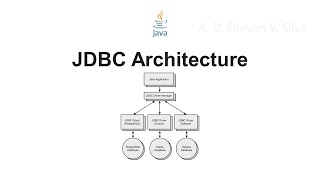
JDBC Architecture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to JDBC Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the architecture of JDBC. Can anyone tell me what JDBC is?

Isn't it Java Database Connectivity? It allows Java applications to connect with databases.

Exactly! JDBC provides the framework for interaction between Java applications and databases. Now, can anyone explain the two-tier architecture?

I think it means the application communicates directly with the database using drivers?

Correct! In two-tier architecture, Java applications do interact directly with databases, often suitable for simple or smaller-scale applications. Now, what about the three-tier architecture?

Does it involve a middle-tier, like a server that manages the database requests?

That's right! The three-tier architecture provides a middle layer that enhances security and scalability.

So, using a middle-tier can make applications more maintainable?

Precisely! Remember the mnemonic 'T3' for Three-Tier: 'Three Tiers = Tighter Security, Terrific Scalability, and Timely Maintenance.'

In summary, we can think of two-tier architecture for simplicity while using three-tier architecture for more complex applications.
Comparing Two-Tier and Three-Tier Architectures
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the differences between the two-tier and three-tier architectures. What do you think could be an advantage of the two-tier architecture?

I guess it has lower latency since there’s no middle tier to deal with?

Good observation! And what about potential downsides?

It could be less secure since clients are directly connected to the database.

Exactly! Security is a crucial factor. Now, moving to the three-tier architecture, what are some benefits associated with it?

It can handle more users without performance issues due to its scalability?

Yes! And its separation of concerns helps in easier maintenance. Remember, 'Middle equals Maintenance!' Now, can someone summarize the key differences for me?

Two-tier is direct and simpler, while three-tier is complex but more scalable and secure.

Great summary! The choice of architecture greatly influences application performance, scalability, and security.
Application Design Implications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss how our architectural choices affect our application design. What do you think about application design in a two-tier architecture?

It seems simpler and quicker to develop, but might not suit large-scale applications?

Correct! Conversely, what about designing in a three-tier architecture?

It requires more setup, but it sounds like it will be better for larger teams.

Exactly! Teams can work separately on the presentation logic, business logic, and database management. This separation enhances collaboration and potentially reduces bugs.

So, it encourages best practices in software development?

Absolutely! One way to remember this is 'Divide and Conquer'—each layer manages its distinct responsibilities well. Can someone summarize how architecture impacts the application?

Two-tier is quick but limited, while three-tier is organized and suited for complex apps.

Well done! Understanding how architecture influences design is key for developers.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The JDBC Architecture section outlines two primary architectural models: the two-tier architecture, where Java applications directly communicate with databases via JDBC drivers, and the three-tier architecture, which incorporates a middle tier to manage interactions. Understanding these models is crucial for designing efficient database-concurrent Java applications.
Detailed
JDBC Architecture
In this section, we delve into the architecture of JDBC, which is essential for understanding how Java applications communicate with relational databases. The JDBC architecture can be categorized into two primary models:
1. Two-Tier Architecture
In the two-tier architecture, the Java application communicates directly with the database using JDBC drivers. This model is suitable for small applications where the client is responsible for the entire database communication. The direct communication allows for faster interactions and is straightforward to implement.
2. Three-Tier Architecture
Conversely, the three-tier architecture introduces a middle-tier between the client application and the database. This middle-tier, often represented by servlets or application servers, is responsible for housing the business logic and managing requests to the database. This separation enhances scalability, maintainability, and security, making it the preferred architecture for larger and more complex applications.
In summary, understanding these two architectures is key to selecting the appropriate design for Java applications that require data manipulation and retrieval from databases.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Two-Tier Architecture
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Java application communicates directly with the database using JDBC drivers.
Detailed Explanation
In a Two-Tier Architecture, the Java application interacts directly with the database. This means that there is no intermediary between the application and the database. The application sends SQL commands directly to the database through JDBC drivers. In this architecture, the application requires to manage its own connections and database communications, which could lead to performance issues if not handled properly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are trying to buy groceries directly from a farmer. You walk up to the farmer (the database), tell them exactly what you need (the SQL commands), and they give you the goods directly. This direct communication is like the Two-Tier Architecture.
Three-Tier Architecture
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Java application communicates with a middle-tier (like a servlet or application server), which in turn communicates with the database.
Detailed Explanation
In Three-Tier Architecture, there is an additional layer between the Java application and the database. This middle tier, which could be a servlet or an application server, handles database interactions. The application sends requests to this middle tier, which processes them and interacts with the database as needed. This approach offers improved scalability and security, as database connections can be managed more effectively and security controls can be applied at the middle layer.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this as a situation where instead of talking directly to the farmer, you go to a grocery store (the middle-tier). The store has employees who take your order (the application), go to the farmer (the database), and then provide you with the groceries. This system allows for better organization and efficiency.
Key Concepts
-
Two-Tier Architecture: A straightforward model where applications communicate directly with the database.
-
Three-Tier Architecture: A model that includes a middle tier for improved organization and security.
-
Database Interaction: The way Java applications utilize JDBC to perform CRUD operations.
Examples & Applications
In a two-tier architecture, a simple student management application may connect directly to a MySQL database for querying student records.
In a three-tier architecture, an e-commerce platform where the client's front-end communicates with a server application that manages requests to the database behind it.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Two-tier for quick and neat, three-tier makes it hard to beat!
Stories
Imagine a chef (the application) cooking directly in a diner’s kitchen (the database) in two-tier, but in three-tier, the chef sends orders through a waiter (the middle tier) to ensure everything runs smoothly!
Memory Tools
To remember the architecture types: '2T for direct Touch and 3T for Teamwork Transaction!'
Acronyms
T2 = Two-Tier, T3 = Three-Tier. "Think twice, two tiers are nice but three is a charm!"
Flash Cards
Glossary
- JDBC
Java Database Connectivity, an API in Java for interacting with databases.
- TwoTier Architecture
A model where the client application communicates directly with the database.
- ThreeTier Architecture
A model including a middle-tier that handles communication between client applications and the database.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
