Multi-Layer Routing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Multi-Layer Routing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into multi-layer routing. Can anyone tell me why using multiple layers could be beneficial in a circuit design?

Maybe it allows for more connections without getting crowded?

Exactly! More layers mean we can place more routes without congestion. Congestion can lead to delays, which we want to avoid. Let's think of it like traffic lanes on a highway—more lanes help reduce traffic jams.

So, does it also help with signal integrity?

Right, Student_2! By having dedicated layers for specific signals, we can better manage interference and maintain integrity.
Routing Algorithms and Optimization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss how routing algorithms work. Why is it important to allocate resources efficiently across layers?

I think it's to make sure we don’t overload one layer while others sit unused?

Precisely, Student_3! Efficient resource allocation prevents bottlenecks and ensures smooth operation all over the chip. These algorithms play a pivotal role in achieving our design goals.

Are there specific types of algorithms for this?

Yes! Common approaches include Dijkstra's or A* algorithms that help find the shortest paths considering layer usage and congestion.
Benefits of Multi-Layer Routing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's consider the benefits of multi-layer routing. How might it influence the overall performance of a VLSI chip?

Maybe it increases speed due to shorter routes?

Exactly! Shorter connections mean less delay and power consumption. Plus, effective routing helps in meeting tight timing constraints.

What about scalability? Does it help with that too?

Absolutely, Student_2! Multi-layer routing supports more complex designs, making it easier to scale up as technology advances.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
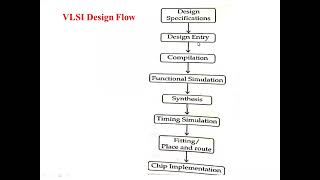
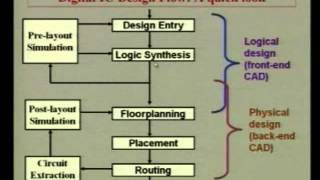
The process of multi-layer routing optimizes the physical design of VLSI circuits by enhancing routing options, thereby minimizing congestion and improving signal integrity through the utilization of multiple layers of metal interconnects.
Detailed
Multi-Layer Routing
Overview
Multi-layer routing is a vital technique in VLSI physical design that addresses the challenges associated with single-layer routing. By allowing the use of multiple metal interconnect layers, designers can achieve greater flexibility in the routing of connections throughout the chip. This technique not only helps in reducing congestion—which can severely impact circuit performance—but also improves overall signal integrity.
Key Points
- Flexible Routing Options: By employing various metal layers, multi-layer routing allows designers to create more efficient paths for signal connections that can mitigate routing congestion.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient algorithms allocate routing resources across different layers to optimize performance and meet design constraints.
- Signal Integrity: Optimized routing across multiple layers helps maintain the integrity of signals, which is crucial for high-speed circuits.
In summary, multi-layer routing is integral to modern VLSI design, facilitating complex applications and enhancing overall circuit performance.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Multi-Layer Routing
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Using multiple layers of metal interconnects allows for more flexible routing options and can reduce congestion.
Detailed Explanation
Multi-layer routing is a technique used in circuit design where multiple layers of metal are utilized to connect different components on a chip. This allows designers greater flexibility in placing wires, making it easier to connect distant parts of the circuit without overcrowding any single layer. The use of multiple layers addresses the complexity of routing, especially in modern circuits, by creating more pathways for signals, thereby reducing the possible congestion that might occur if only one layer were used.
Examples & Analogies
Think of multi-layer routing like the multiple roads in a city. If all cars had to use the same road, there would be traffic jams and delays. However, by using several different roads (or layers), cars can spread out and move more freely. Similarly, in electronics, multiple routing layers allow signals to navigate the chip without interference or bottlenecks.
Efficient Multi-Layer Routing Algorithms
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Efficient multi-layer routing algorithms allocate resources across different layers to minimize congestion while maintaining signal integrity.
Detailed Explanation
Routing algorithms are crucial for implementing multi-layer routing. These algorithms intelligently decide how to distribute the connections between components across the various layers. The goal is to minimize congestion, which occurs when there are too many wires competing for space. A good routing algorithm will ensure that signals can travel with minimal delay and interference, all while preserving the integrity of the signals so that they reach their destination without errors or distortion.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a highway system minimizes congestion. Just like traffic engineers create plans to route cars through different lanes and exits to avoid traffic jams, routing algorithms strategically plan how to place connections in multiple layers. By optimizing these routes, we ensure that 'traffic' flows smoothly, avoiding collisions and ensuring deliverables arrive on time.
Key Concepts
-
Multi-Layer Routing: A routing strategy using various metal interconnect layers to optimize signal paths.
-
Congestion Management: Techniques that ensure effective routing to avoid area overcrowding and maintain performance.
-
Signal Integrity: Maintaining the quality of signals during transmission across different routing paths.
Examples & Applications
Using multiple layers to separate power distribution from signal routing to prevent interference.
Implementing dedicated layers for critical signal paths to enhance timing performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Layers in play, helping signals stay, routing true, clear and fast, multi-layer routes unsurpassed.
Stories
Imagine a busy city where each road represents a single layer. Multi-layer routing is like building multiple highways above and below, allowing cars to flow without stopping at every light.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CIS': Congestion is minimized, Integrity is maintained, Scalability is enhanced.
Acronyms
MAP
More Active Paths - Helps to recall that multi-layering allows for more and better connections.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- MultiLayer Routing
A technique in VLSI design that uses multiple metal interconnect layers to enhance routing flexibility, reduce congestion, and improve signal integrity.
- Congestion
The scenario where excessive connections in a specific area lead to delays and increased power consumption.
- Signal Integrity
The ability of a signal to maintain its quality during transmission across circuit elements.
- Routing Algorithms
Algorithms used to determine the most efficient paths for routing signals in circuit design.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
