Retiming
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Retiming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about an important concept in digital design called 'retiming'. Can anyone tell me what they think retiming means?

I think it means changing something about timing in a circuit.

That's correct! Specifically, retiming is about moving flip-flops within your circuit design to optimize timing without changing the circuit's functionality.

Why would we want to move flip-flops around?

Great question! By doing so, we can better balance delays along the critical path. This helps in ensuring that our circuit meets the required timing constraints for effective performance.

So it helps make the circuit faster?

Exactly! A key benefit of retiming is improving performance without altering the actual operation of the design. Let's summarize: retiming involves redistributing flip-flops to balance delays and optimize circuit timing.
Applying Retiming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered what retiming is, can someone give an example of when retiming might be beneficial in a design?

I think it could help if there are long delays in certain paths of the circuit.

Absolutely! When certain paths are delayed, retiming can help redistribute the timing requirements to even out the delays across the circuit. Any other examples?

What happens if we move too many flip-flops though?

That's an insightful question! If we move too many flip-flops, we might inadvertently violate other timing constraints, so careful analysis is required. Remember, the objective is to optimize performance without affecting functionality.

Thanks! That makes it clearer.

To recap, retiming helps improve performance by balancing delays without changing circuit functionality, but it must be handled with care to avoid introducing new timing issues.
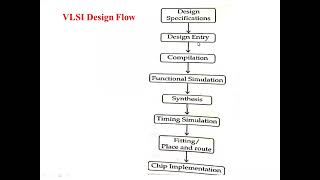
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the concept of retiming, which involves moving flip-flops in the circuit design to balance delays more effectively. It emphasizes how this technique can optimize the timing characteristics of the circuit, ultimately leading to improved performance without altering functionality.
Detailed
Retiming
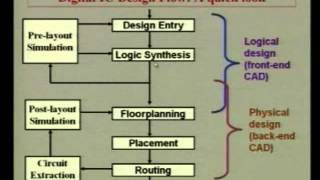
Retiming is an essential optimization strategy within the context of timing optimization in physical design, particularly focused on improving circuit performance by managing critical paths. The main goal of retiming is to adjust the placement of flip-flops (registers) in a digital circuit without changing the overall functionality of the design. This is achieved by shifting flip-flops along the critical path to balance delays and optimize the timing of the circuit.
Key Points of Retiming:
- Definition: Retiming involves redistributing flip-flops, enabling a more even delay across the critical path without affecting the logical operation of the circuit.
- Improvement of Timing: By effectively repositioning registers, the overall timing characteristics can be enhanced, ensuring that data propagates through the circuit efficiently and that timing constraints are met.
- Functional Preservation: One of the significant advantages of using retiming is that it preserves the circuit's functionality while optimizing performance, making it a valuable tool in the design process.
In summary, retiming acts as a crucial method in digital circuit design for improving performance and meeting timing constraints, integrating seamlessly with other timing optimization techniques.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Retiming?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Retiming involves shifting flip-flops along the critical path to balance delays and reduce the overall timing of the design.
Detailed Explanation
Retiming is a technique used in digital circuit design to improve timing performance. Specifically, it allows designers to reposition flip-flops (which are storage elements in circuits) along the critical path. By moving these flip-flops, designers can balance the electrical delays that might occur in different parts of the circuit. The ultimate goal of retiming is to optimize timing without altering the functional behavior of the circuit, ensuring it operates correctly and meets speed requirements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of retiming like rearranging furniture in a room for better flow. Imagine you have a living room where people keep bumping into each other because of where the chairs are placed. By moving some chairs to different spots or even swapping their positions, you can make it easier for people to navigate through the room. In circuit design, just like moving chairs improves movement, retiming encourages signal flow without changing what the room (or circuit) is supposed to do.
Balancing Delays
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
By redistributing the registers, the timing of the circuit can be optimized without changing its functionality.
Detailed Explanation
Balancing delays is a critical aspect of the retiming process. In a circuit, different paths can have varying delays, which may cause some signals to arrive earlier than others, potentially leading to timing violations. By redistributing registers (the storage locations for signals), designers can equalize the delays across different paths. This equalization helps ensure that signals arrive at their destinations simultaneously, helping to maintain correct operation and allowing for higher clock speeds.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a relay race where each runner has to pass a baton to the next. If one runner is much faster than another, they may finish their leg before the next runner is ready, causing delays at the baton hand-off. By training the slower runner to improve their speed (like redistributing registers for balanced delays), the team can ensure smoother transitions and faster overall times, representing how retiming equalizes delays in circuit paths.
Key Concepts
-
Retiming: Adjusting the placement of flip-flops to optimize timing without changing functionality.
-
Critical Path: The longest path in the design that dictates performance constraints.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: In a circuit where signal delays are unequal, moving flip-flops can help even out the delays, leading to a more efficient design.
Example 2: Retiming can be applied in a pipelined architecture to balance the stages, thus improving overall throughput.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In retiming designs, flip-flops go around, improving timing, making circuits sound.
Stories
Imagine flipping pancakes; each pancake represents a flip-flop. By rearranging them on the grill, you ensure they cook evenly—just like retiming balances delays for a circuit to perform better.
Memory Tools
R.E.T.I.M.E - Repositioning Each Timing Involves Moving Elements.
Acronyms
RET - Redistribute, Enhance, Timing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Retiming
A timing optimization technique that redistributes flip-flops in a circuit to balance delays along the critical path.
- Critical Path
The longest path in a circuit that determines the maximum delay and, consequently, the maximum clock frequency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
