Handling Exceptions and Closing Resources
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Closing Resources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about handling exceptions and closing resources in JDBC. Why do you think it's important to close resources like Connection and Statement?

I think closing them prevents memory leaks.

Exactly! Not closing these resources can lead to memory leaks as they hold onto resources, which can slow down the application or even lead to it crashing. Can anyone name what types of resources we should close?

ResultSet, Statement, and Connection?

Correct! Always remember to close those three types of resources. To help you remember, think 'RSC' — ResultSet, Statement, Connection. Can you all repeat that?

RSC!

Great! Let’s see an example of how we can close these resources effectively.
Using try-with-resources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about try-with-resources. Who knows what this feature does?

Isn’t it a way to automatically close resources?

Exactly! In the try-with-resources statement, any resource declared in the parentheses will be closed automatically once it is no longer needed. Can you see how this simplifies our code?

Yes, that means we don't have to write extra code to close them!

Spot on! This feature was introduced to help us manage resources better and prevent errors. Would you like to see an example code snippet?

Yes!
Error Handling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss how to handle errors effectively in our JDBC code. Why is it necessary to catch SQL exceptions?

To prevent the application from crashing and to log errors?

Exactly! Catching SQL exceptions allows us to handle any issues gracefully. When working with databases, many things can go wrong. How do we log these exceptions effectively?

By using the printStackTrace method?

Correct! Using printStackTrace is a good way to understand what happened. What should you do in a production environment?

We should log errors to a file or monitoring system.

Exactly! Always ensure that your logging is set up correctly in production to avoid losing important information.
Summary and Key Takeaways
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up today’s lesson, can anyone summarize why handling exceptions and closing resources is important?

It prevents memory leaks and ensures our application runs smoothly!

Perfect summary! Remember to always use RSC. Can someone remind me what that stands for?

ResultSet, Statement, Connection!

Great job! And don’t forget to use try-with-resources for cleaner code. Keep practicing, and let’s continue to enhance our JDBC skills!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we learn how to effectively manage exceptions while working with JDBC, specifically the necessity of closing resources such as ResultSet, Statement, and Connection. The use of the try-with-resources statement is highlighted as a recommended practice to ensure that resources are managed efficiently, reducing the risk of memory leaks and other issues.
Detailed
Handling Exceptions and Closing Resources in JDBC
In JDBC programming, effective exception handling is crucial to ensure that database connections and other related objects are properly managed. This section emphasizes the significance of closing resources like ResultSet, Statement, and Connection after their use to prevent memory leaks and other potential issues.
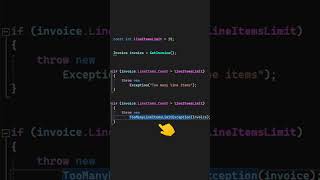
A common approach to manage exceptions and ensure resource closure is the try-with-resources statement, introduced in Java 7. This statement automatically closes resources when the try block is exited, either normally or due to an exception. Using try-with-resources can lead to cleaner code and reduces the risk of errors during resource management. An example of its usage is shown below:
In this example, both the Connection and PreparedStatement objects are closed automatically when the try block completes. Proper error handling is also critical, with SQL exceptions being caught and logged appropriately, ensuring that the application behaves predictably even when errors arise.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Closing Resources
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Always close:
• ResultSet
• Statement/PreparedStatement
• Connection
Detailed Explanation
When working with databases in Java, it's essential to close various resources after their use to prevent memory leaks and other issues. Specifically, when you interact with a database, you create connections and statements. If you do not close these resources, they remain open and can lead to performance degradation or even exhaustion of database connections. This is particularly crucial in web applications that may handle many database requests simultaneously.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where you can borrow books. If many people borrow books but don't return them, the library eventually runs out of books to lend. Similar to returning books, closing resources in database programming ensures that connections and statements are always available for use. Failing to return borrowed books would hinder others from accessing those resources, just like not closing database connections can hamper your applications' performance.
Try-with-Resources
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Try-with-resources is recommended:
try (Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(...);
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(...)) {
// execute query
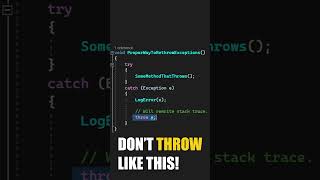
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Detailed Explanation
The try-with-resources statement in Java automatically closes all resources defined within the parentheses once the try block is exited. This means you don’t have to write separate code to close each resource. In the example, if a Connection and PreparedStatement are declared in the try statement, they will be closed automatically when the block finishes, whether it exits normally or due to an exception. This feature simplifies error handling and makes code cleaner.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant where the waiter prepares a table for a customer and automatically clears it after the customer leaves. The waiter does not need to wait for the customer to remind them to clear the table. Similarly, the try-with-resources statement in Java ensures that resources are cleaned up automatically, freeing developers from manual resource management.
Error Handling with Exceptions
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
// execute query
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Detailed Explanation
The catch block is a crucial part of error handling in Java. When working with databases, errors (SQLException) can occur during connection attempts, query executions, or data retrievals. By catching exceptions, you can handle these errors gracefully. In the example provided, if an SQLException occurs, the error message will be printed to the console. This allows developers to diagnose problems without crashing the application.
Examples & Analogies
Think of driving a car. If something goes wrong, such as a tire blowout, the driver must respond appropriately by pulling over safely and checking the issue. Similar to this, when a database operation fails, the catch block allows you to manage the problem efficiently rather than letting it disrupt the entire application, providing clarity to what has gone wrong.
Key Concepts
-
Closing Resources: Essential for preventing memory leaks, always close ResultSet, Statement, and Connection.
-
Try-with-Resources: A Java feature that auto-closes resources, simplifying resource management.
-
Exception Handling: Handling SQL exceptions gracefully to prevent application crashes.
Examples & Applications
Using try-with-resources in JDBC to automatically close connection and statement objects.
Catching SQL exceptions to log errors without crashing the application.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Close the con, the stmt so fair, ResultSet ends the resource layer.
Stories
Imagine a programmer who forgets to close connections. Every night they find their application running slow, as it forgets to put resources back to sleep. They learn to close them every day after coding.
Memory Tools
Remember 'RSC' to keep your JDBC clean: ResultSet, Statement, Connection!
Acronyms
RSC - ResultSet, Statement, Connection; keep these in mind to avoid resource leaks!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SQLException
An exception thrown when there is an error accessing or interacting with a database using JDBC.
- Resource Leak
A condition that occurs when program resources are not released after their use, potentially exhausting system resources.
- trywithresources
A Java feature that automatically closes resources when finished, improving resource management in code.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
