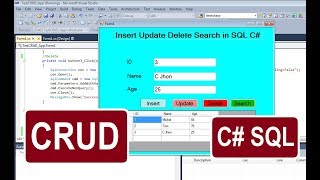
Inserting, Updating, and Deleting Records
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
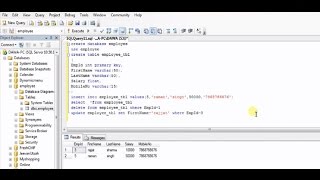
Inserting Records
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with inserting records. Can anyone tell me the importance of inserting data into a database?

Inserting records is essential for adding new data to our database.

Exactly! We need to track students' information, right? Now, here’s how you can insert records using a `PreparedStatement`. Let’s look at this example.

"```java
Updating Records
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss updating records. Has anyone here ever changed data in a database?

Yes, I updated a student's grade once!

Perfect! In databases, you can update records using the `UPDATE` statement. Let’s examine this example.

"```java
Deleting Records
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve discussed insertions and updates, let's move on to deletions. Why would we delete records?

We might need to remove outdated information or incorrect entries!

Exactly! Now, here’s how you can delete records using JDBC.

"```java
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the practical execution of CRUD operations, focusing on how to insert new records, update existing data, and delete records from a database using the PreparedStatement in JDBC. We provide example code snippets to illustrate these processes.
Detailed
Inserting, Updating, and Deleting Records
In the context of database management, the ability to insert, update, and delete records is fundamental. This section elaborates on these key operations using the JDBC API in Java.
Key Operations Covered:
- Inserting Records: We use the
INSERT INTOstatement through aPreparedStatement. An example demonstrates how to insert student data into a database.
- Updating Records: The section also covers how to update existing records using the
UPDATEstatement. The use of placeholders in parameterized queries prevents SQL injection threats while improving performance.
- Deleting Records: Lastly, we detail how to remove records from a database using the
DELETEstatement. Again, parameterized queries ensure security and efficiency.
These operations are crucial for managing data in an application. Proper use of the PreparedStatement helps maintain the integrity of the database while safeguarding against SQL injection risks.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Inserting Records
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
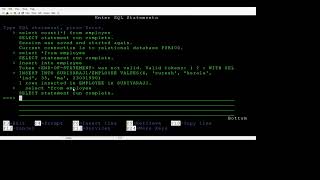
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO students VALUES (?, ?, ?);");
pstmt.setInt(1, 103);
pstmt.setString(2, "Aman");
pstmt.setString(3, "B.Tech");
int rows = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows inserted.");
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we cover the process of inserting records into a database using JDBC. First, we prepare a SQL statement that defines how we want to insert data into the 'students' table. We use placeholders (question marks) to indicate where data will be inserted. We then set the actual values for these placeholders using the setInt and setString methods. Finally, we execute the update using executeUpdate(), which returns the number of rows affected by the operation, allowing us to confirm how many records were inserted.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this process like filling out a form for a new student at a school. Just as you fill in different fields like ID, name, and course, here we define the data we want to insert into our database. Once the form is complete and submitted, the student is officially added to the school records just like our data is added to the database.
Updating Records
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement("UPDATE students SET name=? WHERE id=?;");
pstmt.setString(1, "Rahul");
pstmt.setInt(2, 101);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we discuss how to update existing records in the database. We prepare a SQL statement for updating a specific student's name based on their ID. Just as before, we use placeholders, but in this case, we specify the new name and the ID of the student we want to update. The executeUpdate() method is used again to perform the operation, updating the necessary record in the database.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this updating process as changing your contact details with a service provider. You provide the updated name (new contact detail) along with your unique account ID (identification), and once you submit the update, they modify their records accordingly. Similarly, we’re modifying the student details in the database.
Deleting Records
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement("DELETE FROM students WHERE id=?;");
pstmt.setInt(1, 101);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains how to delete records from the database. We prepare a SQL statement that specifies which record to remove by identifying it with an ID. Using the setInt method, we provide the ID of the student we wish to delete. The executeUpdate() method executes the deletion. Just like insertion and updating, this method affects the number of records removed from the table.
Examples & Analogies
Think of deleting a record like removing a page from a book. When you realize a page is no longer needed (for example, if a student leaves the school), you simply rip it out. In our case, we identify the specific page (student record) to remove using its ID and then execute the deletion process.
Key Concepts
-
Inserting Records: Inserting new data into a database using SQL commands through JDBC.
-
Updating Records: Changing existing data using the UPDATE SQL command in JDBC.
-
Deleting Records: Removing specified data from a database using the DELETE SQL command.
Examples & Applications
Inserting a new student with ID=103, name='Aman', and course='B.Tech' into the students table.
Updating the student's name from 'OldName' to 'Rahul' for the record with ID=101.
Deleting the record of the student with ID=101 from the database.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Insert, Update, Delete, making your data neat!
Stories
Imagine a librarian who organizes books. She adds new books (insert), changes the author’s name (update), and removes old books (delete) to keep the library updated.
Memory Tools
IUD: Insert, Update, Delete – the three actions you need to remember!
Acronyms
CRUD
Create
Read
Update
Delete - core database operations.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- PreparedStatement
A precompiled SQL statement that can be executed multiple times efficiently and safely.
- CRUD
An acronym for Create, Read, Update, and Delete; basic operations of persistent storage.
- SQL Injection
A code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications by inserting malicious SQL statements.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
