Effect of Inert Gas Addition
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Inert Gases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss what happens when we add inert gases to a system at equilibrium. Can anyone tell me what an inert gas is?

An inert gas is a gas that doesn’t react with other substances, like argon or helium.

That's right! Inert gases are chemically nonreactive. Now, let's explore how adding an inert gas affects an equilibrium system. When we add an inert gas at constant volume, does it change the partial pressures of the reactants and products?

No, it shouldn't change their partial pressures.

Exactly! The concentrations remain unaffected, meaning the equilibrium position does not shift. Remember this acronym: IGC - Inert Gases Don't Change equilibrium.

So, the addition of an inert gas keeps the equilibrium state stable?

Precisely! Let's continue delving deeper into this.
Equilibrium Dynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at what happens when we introduce an inert gas into a sealed container at equilibrium. If we add argon to a system, what can we expect to see?

The total pressure increases because we have more gas in the container.

Correct! But remember, since neither reactants nor products have changed in terms of concentration, the reaction itself remains at equilibrium. Therefore, the reaction quotient remains the same as the equilibrium constant. Let’s summarize this with a question. What do we conclude about the concentration of reactants and products when an inert gas is added?

Their concentrations don't change.

Perfect! That reinforces your understanding of how gas behavior in equilibrium can be controlled.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
When inert gases are added to a closed equilibrium system at a constant volume, the equilibrium remains unaffected because the partial pressures of the reactants and products remain unchanged. This section explains how inert gases influence the dynamics of equilibrium without altering the concentrations involved.
Detailed
Effect of Inert Gas Addition
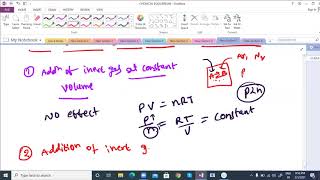
In a system at equilibrium, where a particular chemical reaction balances products and reactants, adding an inert gas like argon will not shift the position of equilibrium. This is because the inert gas does not take part in the chemical reaction, thus its introduction at constant volume does not change the partial pressures of the reactants or products involved.
When the volume is kept constant, the increase in total pressure does not imply a change in the concentration of the reacting species involved. The equilibrium constant expression remains unchanged, implying that the dynamics of the system remain stable as long as there are no alterations to the concentrations of the participants in the reaction.
This principle is important in understanding how gases interact in chemical processes, particularly in industrial applications where controlling the environment around a reaction is crucial for optimizing yields and efficiencies.
Youtube Videos
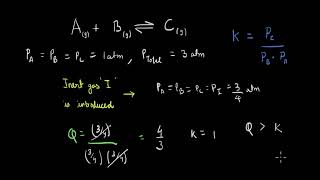






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact on Equilibrium with Inert Gas Addition
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
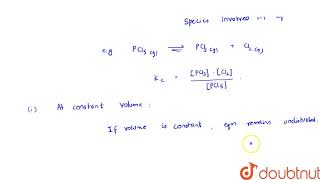
If the volume is kept constant and an inert gas such as argon is added which does not take part in the reaction, the equilibrium remains undisturbed. It is because the addition of an inert gas at constant volume does not change the partial pressures or the molar concentrations of the substance involved in the reaction. The reaction quotient changes only if the added gas is a reactant or product involved in the reaction.
Detailed Explanation
When an inert gas like argon is added to a system at constant volume, it does not react with the components of the chemical reaction. Thus, the total pressure increases, but the partial pressures of the reactants and products remain the same. Since the equilibrium condition relies on the concentration (or partial pressure) of the reactive species, their unchanged state means that the equilibrium does not shift. Therefore, the overall reaction's balance remains stable post addition.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a party in a room where the number of guests (reactants and products) is fixed. If you add balloons (the inert gas), although the atmosphere gets a bit more crowded, the actual number of guests remains unchanged. Thus, the dynamics between them (equilibrium) stay the same, with no one reacting differently to the balloons.
Key Concepts
-
Inert gases do not participate in reactions and do not change equilibrium.
-
System at equilibrium remains at stability with addition of inert gases at constant volume.
-
Total pressure may increase, but concentrations remain unchanged.
Examples & Applications
Adding argon to a closed container of gas does not change the established equilibrium.
Inert gases maintain the same concentration ratios even if total pressure changes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Inert and still, they don’t change the game, Equilibrium holds, it stays the same.
Stories
Imagine a dance party where everyone changes partners but the music remains the same; that's the inert gas in equilibrium.
Memory Tools
IER - Inert gases may Elevate Pressure but don't change Reaction.
Acronyms
GIE - Gases Inert Don't Effect equilibrium.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Inert Gas
A gas that does not chemically react with other substances.
- Equilibrium
A state in a chemical process where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time.
- Partial Pressure
The pressure exerted by a single type of gas in a mixture of gases.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
