Advanced Optimization Techniques
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Genetic Algorithms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s begin with Genetic Algorithms. Can anyone tell me how they think those might work in optimization?

I think they mimic the process of natural selection?

Exactly! Genetic Algorithms simulate natural evolution by maintaining a population of solutions, evolving them through selection and crossover. This helps in finding near-optimal solutions to complex problems.

How do they ensure diversity within the population?

Great question! Diversity is maintained through mutation, which introduces random changes in some solutions, allowing exploration of new areas in the solution space.

So, they’re really useful for large design problems?

Precisely, they’re particularly effective for large, multi-variable optimization problems.

To wrap up, Genetic Algorithms evolve solutions just like nature, helping us tackle complex design issues. Can anyone summarize what we’ve learned?

They use populations of solutions that evolve over time to find near-optimal designs.
Simulated Annealing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss Simulated Annealing. Who has heard of this approach?

Isn’t that the one where you cool a system gradually to find the best state?

Exactly! It mimics the annealing process in metallurgy. By gradually lowering the temperature, it allows the algorithm to escape local minima and potentially find a global optimum.

What makes it different from the Genetic Algorithm?

Good observation! While Genetic Algorithms evolve solutions through natural selection, Simulated Annealing explores the solution space by accepting worse solutions with a defined probability, thereby avoiding local optima.

And it’s particularly useful for placement and routing, right?

Yes, indeed! It can effectively minimize cost functions in these applications.

To summarize, Simulated Annealing uses the concept of gradual cooling to optimally adjust design parameters and escape local minima.
Particle Swarm Optimization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about Particle Swarm Optimization. Who can explain what this term means?

I think it’s about simulating the movement of particles in a group, like birds flying together?

Correct! It’s inspired by social behavior, where individuals in a swarm share information and adjust their positions based on their own experience and their neighbors. This allows them to converge towards an optimal solution.

So this means they can explore different areas of the solution space simultaneously?

Exactly! This parallel search is one of the reasons PSO is effective for complex optimization problems.

Can it be used for any type of problem?

While it’s versatile, PSO works best in continuous optimization problems. Each particle’s movement can be adjusted based on the fitness value they experience.

In summary, Particle Swarm Optimization simulates social behavior to find optimal solutions in complex design scenarios.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Advanced optimization techniques including genetic algorithms, simulated annealing, and particle swarm optimization are essential in modern VLSI design. These methods address increasingly complex design problems by iteratively evolving solutions, thereby improving performance and efficiency.
Detailed
Advanced Optimization Techniques in VLSI Design
In the field of VLSI design, the complexity of circuits has increased tremendously, necessitating more sophisticated methods of optimization. Advanced optimization techniques are crucial for handling large designs with multiple constraints. Among these methods are:
- Genetic Algorithms (GA): These algorithms draw inspiration from natural selection to find optimal or near-optimal solutions for complex problems. GA involves creating a population of solutions that evolve over generations through selection, crossover, and mutation processes.
- Simulated Annealing (SA): This technique is often utilized for placement and routing in VLSI design. SA works by gradually cooling the system to find a state of minimum energy, where the cost function is minimized. It accepts both good and worse solutions with decreasing probabilities, thus escaping local minima and aiming for global optimization.
- Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO): Inspired by social behavior of birds or fish, PSO optimizes complex systems by simulating movements within a defined space, allowing individuals (particles) to share information and converge towards optimal solutions.
These advanced techniques not only improve the efficiency of the design process but also render it feasible to meet increasingly stringent performance metrics required in modern circuits.
Youtube Videos
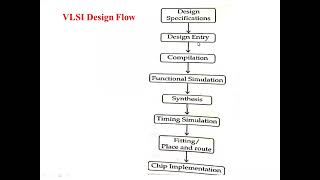

