Losses in Pipe Fittings
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Pipe Losses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the concept of losses in pipe fittings. Can anyone tell me what we mean by major and minor losses?

I think major losses are related to friction in the pipes, while minor losses occur due to bends, fittings, and valves?

Exactly! Major losses are attributed to friction along the pipe walls, while minor losses arise from disturbances like fittings. Now, why do you think it's important to understand these losses?

It helps in optimizing the design of pipe systems to reduce energy consumption, right?

Correct! Analyzing these losses allows engineers to design more efficient systems. Remember, minimizing losses is key to an effective hydraulic system.
Turbulent vs Laminar Flow
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss flow characteristics. Who can explain what the Reynolds number indicates in fluid flow?

Isn't it a ratio of inertia forces to viscous forces? It helps determine whether the flow is laminar or turbulent.

Absolutely! A Reynolds number below 2300 indicates laminar flow, while above 4000 indicates turbulent flow. Can you explain why understanding this distinction is critical?

It affects how we calculate friction losses, as different formulas apply based on the flow type!

Exactly! We must use the appropriate equations to compute losses accurately, depending on the flow regime.
Use of Bernoulli’s Equation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Using Bernoulli’s equation is essential in our analysis. How does it help determine energy losses in pipe fittings?

It allows us to relate pressure differences to flow velocity, helping quantify losses in energy when passing through fittings.

Exactly! And what role do experimental setups play in this context?

They help measure pressure losses and confirm our calculations from Bernoulli’s equation, correct?

Yes! Practice and verify your calculations through practical experiments to understand the actual impacts of losses.
Calculating Minor Losses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about calculating minor losses. Who can provide an example of where minor losses occur?

Bends or elbows in the pipe system can create minor losses!

Great point! How would you go about quantifying these losses?

We could measure the pressure before and after the fitting and apply the appropriate loss coefficients.

Exactly! Each fitting has a specific loss coefficient that helps determine how much energy you’ll lose from it.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delves into minor and major losses occurring in fluid systems, particularly through pipe fittings. It highlights the significance of understanding turbulent flow, pressure differences, and the application of Bernoulli's and momentum equations to analyze energy losses effectively.
Detailed
Losses in Pipe Fittings
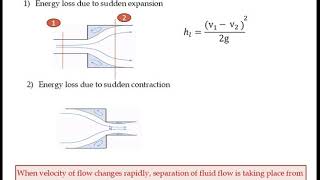
This section is a critical part of understanding fluid mechanics, specifically in analyzing losses in pipe fittings during fluid flow. In hydraulic systems, losses can be classified mainly into major losses, which refer to losses due to friction along the pipe walls, and minor losses which occur from fittings, bends, valves, and other disturbances in flow.
A key aspect discussed is the behavior of turbulent flow characterized by high Reynolds numbers, where flows exceeding 4000 are deemed turbulent while those below 2300 are considered laminar. The transition between these states yields critical insights into energy losses.
Experimental setups are vital for quantifying these losses, involving the use of manometers to measure pressure differentials. The energy gradient lines, hydraulic gradient lines, and the use of Bernoulli’s equations aid in understanding how these losses can be estimated. Moreover, the section incorporates practical examples like water supply systems to illustrate the application of these principles in real-world scenarios, the importance of minimizing losses, and the likely required pumping energy in fluid transport systems through effective design. By comprehensibly grasping these concepts, engineers can efficiently design fluid systems ensuring minimal energy expenditure and maximum efficacy.
Youtube Videos





![[MAE 242] Pipe flow with major and minor head losses](https://img.youtube.com/vi/WH1fn6dMYiw/mqdefault.jpg)



