Voltage Scaling
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Voltage Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we're diving into Voltage Scaling—specifically, Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling or DVFS. Can anyone tell me why power consumption is a critical issue in VLSI design?

I think it's due to battery life, especially in mobile devices.

Exactly, Student_1! Reducing power consumption can extend battery life in portable devices. DVFS helps decrease power draw by lowering the voltage and frequency when full performance is not needed. Remember, power is proportional to the square of the voltage. Can anyone recall the equation related to power?

It's P equals V squared, right?

Right! This means if we reduce V, we can significantly reduce power. What's that property called?

It's called quadratic scaling.

Good job, Student_3! So, the challenge lies in finding that balance between performance and power. Let’s discuss how DVFS is applied in practical scenarios.
Implementing Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s elaborate on how DVFS is utilized in modern circuits. By dynamically adjusting the voltage and frequency according to real-time workloads, how do you think this affects performance?

It seems like it would slow things down when the voltage is lowered, right?

That's a valid point, Student_4. Lowering voltage can indeed impact speed. But in many idle scenarios or under lower workload, the performance may still suffice. Can someone remind us what trade-off needs to be managed here?

It's the trade-off between performance and power savings!

Exactly! Effective DVFS requires careful monitoring of the workload and workload characteristics. If we lower voltage too much, we might encounter issues such as instability or errors. Let’s summarize the key points.
Challenges and Considerations of Voltage Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our final session today, let's tackle some challenges of implementing voltage scaling. What are some potential issues designers need to consider?

What if the workload changes suddenly? Would that create problems?

Excellent point, Student_2! Sudden changes in workload can indeed lead to performance drops or instability with poorly implemented scaling. Also, how would thermal dynamics play a role in this?

Lower voltage could mean less heat generated, but too much change might still cause instability.

Spot on! Stability and heat management are critical considerations. The key takeaway is that while voltage scaling, especially DVFS, is a powerful tool for reducing power consumption, its implementation requires careful planning and understanding of the respective workload. Let’s summarize everything we’ve learned today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) allows circuits to lower their voltage and frequency based on workload needs. This technique helps in significantly reducing power usage while ensuring performance trade-offs are managed effectively.
Detailed
Voltage Scaling
Voltage Scaling is a crucial power optimization strategy in VLSI design aimed at reducing power consumption. In modern electronic circuits, such as VLSI systems, the demand for efficiency is paramount, particularly in mobile and portable devices where battery life is a priority.
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) allows systems to adjust their operational voltage and frequency in real-time according to workload requirements. Lowering the voltage results in decreased power consumption since power (P) is proportional to the square of the voltage (P ∝ V²). However, managing this trade-off is critical since decreasing voltage too much can lead to performance issues. Therefore, VLSI designers must carefully analyze workload characteristics and circuit behavior to implement DVFS effectively.
In implementing DVFS, it is important to balance between performance and power savings, ensuring that the system remains responsive while maximizing power efficiency.
Youtube Videos
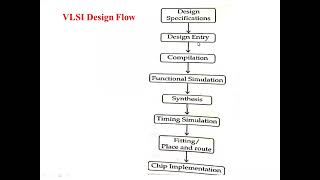

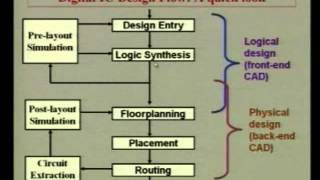
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) adjusts the voltage and frequency of circuits based on workload requirements.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) is a power management technique used in modern electronic devices to adjust the operating voltage and frequency of a processor according to its workload. When the workload is low, the voltage and frequency are decreased, which reduces power consumption. Conversely, when the workload increases, both voltage and frequency are raised to meet performance demands. This technique allows devices to save battery life while still providing necessary performance when required.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine driving a car: when you're on a straight, open road with minimal traffic (low workload), you can drive at a slower speed to save fuel. However, when you encounter a steep hill or heavy traffic (high workload), you need to speed up and use more gas to maintain your pace. DVFS works in a similar way for electronic circuits, optimizing performance while conserving energy whenever possible.
Impact of Lowering Voltage
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Lowering the voltage reduces power consumption but can affect performance.
Detailed Explanation
One of the primary benefits of scaling down the voltage is a significant reduction in power consumption. Power consumption in digital circuits is related to the square of the voltage (P ∝ V²). Therefore, reducing the operating voltage can lead to substantial power savings. However, this also poses risks: lowering the voltage too much can adversely affect the performance of the circuit, leading to slower operation or even potential malfunction. Thus, engineers must find a careful balance between power savings and circuit performance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a battery-powered flashlight: if you lower the brightness (similar to lowering voltage), it lasts longer (saves power), but if you dim it too much, it becomes ineffective for lighting your way (affecting performance). This balance is crucial in electronic designs, just like ensuring your flashlight is bright enough to see by while still lasting through the night.
Trade-offs in Voltage Scaling
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This trade-off must be carefully managed.
Detailed Explanation
In the context of voltage scaling, trade-offs involve balancing power efficiency with performance requirements. Reducing voltage increases power efficiency, but it may lead to slower processing speeds or instability in data transfers, especially with high-speed applications. Each application may require a different approach to voltage scaling based on its specific operational needs. Engineers often use simulations and prototyping to find the optimal settings for voltage and frequency to ensure reliable performance across varying workloads.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef preparing a dish: if they decide to reduce the cooking time (like lowering performance) to save energy (like reducing power consumption), it might not cook evenly, leading to an unsatisfactory meal. Similarly, adjusting voltage in circuits requires careful timing to ensure everything still ‘cooks’ right—and functions effectively—while using less energy.
Key Concepts
-
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS): A method to adjust voltage and frequency for workload-specific power efficiency.
-
Power Consumption: The total power utilized by an electronic device during its operation, important for efficiency.
-
Voltage Scaling: Adjusting circuit voltage to manage performance and power demands effectively.
Examples & Applications
In mobile devices, DVFS is often used to lower voltage when the device is on standby, conserving battery life.
In graphics processors, voltage scaling might adjust to handle varying graphical workloads by scaling power usage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When voltage's low, power does flee, // It saves energy—just wait and see!
Stories
Picture a car slowing down at a red light. It doesn't need to use full power, similar to how DVFS eases voltage in idle times.
Memory Tools
DVFS = Drive Voltage Fast or Slow.
Acronyms
DVFS
'Dynamic Very Flexibly Saves' energy.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)
A power-saving technique that adjusts the voltage and frequency according to the workload requirements.
- Power Consumption
The amount of power used by a circuit during its operation, crucial for efficiency in VLSI design.
- Voltage Scaling
The process of adjusting the operating voltage of a circuit to optimize performance and power usage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
