Delegation Event Model (Used in Java)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Delegation Event Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today, we will explore the Delegation Event Model used in Java. This model separates event generation from event handling. Can anyone explain what they think that means?

Does it mean that one part of the program creates the events, and another part responds to them?

Exactly! The event source generates events, and the listeners handle those events. This allows for better organization of the code. Think of it as each part having a specialized function.

So, if I click a button, that's the event, and the action taken after that click is handled by a listener?

You got it! To help remember, think of ‘D’ for ‘Delegation’ being like ‘Directing’ that responsibility to another. Let’s continue exploring more examples.
Event Sources and Listeners
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dig deeper into event sources and listeners. Who can tell me what an event source is?

Is it the object that generates the event, like a button or a text field?

Absolutely! And can anyone share what a listener does?

The listener responds to the events generated by an event source?

Right again! Listeners are typically implemented using interfaces such as `ActionListener` for buttons, and `KeyListener` for keyboard events. This separates the logic of handling the events from the components themselves.

This is like a team working together: the buttons generate events while the listeners complete the task!

Well put! Teamwork is essential here. Now, let's summarize what we’ve discussed.
Benefits of the Delegation Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What advantages do you think the Delegation Event Model can offer developers?

I think it allows for cleaner code since the event handling is separate from the event creation.

It must also help when you want to modify just part of the event handling without changing the source!

Great insights! The separation promotes modularity and flexibility in applications, making maintenance easier. Additionally, it supports the handling of multiple events effectively.

That makes building larger applications simpler, I imagine!

Indeed! Remember, separating concerns is a key principle in software design. Now, what have we learned about the Delegation Event Model?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
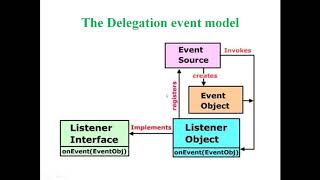
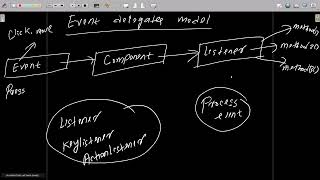
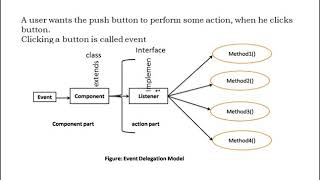
In the Delegation Event Model, event sources (components) generate events, while listeners handle those events. This model utilizes interfaces like ActionListener and KeyListener to facilitate the handling of various user interactions efficiently.
Detailed
Delegation Event Model in Java
The Delegation Event Model plays a critical role in Java's event-driven programming paradigm, specifically tailored for creating interactive GUI applications. This model relies on separating the responsibilities of generating events from the handling of those events. Each component, such as buttons or text fields, acts as an event source and produces specific event objects when user interactions occur, like clicks or key presses. Listeners, which implement predefined interfaces like ActionListener and KeyListener, are responsible for responding to these events. This structure enhances flexibility and modularity, as developers can associate different listeners with the same event source to handle various actions. This model ultimately fosters clean code maintenance and enhances the responsiveness of applications, as it allows for a more systematic approach to event management.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Separation of Event Generation and Handling
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Separates event generation from event handling.
Detailed Explanation
In the Delegation Event Model, the process of generating events and handling those events are separated into different components. This means that a component (like a button) is responsible for generating an event when a user interacts with it (e.g., clicks it). However, the actual handling of that event (what happens when the button is clicked) is managed by a different entity, usually called an event listener. This separation makes the program more modular and easier to maintain and extend.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a concert. The event (the concert itself) is generated by the band (the event-generating component). However, the event is experienced by the audience (the event listeners), who react in their own way - clapping, singing along, or dancing. Each group's role is distinct, yet both are essential for the concert to happen successfully.
Event Generation by Components
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Components generate events, and listeners handle them via interfaces like ActionListener, KeyListener, etc.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, components such as buttons or text fields are capable of creating events. These components are equipped with interfaces that define specific ways to handle different types of events. For example, an ActionListener is an interface that can handle action events (like clicks), while KeyListener handles keyboard events. When a user interacts with the component, the appropriate interface method is triggered, passing information about the event to the event handler.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant where customers can place orders (the event generation). Each waiter (the listeners) has specific instructions to handle different types of orders (like drinks, appetizers, or main dishes). When a customer places an order, the waiter retrieves it, processes it, and serves the food. The rules of communication (interfaces) ensure that everyone knows how to react appropriately to the orders they receive.
Key Concepts
-
Delegation Event Model: A programming model where event creation and handling are separated.
-
Event Source: The component that generates events (e.g., a button).
-
Event Listener: The component or method that responds to events generated by event sources.
Examples & Applications
Example of ActionListener in Java: JButton button = new JButton('Click'); button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println('Button clicked!'); } });
Example of KeyListener in Java: component.addKeyListener(new KeyListener() { public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) { System.out.println('Key pressed!'); } });
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the Delegation Model, tasks are shared, event sources create, while listeners pared.
Stories
Imagine a team at a restaurant: the chef (event source) cooks while the waiter (listener) serves the food to customers.
Memory Tools
D.E.L.E.G.A.T.E - Differentiate Event Listeners from Event Generators And Tame Everyone!
Acronyms
S.E.V.E.N - Sources Emit, Various Event Notifiers.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Event Source
An object that generates events in an event-driven system.
- Event Listener
A method or object that receives and handles events generated by event sources.
- ActionListener
An interface in Java used to handle action events, such as button clicks.
- KeyListener
An interface in Java that receives keyboard events.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
