Effect of Temperature Change
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Impact of Temperature on Chemical Equilibrium
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore how temperature changes can impact the equilibrium of chemical reactions. Can anyone explain what happens to a reaction's equilibrium when the temperature is increased?

I think it depends on whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic, right?

Exactly! For endothermic reactions, an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right towards the products. Can anyone give me an example of an endothermic reaction?

What about the photosynthesis reaction?

Good point, photosynthesis is indeed endothermic. Now, what happens in an exothermic reaction when we increase the temperature?

The equilibrium shifts to favor the reactants, right?

Correct! This understanding is based on Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change, the system will adjust to counteract that change. Let's remember this using the mnemonic LE CHÂTEAU—'Le' for Le Chatelier, 'Château' for the castle reacting against forces. So we 'fortify' the equilibrium!
Exothermic vs. Endothermic Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into exothermic and endothermic reactions. When we heat up an exothermic reaction, what do we expect to see in terms of the products?

The concentration of products decreases as they shift to the left.

Right! And this is the opposite for endothermic reactions. What’s crucial here is how the equilibrium constant changes with temperature. Can someone summarize this?

For endothermic, Kc increases with temperature; for exothermic, Kc decreases!

Great! Here’s a simple memory aid: If 'Endothermic' is 'Enter-ing' heat, Kc is 'Increasing'! Conversely, think of exothermic as 'Exit-ing'; hence Kc is 'Decreasing'.
Practical Implications of Temperature Changes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s connect this to the real world, specifically in chemical manufacturing. Consider the Haber process for ammonia production. How does temperature influence this reaction?

Higher temperatures would decrease ammonia yield since the reaction is exothermic!

Exactly! To optimize yield, industries often find a balance, using catalysts to facilitate the reaction without raising temperatures excessively. Remember, the aim is to optimize conditions while keeping costs reasonable. Any thoughts on this approach?

So, they could use lower temperatures with catalysts to still get good yields!

Right! Always think of it as a balance. This strategy not only enhances efficiency but also is cost-effective. Always keep in mind—'Balance is Key!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The key takeaway from this section is that changes in temperature influence the position of equilibrium for chemical reactions, being different for exothermic and endothermic processes. An increase in temperature favors endothermic reactions, increasing their equilibrium constant, while exothermic reactions decrease their equilibrium constant. The section also emphasizes the implications for industrial processes and product yields.
Detailed
The section on the Effect of Temperature Change delves into the relationship between temperature and chemical equilibrium, noting that temperature profoundly affects the position of equilibrium and the equilibrium constants (Kc) of reactions. For exothermic reactions, an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the left (toward reactants), reducing the yield of products, while decreasing temperature favors product formation. Conversely, for endothermic reactions, raising the temperature shifts equilibrium to the right, enhancing product yield. Several examples and practical implications for industrial processes, such as the synthesis of ammonia, are illustrated, emphasizing the significance of optimizing temperature conditions for favorable product yields. Understanding these temperature effects is crucial for chemists and industry practitioners to control reactions effectively.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Temperature Change Impact on Equilibrium Constant
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Whenever an equilibrium is disturbed by a change in concentration, pressure or volume, the composition of the equilibrium mixture changes because the reaction quotient, Qc no longer equals the equilibrium constant, Kc. However, when a change in temperature occurs, the value of equilibrium constant, Kc is changed.
Detailed Explanation
When we change the temperature of a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium constant will also change. This means that if the temperature increases or decreases, it affects the balance between the reactants and products in such a way that the ratio of their concentrations at equilibrium will no longer reflect the previous equilibrium constant.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seesaw. If one side (temperature) is raised, the balance (equilibrium) shifts. In a chemical reaction, increasing temperature can favor the side with more energy (often the products in endothermic reactions) and decrease the concentration of the other side.
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In general, the temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant depends on the sign of ∆H for the reaction.
• The equilibrium constant for an exothermic reaction (negative ∆H) decreases as the temperature increases.
• The equilibrium constant for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆H) increases as the temperature increases.
Detailed Explanation
Exothermic reactions release heat, so raising the temperature causes the reaction to shift back towards the reactants, thus decreasing the equilibrium constant. Conversely, endothermic reactions absorb heat, and raising the temperature favors the products, increasing the equilibrium constant.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cooking: when cooking a steak (exothermic), if you lower the heat, it won't cook well (shifts back toward raw). While making a cake (endothermic), turning up the heat helps bake it properly (shifts to finished cake).
Real-World Application in Ammonia Production
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Production of ammonia according to the reaction,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g); ∆H= −92.38 kJ mol–1
is an exothermic process. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, raising the temperature shifts the equilibrium to left and decreases the equilibrium concentration of ammonia.
Detailed Explanation
In the synthesis of ammonia, because the reaction releases heat (it's exothermic), increasing the temperature will shift the reaction towards the reactants (N2 and H2) and away from the product (NH3). This is not desirable in industrial processes where ammonia production is sought, which is why lower temperatures are generally used, despite the slower reaction rates.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine making ice cream: if the ice (a colder environment) melts (increasing temperature), the ice cream won't freeze properly. Similarly, in industry, they prefer lower temperatures to keep the reaction favoring ammonia production.
Demonstration of Temperature Effect
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
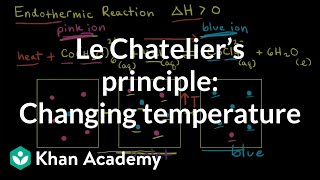
Effect of temperature on equilibrium can be demonstrated by taking NO2 gas (brown in colour) which dimerises into N2O4 gas (colourless).
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g); ∆H = −57.2 kJ mol–1.
At low temperatures in beaker 1, the forward reaction of formation of N2O4 is preferred, as the reaction is exothermic, and thus, intensity of brown colour due to NO2 decreases.
Detailed Explanation
When NO2 gas is cooled, it favors the formation of the colorless N2O4 gas, showing that lower temperatures promote the formation of products in exothermic reactions. This effect can be visually observed by the change in color from brown to colorless.
Examples & Analogies
It's like wearing a sweater in winter: when it's cold (low temperature), you bundle up. Conversely, when it’s hot outside, you shed your coats. In chemistry, cooling a reaction shifts it to favor creating products, similar to how cooler weather favors bundling up.
Key Concepts
-
Impact of Temperature: Changing temperature affects equilibrium states.
-
Exothermic Reactions: Higher temperature shifts equilibrium towards reactants.
-
Endothermic Reactions: Higher temperature shifts equilibrium towards products.
-
Equilibrium Constant: Temperature changes can alter the equilibrium constant.
-
Le Chatelier's Principle: The principle guiding equilibrium responses to changes.
Examples & Applications
The effect of temperature on the formation of ammonia in the Haber process.
Melting and freezing of ice-water equilibrium, demonstrating temperature-driven changes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heat makes endo go, while exo feels the flow!
Memory Tools
E + P (Equilibrium + Products): Increase in temperature favors Endothermic reactions toward Products.
Stories
Imagine a balance scale; when you add weights to one side (increase temperature), it tilts to show the favored reaction direction!
Acronyms
EFFECT
'Equilibrium Fluctuates with External Changes in Temperature'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Exothermic Reaction
A reaction that releases heat, resulting in a temperature increase.
- Endothermic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs heat, leading to a temperature decrease.
- Equilibrium Constant (Kc)
A numerical value that expresses the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium.
- Le Chatelier's Principle
A principle stating that if an external change is applied to an equilibrium, the system adjusts to counteract that change.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
