Two-Tier Architecture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss Two-Tier Architecture in database systems. Does anyone know what this implies?

Does it mean the application talks directly to the database?

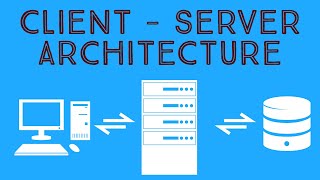
Exactly! This architecture allows the Java application to communicate directly with the database using JDBC. We can remember it as 'Direct Communication'.

What are the benefits of having direct communication?

Good question! Benefits include simplification in deployment and potentially better performance. However, it has its limitations, especially when dealing with scalability.

So, if we expand our application, will this architecture still be efficient?

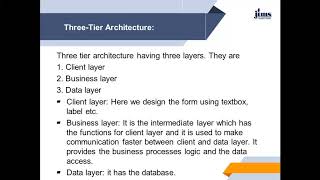
Not necessarily. As the application grows, a Three-Tier Architecture may be more suitable due to added layers for better management.

To summarize, Two-Tier Architecture is efficient and straightforward for smaller applications but can be limiting in larger, complex systems.
Advantages of Two-Tier Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into the advantages of Two-Tier Architecture. What do we think some of these might be?

It seems less complex because there are fewer layers.

Correct! The simplicity is a major advantage. It also often leads to faster interactions, as there's no middle layer processing requests.

Is it primarily used in small applications?

Yes, typically it is suitable for smaller applications requiring direct data access. We often use it in local or less complex environments.

Does that mean we shouldn't use it for responsive web applications?

Exactly, while it's great for smaller tasks, larger applications benefit more from more elaborate architectures. But for quick prototypes, Two-Tier can be effective.

To wrap up, remember: simplicity and performance make Two-Tier a go-to for small applications, but consider scalability for larger needs.
Challenges in Two-Tier Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's examine some challenges of Two-Tier Architecture. What do we think might be a disadvantage?

If all requests go directly to the database, might that create a bottleneck if many users connect?

Exactly! That's one of the key challenges. High user demand can strain database resources.

So, it's not good for applications that might scale rapidly or get many simultaneous users?

Correct again! This architecture can limit scalability and flexibility as the user base expands.

Would you suggest a different architecture then?

Indeed! For larger applications, a Three-Tier Architecture is often more manageable. It introduces a middle layer for better resource handling.

In summary, Two-Tier is advantageous for its simplicity but be cautious of its limitations regarding scalability and user load.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In Two-Tier Architecture, the client application communicates directly with the database, allowing for efficient data operations through JDBC drivers. This structure provides simplicity in building applications but may have scalability limitations compared to Three-Tier Architecture.
Detailed
Two-Tier Architecture
Overview
Two-Tier Architecture is a design paradigm in database connectivity where the client application directly interacts with the database using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC). This approach allows developers to execute SQL commands and manage database records seamlessly.
Key Features
- Direct Communication: The Java application communicates directly with the database, which eliminates the need for an intermediate server layer.
- Simplicity: This architecture simplifies deployment and maintenance due to fewer components involved.
- Performance: Direct database communication can result in better performance for applications that require immediate data access.
- Use Cases: Ideal for smaller applications or scenarios where direct database interaction is necessary.
Limitations
However, this architecture can lead to scalability issues as it places more demands on the client while growing, which may not be optimal for larger, enterprise-level applications.
The Two-Tier Architecture serves as a foundation for understanding how database connectivity functions in a more complex environment, such as the Three-Tier Architecture, which introduces additional layers for better management and scalability.
Youtube Videos



![What is 2 Tier Architecture in Advanced Java [Hindi]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Y1c3L2QW0T8/mqdefault.jpg)


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Direct Communication
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Java application communicates directly with the database using JDBC drivers.
Detailed Explanation
In a two-tier architecture, the application that you build in Java communicates directly with the database. This means that the Java application needs to use JDBC drivers to connect to the database without any intermediaries. The JDBC drivers act as a bridge between the Java application and the database system, enabling SQL queries to be sent to the database and results to be retrieved back to the application seamlessly.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a direct phone call between two friends. One friend is calling to ask a question directly, without needing a secretary to relay the message back and forth. In this analogy, the Java application is the caller, and the database is the friend on the other end of the line, providing direct access to information.
Benefits of Two-Tier Architecture
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this architecture, the application manages data access and business logic on the client side.
Detailed Explanation
One of the major advantages of two-tier architecture is that it allows the application to handle both data access and business logic within the client side itself. This approach can lead to increased performance since there is no middle layer that adds overhead, and it can simplify the application development process. However, it can also mean that certain updates or changes may need to be managed by every client that connects to the database, which can be cumbersome in larger deployments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a coffee shop where a customer orders a coffee from the barista directly. The barista prepares and serves the coffee (client-side processing), whereas, in a cafe with multiple staff, orders might go through a waiter (middle tier) before reaching the barista, which can complicate or slow down service.
Limitations of Two-Tier Architecture
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
While it offers simplicity and performance, it can face challenges with scalability and maintenance as the size of the application grows.
Detailed Explanation
Despite its benefits, two-tier architecture can have limitations, especially in terms of scalability and maintainability. As more users access the application and the database, the direct connections can become overwhelmed. Each client directly handles database requests, which can lead to load issues. Additionally, with multiple clients running similar code, updates need to be made individually unless there is a shared library approach, complicating maintenance.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a small library that has a single librarian who directly serves each patron. This works perfectly well for a few visitors but becomes chaotic if the library experiences a sudden influx of visitors. All patrons have to wait in line, meaning some patrons might leave unhappy. This situation mirrors the scalability issues of two-tier architecture when dealing with larger user bases.
Key Concepts
-
Two-Tier Architecture: Direct interactions between Java applications and databases.
-
JDBC: The API used to facilitate database communication.
-
Direct Communication: Simplifies operations by removing middle layers.
Examples & Applications
Connecting a Java application to a MySQL database using JDBC for user login.
Deploying a local application that fetches and displays student records directly from a database.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Two-Tier's smooth, no middle layer, for small apps, it's a great player.
Stories
Imagine a direct highway from a city (the application) to a warehouse (the database). It's quick but can get congested.
Memory Tools
Use 'DATADIRECT' to remember Two-Tier's characteristics: Direct access to the database with Application in between.
Acronyms
DRY - Direct, Robust, Yet simple!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- TwoTier Architecture
A structure where applications communicate directly with databases, typically through JDBC.
- JDBC
Java Database Connectivity; an API allowing Java applications to interact with databases.
- Direct Communication
The process of two systems communicating directly without intermediaries.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