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Fluid Flow in Pipes
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fluid Mechanics
Prof. Subashisa Dutta
Department of Civil Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology-Guwahati
Lecture - 22
Welcome all of you again for the second lectures on viscous flow through pipes...
Detailed Explanation
This introduction sets the stage for the study of fluid mechanics, specifically focusing on how fluids behave in pipe systems. The mention of Bernoulli's and momentum equations highlights the analytical tools essential for understanding flow. It's critical to note that the course is designed to bridge theory with practical applications, especially relevant for students preparing for competitive exams.
Examples & Analogies
Think of fluid dynamics in pipes as similar to how electricity flows through wires. Just as electrical engineers need to understand how much power is lost due to resistance in wires, civil engineers need to understand energy losses in pipes due to friction and fittings.
Understanding Major and Minor Losses
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
On the next slides what I am showing it... we compute the velocity, we can know the pressure difference, then we can quantify the energy losses...
Detailed Explanation
In fluid mechanics, losses in flow can be categorized as major or minor losses. Major losses are primarily caused by friction along the length of the pipe, while minor losses occur at fittings, bends, and valves. The lecture emphasizes that understanding these losses is essential for accurate calculations and designs in engineering projects.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine water flowing through a garden hose. The longer the hose, the harder it is for the water to push through due to friction (major losses). If you attach a nozzle or bend the hose sharply, water flow can also decrease at those points (minor losses).
Importance of Reynolds Numbers
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When you talk about the turbulence, do not look at the figures like these type of vortex phenomena and all. Always we quantify the turbulence with respect to Reynolds numbers...
Detailed Explanation
Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity used to predict flow patterns in different fluid flow situations. A value below 2300 indicates laminar flow (smooth), while above 4000 indicates turbulent flow (chaotic). This helps engineers determine the appropriate models for analyzing the flow behavior.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a river. When the water flows smoothly and calmly (laminar flow), you can see everything beneath the surface. But during a storm, the water becomes choppy and turbulent, making it hard to see through (turbulent flow). The Reynolds number helps us predict when the river will behave in each of those ways.
Energy Losses in Pipe Systems
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Now let us go to the minor losses in the pipe systems. As I told it when you have the pipes, it can have a regions you have a smaller pipe to bigger pipe...
Detailed Explanation
Minor losses occur during transitions between different pipe sizes or through fittings. These losses arise due to disturbances in the flow pattern, leading to energy losses due to turbulence and vortex formations. Quantifying these losses is essential for designing efficient piping systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a highway that narrows into a smaller road. Just as cars slow down and bunch up when the road narrows (leading to energy loss in terms of speed), fluid flow through pipes experiences similar slowdowns and energy losses at fittings and transitions.
Vortex Formation and Its Impact
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If I consider the virtual fluid balls okay. If I consider the virtual fluid balls, the balls which is going very close to the wall...
Detailed Explanation
This concept introduces how vortex formations near pipe walls can lead to energy losses. These vortices create disturbances in flow patterns, which result in additional energy required to maintain flow. Understanding vortex behavior is crucial for predicting and mitigating energy losses in pipe systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how whirlpools form in a bathtub when water drains. The swirling motion disrupts the smooth flow, just like vortices disrupt fluid flow in pipes. By understanding these whirlpool-like behaviors, engineers can design systems that minimize energy loss.
Designing Efficient Pipe Systems
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If you do not have a this chart okay then there are two parts as I say that for the transition zone...
Detailed Explanation
Effective pipe design involves calculating potential energy losses due to friction and fittings using empirical data (like Moody's charts) or explicit formulas. By understanding these calculations, engineers can optimize designs to use resources efficiently and maintain desired flow rates.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water slide at a theme park. Engineers need to calculate angles and materials to ensure that swimmers slide down quickly without losing speed. Similarly, in pipe design, calculations help ensure fluid flows smoothly and swiftly without unnecessary energy losses.
Key Concepts
-
Major Losses: Losses due to friction along the pipe walls.
-
Minor Losses: Losses arising from junctions, bends, and fittings.
-
Reynolds Number: Essential for determining flow type and calculating losses.
-
Bernoulli’s Equation: Key tool for analyzing energy in fluid flow.
Examples & Applications
In a water supply system, if following a bend in the piping, an engineer observes increased energy losses which could necessitate more pumping energy.
When designing a system with valves, calculating the minor losses can lead to effective adjustments in the flow and reduce energy expenditure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In pipes it’s clear, friction draws near; turbid or tame, they play the game.
Stories
Once upon a time, a water flow met a bend. They fought with friction but were friends in the end.
Memory Tools
FLAME: Friction (Major losses), Losses (Minor), Analysis (Bernoulli), Measurement (Experiments), Efficiency.
Acronyms
PIPE
Pressure differences
Ignition of flow
Pipe fittings
Efficiency in systems.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Major Losses
Losses that occur due to friction along the internal surface of piping.
- Minor Losses
Losses due to fittings, valves, bends, and other disturbances in the flow.
- Reynolds Number
A dimensionless number used to predict flow patterns in different fluid flow situations.
- Bernoulli’s Equation
An equation that describes the conservation of energy in a flowing fluid.
- Hydraulic Gradient Line
A graphical representation of piezometric head of flowing fluids in a pipe.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
