Three-Tier Architecture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Three-Tier Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss the three-tier architecture of JDBC. Can anyone tell me what a tier means in this context?

I think a tier refers to a separate layer of architecture that groups similar functionalities together.

Exactly! The three-tier architecture divides these functionalities into three distinct layers: client, middle, and data. This separation allows each tier to interact independently. Why do you think that might be beneficial?

I guess it could make the application easier to maintain. If one part has a problem, you can fix it without messing everything up.

Correct! Let's remember this with the acronym 'CMD' for Client, Middleware, and Database. It emphasizes that each layer has a specific role.
Client Tier
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the client tier. This is the face of the application that users interact with. What do you think happens here?

The users enter data and maybe see results from the database?

Exactly! This interaction involves sending requests to the middle tier, which then processes them. Can someone give an example of such interactions?

Filling out a form to register or view student grades could be examples.

Good examples! This tier is crucial for providing a user-friendly experience. Let's remember that the client tier is all about interaction.
Middle Tier
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next up is the middle tier. Who can explain its role in the architecture?

It acts like a bridge between the client and the database, right?

Yes! It processes requests from the client and handles business logic. By doing this, it abstracts the complexities of direct database access. Why is that abstraction important?

It helps to secure the database and keeps the client simpler, focusing only on the user interface.

Exactly! Remember, we can think of the middle tier as the 'thinking' tier where data processing occurs.
Data Tier
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about the data tier. What does this part do?

It stores and retrieves all of the application’s data from the database!

Correct! It is crucial for this tier to manage data effectively. What do you think would happen if this tier was not well-implemented?

There could be data loss or inefficient data retrieval, which would slow down the entire application.

Right! The reliability and performance of the data tier are vital for the overall structure’s success. Let's recap: The three tiers work in unison—Client for user interaction, Middle for processing, and Data for storage.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the three-tier architecture of JDBC, highlighting how it improves communication between Java applications and databases through a middle tier. It emphasizes the separation of concerns among presentation, business logic, and data storage, enabling better maintainability and scalability of applications.
Detailed
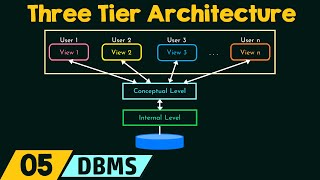
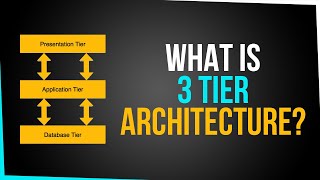
Three-Tier Architecture in JDBC
The three-tier architecture in JDBC distinguishes three layers: the client tier (presentation layer), middle tier (application logic), and data tier (database). This separation allows for enhanced modularity and scalability in application design, as each layer can be developed and maintained independently.
Key Components:
- Client Tier: This is where the user interface is located, typically in a web browser or a desktop application. User actions are captured and sent to the middle tier.
- Middle Tier: Often implemented using servlets or application servers, it acts as an intermediary between the client and the database. It processes user requests, contains business logic, and manages communication to and from databases.
- Data Tier: This layer includes the database and its management system. It handles data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
Significance:
This architecture supports more complex applications that require a clear separation of concerns, leading to easier debugging and enhancement over time. Developers can update the user interface without affecting the database code, and vice versa. This flexibility is essential for large-scale enterprise applications where scalability and maintainability are paramount.
Youtube Videos

![What is Three-Tier Architecture in Advanced Java [Hindi]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Flarv3PJL5Y/mqdefault.jpg)

![What is 2 Tier Architecture in Advanced Java [Hindi]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Y1c3L2QW0T8/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Three-Tier Architecture
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Java application communicates with a middle-tier (like a servlet or application server), which in turn communicates with the database.
Detailed Explanation
The Three-Tier Architecture is a design pattern that separates applications into three distinct layers: the presentation layer (client side), the business logic layer (middle tier), and the data layer (database). In this architecture, the Java application does not directly connect to the database; instead, it communicates with a middle tier. This middle tier acts as an intermediary, handling requests from the Java application and managing interactions with the database. This separation of concerns allows for improved scalability, maintainability, and security, as the database interactions can be centralized and managed in one place.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant: the customers (Java application) place their orders with a waiter (middle tier), who then relays the orders to the kitchen (database). The waiter is essential as they help manage the interaction between the customers and the kitchen staff, ensuring that orders are received correctly and that the kitchen can prepare the meals without being directly disturbed by the customers.
Advantages of Three-Tier Architecture
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This architecture provides multiple benefits including scalability, maintainability, and security.
Detailed Explanation
Using the Three-Tier Architecture offers several advantages. Scalability is improved as we can enhance or expand the middle tier without altering the client or database. Maintainability is also enhanced because changes to business logic or database interactions can be managed centrally in the middle tier, minimizing the risk of impacting the client application. Furthermore, security is increased since direct access to the database by the client is removed, reducing exposure to potential threats.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a ticket booking system for a concert. With a Three-Tier Architecture, the app on your phone (client) talks to a server that manages the logic of ticket availability (middle tier), which then interacts with a database that stores ticket information (data layer). If there's a need to upgrade the server to handle more requests during a ticket sale, this can be done without changing how the app or the database works, much like upgrading the kitchen in a restaurant without changing the way customers order their meals.
Key Concepts
-
Client Tier: The user interface where interactions occur.
-
Middle Tier: Processes business logic and interacts with the database.
-
Data Tier: Responsible for data storage and management.
Examples & Applications
Example of Client Tier: A web application form where students submit their information.
Example of Middle Tier: A servlet that processes registration requests.
Example of Data Tier: A MySQL database storing student records.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In three tiers, we find our way, Client, Logic, Data play, Separate roles on this grand stage, Improving apps, no need for rage.
Stories
Imagine a bookstore. The customers (Client) browse books, the staff (Middle) processes orders, and the stockroom (Data) holds supplies. Just like that, communication flows between tiers ensuring smooth transactions.
Memory Tools
CMD stands for Client, Middle, Data, helping to remember the three layers.
Acronyms
The acronym 'CMD' helps students remember Client, Middle, and Data.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ThreeTier Architecture
A software architecture pattern that separates applications into three layers: client, middleware, and data, enhancing modularity and scalability.
- Client Tier
The user interface layer where users interact with the application.
- Middle Tier
The intermediary layer that processes business logic and manages communications between the client and data tiers.
- Data Tier
The layer that manages database operations, including data storage and retrieval.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
