Clock Gating
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Clock Gating
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into clock gating, a vital method in VLSI design for saving power. Can anyone tell me what they understand by clock gating?

Is it something that helps to turn off parts of the circuit?

Exactly! Clock gating turns off the clock to certain sections of the circuit when they are not in use, which cuts down dynamic power consumption. Let’s remember it as CG—‘Cutting off Glitches’ to keep power efficient!

What does ‘dynamic power consumption’ mean, though?

Dynamic power consumption refers to the power used when transistors switch on and off. It decreases when the activity—like clock signals—stops.
Dynamic Power Consumption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's expand on dynamic power consumption. Can anyone guess how it impacts our devices?

I think it can make our devices hotter, right?

Absolutely! High dynamic power can lead to increased heat dissipation, which is detrimental in high-performance chips. This is why clock gating is essential; it helps keep the temperature in check. A good mnemonic might be to think of 'Power Down and Cool Down!'

So, it also affects battery life then?

Yes! By reducing dynamic power, we enhance battery longevity, especially in mobile devices.
Implementation of Clock Gating
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how do we actually implement clock gating in designs?

Maybe using some logic to detect when blocks are idle?

Exactly correct! Logic circuits can monitor the activity of a block and enable or disable the clock accordingly. Think of it as a 'Gatekeeper' for power savings!

Does this affect how quickly we can process information?

It can, but if done correctly, clock gating won’t trade off performance significantly. It’s about finding that right balance.
Impact of Clock Gating on Designs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think are the overall impacts of clock gating on designs?

It likely saves power!

Correct! It saves power and reduces heat, but are there any possible downsides?

Maybe it could complicate the design?

Right again! While it provides power benefits, it does add complexity to the design process, which we need to manage. Let’s remember: 'Power Up, But Don’t Clog Up!'
Summary of Clock Gating
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, let’s wrap up what we’ve learned about clock gating.

We learned it reduces dynamic power by turning off the clock!

Exactly! And that it’s essential for battery life and heat management. A great way to think of it is that it’s both a power saver and a gatekeeper!

It can make design more complex, too, right?

Yes! Good summary! Remember, it’s all about balancing power savings with design simplicity!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Clock gating is a crucial power optimization strategy in VLSI design that minimizes dynamic power consumption by disabling clock signals in sections of the circuit that are not in use. This technique enhances battery life in mobile devices and reduces heat generation in high-performance chips, thereby playing a vital role in modern digital designs.
Detailed
Clock Gating
Clock gating is a widely used power optimization technique in the realm of VLSI design, particularly in the context of reducing dynamic power consumption. The primary objective of clock gating is to shut off the clock signals supplied to portions of the circuit that are not currently active or needed, thereby saving power. This process is particularly important in modern integrated circuits, where many functional blocks remain idle for extended periods.
Key Points:
- Dynamic Power Reduction: By disabling the clock signals to inactive blocks, clock gating significantly cuts down on dynamic power consumption, as power is directly proportional to the frequency of switching activities.
- Application in Designs: Clock gating is essential in designs where multiple blocks may be idle, such as digital signal processors (DSPs) and microcontrollers, helping to prolong battery life in devices and lower operational heat.
- Implementation Strategies: The implementation of clock gating can variously involve control logic that detects when blocks are idle, enabling the clock gating mechanism without affecting the circuit's functionality.
- Impact on System Performance: Proper integration of clock gating can lead to substantial power savings without critical performance trades-off, contributing positively to the overall system efficacy.
In conclusion, clock gating is a fundamental strategy in optimizing power within VLSI designs, aligning with the broader goals of minimizing power consumption, ensuring performance, and enhancing manufacturability.
Youtube Videos
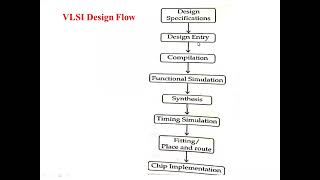

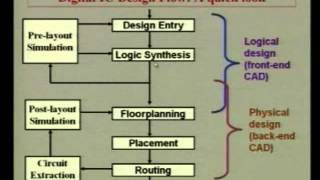
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Clock Gating
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Clock gating involves turning off the clock to certain parts of the circuit when they are not in use. This reduces dynamic power consumption, especially in designs where many blocks are idle for extended periods.
Detailed Explanation
Clock gating is a power-saving technique used in VLSI circuits. When a specific part of a circuit is not performing any operations, it is not necessary for that part to receive a clock signal. By turning the clock off for these inactive parts, the circuit consumes less power, specifically reducing dynamic power consumption. This is particularly useful in circuits where many components may remain idle for long periods, such as in mobile devices or low-power computing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory where different machines work on different tasks at various times. If some machines are not needed, they can be turned off to save energy, just like clock gating turns off parts of the circuit when they’re not in use. This way, the overall energy consumption of the factory is minimized even though it can still operate efficiently when all machines are needed.
Benefits of Clock Gating
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This technique reduces dynamic power consumption, especially in designs where many blocks are idle for extended periods.
Detailed Explanation
The main benefit of clock gating is the reduction it brings to dynamic power consumption. Unlike static power, which occurs even when the circuit is idle, dynamic power is only consumed when transistors switch states. By disabling the clock in idle parts of the circuit using clock gating, the frequency of unnecessary switching is lowered, thereby reducing dynamic power losses. This technique is crucial in battery-operated devices where efficient power management is key to extending battery life.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a light switch in a room with multiple lights. When a light isn’t needed, turning it off prevents energy wastage. Clock gating acts similarly in a circuit, ensuring that only the necessary components are 'lit up', thereby saving power when certain parts of the circuit are not operating.
Key Concepts
-
Dynamic Power Consumption: The power used when transistors within the circuit switch states.
-
Clock Gating: The act of turning off the clock signal to portions of the circuit to save power.
Examples & Applications
In a mobile phone, when the display is off, clock gating disables the circuit functions that drive the screen, conserving battery life.
In a microcontroller managing sensors, clock gating turns off the clock to sensors that are not currently being utilized, thus optimizing power usage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When your circuits are still, let the clock chill, save power and keep the heat at a thrill!
Stories
Imagine a busy intersection where traffic lights keep changing. But sometimes, they’re not needed. Clock gating is like making the traffic lights turn off at midnight when there's no traffic, saving energy and reducing congestion.
Memory Tools
CG—‘Cutting the Glow’ not just for looks, but for saving power!
Acronyms
C.G. = Clock is Gone when circuits are Idle!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Clock Gating
A technique used to reduce dynamic power consumption by turning off the clock signal to idle circuit blocks.
- Dynamic Power Consumption
Power used by components in a circuit during their switching activity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
