Event Queue and Concurrency
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Event Queues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore how event queues operate within event-driven programming. Can anyone tell me what happens when an event occurs?

I think the event is just processed immediately.

That's a common misconception! In reality, the event is placed in an event queue. This allows the program to handle events sequentially. Can someone explain why this is necessary?

I guess it helps avoid race conditions where multiple events get processed at the same time.

Exactly! This sequential processing ensures that no two events interfere with each other. Remember, we use the acronym 'EASY' — **E**vent, **A**dd to queue, **S**equentially process, and **Y**ield control — to keep this in mind!

Could this lead to delays if too many events stack up?

Absolutely! While event queues help prevent conflicts, if events are not handled quickly, it can lead to responsiveness issues. We'll delve deeper into this shortly.

In summary, event queues are crucial for managing concurrency, allowing sequential processing to avoid race conditions but introducing a risk of slowdown if not managed well.
Concurrency Management Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Continuing from our last session, let's discuss challenges. What issues arise from event queues?

If too many events come in, they might lag behind in processing.

That's right! This leads to a 'bottleneck' effect. Can anyone think of a method to mitigate this?

Maybe prioritize important events over less critical ones?

Great suggestion! Prioritizing events can help manage responsiveness. Remember to keep an eye on real-time applications where this is most critical.

What happens if an event takes too long to process?

It can block the event loop, causing delays for subsequent events. That's why efficient event handler design is essential.

To summarize, while event queues manage concurrency effectively, developers must ensure that event handling is efficient to avoid bottlenecks.
Real-World Applications of Event Queues
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at real-world applications. How do you think event queues are used in web applications?

They probably handle user clicks and server responses efficiently.

Exactly! Event queues manage user interactions like clicks and incoming server responses without freezing the interface. Any examples you can think of?

In a chat app, messages would queue up so new notifications don't get lost.

Right! Queuing ensures messages are displayed in the correct order and minimizes data loss. What do we learn from using event queues?

They help keep applications responsive while managing multiple events at once.

Perfect! Remember that effective queue management is vital for smooth user experiences.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
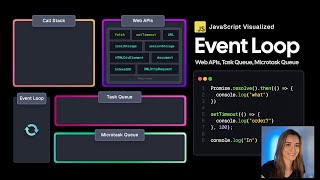
In modern event-driven programming, event queues play a critical role in managing concurrency and event processing. When an event occurs, it is placed in a queue, allowing the event loop to handle these events sequentially, mitigating issues like race conditions but potentially leading to responsiveness challenges if events are handled slowly.
Detailed
Event Queue and Concurrency
Modern event-driven systems capitalize on event queues to efficiently manage concurrency. When an event is triggered, it is deposited into a queue, where the event loop sequentially processes the events. This model helps in avoiding race conditions that often plague multi-threaded applications by ensuring that events are handled one at a time.
However, this method can introduce responsiveness issues, particularly if events pile up in the queue and the event loop cannot process them quickly enough. Understanding the balance between efficient event handling and maintaining a responsive application is vital for developers in the field of event-driven programming.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Role of Event Queues
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Modern event-driven systems often utilize event queues to manage concurrency.
Detailed Explanation
In event-driven programming, an event queue is a data structure that stores events that occur in the system. When an event happens, it gets placed in the event queue, meaning that the event will be processed later by the event loop. This structure helps manage multiple events that may occur in quick succession, ensuring that they are dealt with in an orderly manner. Each event is processed one after the other, which helps the program remain stable and avoids confusion about which event should be handled first.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an event queue like a line at a coffee shop. Each customer (event) queues up (enters the event queue) to be served by the barista (event loop). The barista serves each customer in the order they arrived, ensuring that everyone gets their coffee (the event is processed) without missing an order.
Processing Events Sequentially
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When an event occurs, it is placed in a queue, and the event loop processes these events sequentially.
Detailed Explanation
The event loop is responsible for picking events from the queue and executing the corresponding event handlers. This sequential processing ensures that each event is handled completely before moving on to the next one. By doing this, the system ensures that resources are not overwhelmed by multiple simultaneous actions, which could lead to errors or inconsistent states.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a train station where multiple trains arrive and depart. The station only allows one train to leave at a time — this means trains must wait in line until it's their turn to depart (events being handled one at a time). This prevents chaos on the tracks, just like processing events one by one prevents issues in the program.
Benefits of Using an Event Queue
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This model avoids race conditions but may lead to responsiveness issues if events are not handled quickly.
Detailed Explanation
Using an event queue helps prevent race conditions, which occur when multiple processes attempt to access shared resources at the same time, leading to unpredictable outcomes. By placing events in a queue and processing them one at a time, the system eliminates these conflicts because each event is handled without interference from others. However, if the events aren't processed quickly enough, the queue can become congested, causing delays in the system's responsiveness.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a restaurant kitchen where all orders (events) are queued up for cooking. The chef prepares each dish one by one. If the chef is efficient, the food comes out quickly, and diners are happy. But if there’s a backlog, diners may have to wait a long time for their meals, leading to dissatisfaction — similar to how unhandled events can make a program seem unresponsive.
Key Concepts
-
Event Queue: A mechanism to sequence event processing.
-
Concurrency: The ability to handle multiple events simultaneously.
-
Race Condition: A problem that can arise from improper event handling.
-
Event Loop: The central control structure in event-driven programming.
Examples & Applications
In a GUI application, clicking a button adds a click event to the event queue, which the event loop processes when it can.
In a web application, incoming HTTP requests are placed in an event queue to be handled by the server sequentially.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Events in a queue, they wait for their cue, handled sequentially, to avoid a race hue.
Stories
Imagine a busy bakery. Customers stand in line (the event queue) asking for pastries. The baker (event loop) serves them one by one, ensuring each order is taken correctly and preventing any mix-ups.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Q-CROSS': Queue, Concurrent, Race condition, Order, Sequential, where each letter reminds you of key event-related terms.
Acronyms
EASY for events
**E**vent occurrence
**A**dd to queue
**S**equential handling
**Y**ield control.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Event Queue
A queue that manages events in an event-driven programming system, allowing them to be processed sequentially.
- Concurrency
The execution of multiple instruction sequences at the same time, managed in the context of event-driven systems through event queues.
- Race Condition
An occurrence in programming where the behavior of software depends on the sequence or timing of uncontrollable events, often leading to unexpected results.
- Event Loop
A programming construct that waits for and dispatches events or messages in event-driven systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