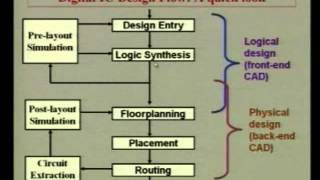
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Genetic Algorithms
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Genetic Algorithms: These are heuristic optimization algorithms that mimic the process of natural selection. Genetic algorithms are used for complex optimization problems where traditional methods are not efficient. They evolve a population of solutions over several generations to find near-optimal solutions.
Detailed Explanation
Genetic algorithms are inspired by biological evolution. They start with a group of potential solutions, often referred to as a 'population'. Each solution is evaluated based on how well it solves the problem at hand. The best-performing solutions are then combined (or 'mated') and randomly altered (or 'mutated') to create a new generation of solutions. This process continues over successive generations, gradually improving the solutions until the algorithm converges on a near-optimal solution. Genetic algorithms are especially useful for problems with a large number of variables where traditional techniques may struggle to find effective solutions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a farmer who is trying to breed the best crops. He starts with a selection of various plants, each with different characteristics: some grow taller, some produce more fruit, some are more resistant to diseases. By choosing the best plants to breed and continuously selecting the most fruitful offspring over several generations, the farmer cultivates crops that produce high yields. Similarly, genetic algorithms create better solutions over iterations by selecting and breeding the best-performing options.
Simulated Annealing
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Simulated Annealing: This optimization technique is widely used for placement and routing. It iteratively adjusts the positions of cells or routing paths to minimize a cost function. By accepting worse solutions with a decreasing probability, it avoids local minima and finds global optima.
Detailed Explanation
Simulated annealing simulates the physical process of heating a material and then slowly cooling it down to remove defects and minimize energy. In this method, a candidate solution is modified slightly to create a new solution. If this new solution is better (lower cost), it is accepted. If it's worse, it may still be accepted based on a probability that decreases over time. This mechanism allows the algorithm to explore a broader solution space initially and then hone in on the best solutions as the process continues, reducing the likelihood of getting stuck in a local optimum.
Examples & Analogies
Think about trying to find the lowest point in a hilly landscape while blindfolded. Initially, you might walk around and accept both uphill and downhill paths. As you feel the slope and determine the direction of the lowest point, you will stop moving upwards as you refine your search towards lower elevations. In a similar way, simulated annealing allows for some random exploration but gradually focuses on finding the best solution.
Particle Swarm Optimization
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Particle Swarm Optimization: This is another evolutionary algorithm inspired by social behavior in nature. It is used to optimize complex systems by simulating the movement of particles through the design space.
Detailed Explanation
Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is inspired by the social behavior of birds or fish. In PSO, potential solutions are represented as 'particles' that move through the solution space. Each particle adjusts its position based on its own experience and the experience of neighboring particles. Over time, the swarm moves towards the best solutions detected by any of the particles, effectively 'collaborating' to find the optimal solution. The interaction among particles helps guide the entire group towards areas of the solution space that may yield improved performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a flock of birds searching for food. Each bird (particle) has its own knowledge of food sources but can also learn from the movements of its companions. When one bird finds a good food source, others will follow its lead, improving the chances of finding the best location for food collectively. Similarly, in optimization problems, the 'flock' of particles shares information and hones in on the best solutions together.
Key Concepts
-
Genetic Algorithms: Heuristic methods evolving solutions through generations.
-
Simulated Annealing: Optimization technique that accepts worse solutions to escape local minima.
-
Particle Swarm Optimization: Method simulating social behavior for converging on an optimal solution.
Examples & Applications
For Genetic Algorithms, a common application is evolving circuit layouts over multiple generations to optimize performance metrics.
Simulated Annealing can be applied to adjust circuit placement in a way that minimizes the overall routing cost in a chip.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
GA leads the way, solutions evolve each day, Simulated Annealing finds the best way.
Stories
Imagine a group of birds (Particle Swarm Optimization) finding the best path to food while teaching each other through their flight experiences, gathering to reach their goal.
Memory Tools
Remember GA for growth, SA as a cooling path, and PSO for social flocks.
Acronyms
GASP
Genetic Algorithms
Annealing
Social Particle.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Genetic Algorithms
Heuristic optimization algorithms that mimic the process of natural selection to evolve optimal solutions.
- Simulated Annealing
An optimization technique that emulates the cooling process of metals by gradually lowering the system's temperature to minimize a cost function.
- Particle Swarm Optimization
An evolutionary algorithm inspired by social behavior, where particles move through the solution space, adjusting their positions based on experience.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
