explanation
A generic interface is defined similarly to a generic class, allowing it to work with any type specified at the implementation level. Here, DataStore<T> is an interface that includes a method save(T item). This method can save an item of any type specified when implementing the interface, thus promoting flexibility and reusability in code.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a generic interface like a recipe template that can be used to create different kinds of dishes. For example, you can have a recipe that asks for any type of protein—chicken, tofu, or beans. You fill in the specific protein you wish to use, and the recipe adapts to make that dish. This way, the same recipe format can be reused for various ingredients!
Key Concepts
-
Generic Class: A class that can be parametrized with types for greater flexibility.
-
Type Safety: Ensuring that the program does not encounter type-related errors at runtime.
-
Generic Interface: An interface that utilizes type parameters, allowing for various data types.
Examples & Applications
The Box<T> class that can hold any object type and includes methods for setting and getting values.
The DataStore<T> interface that defines a method to save objects of any specified type.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Generics are neat; they help code compete, with types that are free, the errors retreat.
Stories
Imagine a toolbox where every tool can adapt. Generics are like that, fitting any project type perfectly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'G.O.N.E.' – Generic Objects Need Examples – to recall why we use generics.
Acronyms
G.I.F.T.
Generic Interfaces For Type-safety.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Generic Class
A class that can operate on objects of various types defined by the user.
- Generic Interface
An interface that allows methods to operate on specified types, enhancing type safety.
- Type Parameter
A placeholder for a data type used in generic classes and interfaces.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
