XML Files
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to XML Files and Their Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about XML files. Can anyone tell me what XML stands for?

Isn't it eXtensible Markup Language?

Correct! And what do you think makes XML so significant for software applications?

I think it helps in data interchange between different systems.

Exactly! XML's structured format allows for effective data representation. Now, let’s discuss how we can work with XML files in Python.
Handling XML in Python
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In Python, we use the `xml.etree.ElementTree` module. Anyone familiar with it?

I've heard of it, but how do we actually use it?

It's quite simple. You can read an XML file using `ElementTree.parse()` method, which loads the XML structure into an ElementTree object. Can you think of what you’d do after that?

We could navigate the tree structure to access specific elements?

Exactly! You can access elements with methods like `.find()` or `.findall()`. Let’s practice by looking at a sample XML.
Handling XML in Java
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, moving to Java, we have two major techniques for XML parsing: DOM and SAX. Who can explain the difference?

I believe DOM loads the entire XML file into memory, while SAX reads it element by element?

Correct! DOM is suitable for small files where you need to manipulate the data, while SAX is efficient for larger files. Why do you think that is?

Because SAX doesn't have to load everything into memory at once!

Exactly! When writing Java, we can use `DocumentBuilderFactory` for DOM and `SAXParser` for SAX parsing. Let's discuss when to choose which approach.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
XML file handling is essential for data interchange between systems. This section highlights methods in Python using xml.etree.ElementTree and Java with DOM/SAX parsers, providing insights into reading, writing, and manipulating XML data.
Detailed
XML Files Handling in Programming
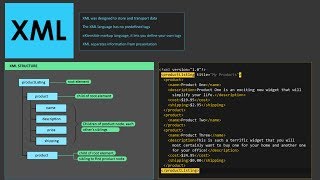
Handling XML files is crucial in various software applications involved in data exchange and configuration management. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a versatile and widely-used format for storing and transporting data due to its ability to represent complex data structures in a human-readable format.
Key Points Covered:
- Python Approach: In Python, the
xml.etree.ElementTreemodule is commonly used for parsing XML files. It allows developers to easily create, read, and modify XML content. - Java Method: For Java, the Java Standard Library provides both DOM (Document Object Model) and SAX (Simple API for XML) parsers for reading and writing XML files. DOM loads the entire document into memory, while SAX processes the XML document sequentially, which is useful for handling large files.
The techniques used in these languages for XML file handling underscore the importance of understanding data formats for software development.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Python XML Handling
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Python: xml.etree.ElementTree
Detailed Explanation
In Python, the xml.etree.ElementTree module is used to parse and create XML documents. XML, or eXtensible Markup Language, is a markup language that defines rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The ElementTree module makes it easy to navigate through the structural components of an XML document. You can read XML files and retrieve data from them, as well as create new XML files from scratch.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine XML as a recipe that lists ingredients and steps to create a dish. The ElementTree module is like a kitchen tool that helps you pick out the ingredients you need or to write down a new recipe. When you read a recipe, you gather the ingredients (data) step by step, and when you write down your own recipe, you organize it in a clear way for future reference.
Java XML Handling
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Java: DOM/SAX parser
Detailed Explanation
In Java, XML files can be processed using two primary methods: the Document Object Model (DOM) parser and the Simple API for XML (SAX) parser. The DOM parser reads the entire XML file into memory and creates a tree structure representing the document, allowing for easy manipulation of elements. The SAX parser, on the other hand, reads the XML file sequentially and triggers events as it encounters elements, making it more memory efficient but less straightforward for modification.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the DOM parser as a chef who when given a recipe, reads it entirely and lays out all ingredients on the counter for easy access while cooking. This method can be great for complex dishes that require alterations. On the contrary, the SAX parser is like a chef who reads the recipe step-by-step while cooking; this method is faster and uses less counter space but requires following the steps strictly without any changes until the next instruction.
Key Concepts
-
XML: A flexible markup language for encoding documents.
-
ElementTree: A Python library for parsing and creating XML.
-
DOM: A tree-based model where the entire XML document is loaded into memory.
-
SAX: A streaming method for parsing XML that reads elements sequentially.
Examples & Applications
Using Python's ElementTree to read an XML file and extract specific elements.
Using Java's DocumentBuilder to parse an XML file and process its elements.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Using XML for data flow, helps our systems to better grow!
Stories
Once upon a time, data needed to travel through different lands. XML was the friendly guide that helped it pass through without getting lost, ensuring everyone understood each other!
Memory Tools
Remember XML is Easily Parsed, meaning it is simple to read and write in programming.
Acronyms
XML
'X' for 'eXtensible'
'M' for 'Markup'
'L' for 'Language'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- XML
A markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable.
- ElementTree
A Python module that provides an efficient way to construct and manipulate XML documents.
- DOM
A programming interface for web documents that allows scripts to update the content and structure of a document.
- SAX
A method for accessing data in a sequential manner, allowing large XML files to be processed without loading them completely into memory.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
