Isobars and Isotopes
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Isobars
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about isobars. Can anyone tell me what an isobar is?

Isobars are atoms that have the same mass number, right?

Exactly! Isobars share the same mass number but have different atomic numbers. For example, ¹⁴C and ¹⁴N are isobars.

So, they have different identities but the same weight?

Yes, they differ in their number of protons but balance out in mass due to the number of neutrons. Remember this concept by associating the initial 'iso' with equal mass!

And what does that imply about their chemical behavior?

Good question! Isobars can exhibit completely different chemical properties despite their similar mass number. They belong to different elements.

Which impact does that have in real-world applications?

Isobars are crucial in nuclear reactions. We'll dive into those applications later. To summarize today, isobars have the same atomic mass but different components. Keep this in mind!
Understanding Isotopes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move to isotopes. Anyone can provide a definition?

Isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.

Exactly! For instance, hydrogen has three isotopes: protium, deuterium, and tritium. Why do you think they behave similarly?

Because they have the same number of electrons?

Correct! Their chemical behavior is similar due to identical electron configurations, though their physical properties, like mass and stability, differ. Remember: 'iso' means same, emphasizing the shared proton count.

What are some applications of isotopes?

Great question! Isotopes are vital in fields like medicine for imaging and treatment, in geology for dating fossils, and in research for tracing biochemical pathways. Summing up, isotopes are crucial for understanding elements' behavior!
Isobars vs. Isotopes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare and contrast isobars and isotopes. Can someone outline a key difference?

Isobars have the same mass number but different atomic numbers?

And isotopes have the same atomic number, but different masses!

Excellent! This fundamental difference affects not only their identity but their stability and chemical reactivity. Can someone summarize why chemical properties would be similar for isotopes?

Because they have the same electrons and thus similar reactions.

Right! So as you explore atomic behavior, remember how these differences manifest in reactions and stability. In conclusion, focus on their definitions and the implications stemming from their structural differences.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Isobars are atoms with the same mass number but different atomic numbers, while isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. This section explores the implications of these differences on chemical properties, ultimately emphasizing that isotopes share chemical behavior due to identical electron configurations.
Detailed
Isobars and Isotopes
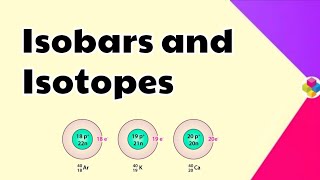
In atomic chemistry, understanding the distinctions between isobars and isotopes is crucial for grasping the nuances of atomic structure. Isobars are defined as atoms that share the same mass number (A) but differ in atomic number (Z). For instance, the carbon-14 (¹⁴C) and nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N) atoms serve as a classic example of isobars, both possessing a mass number of 14 yet differing in their nuclear charge and thus their identity as elements. This unique characteristic imparts different chemical properties to isobars despite their equal mass number.
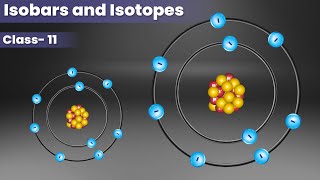
Conversely, isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. They vary in the number of neutrons within the nucleus; for example, the hydrogen atom has three isotopes: protium (¹H), deuterium (²H), and tritium (³H). Each isotope displays the same chemical behavior due to having an identical electron count, despite variations in their neutron number affecting their mass and stability.
The fundamental difference in behavior between isobars and isotopes not only affects atomic mass but also influences atomic stability, decay, and application in fields such as nuclear medicine, dating techniques, and environmental studies. This section underscores how understanding isotopic and isobaric relationships enhances our comprehension of chemical reactions, stability, and the fundamental nature of matter.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Isobars
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Isobars are the atoms with same mass number but different atomic number; for example, \(^{14}C\) and \(^{14}N\).
Detailed Explanation
Isobars are different elements that have the same mass number. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. However, isobars have different atomic numbers, which means they contain a different number of protons. For example, \(^{14}C\) (which has 6 protons) and \(^{14}N\) (which has 7 protons) are both isobars because they both have a combined total of 14 nucleons (6+8 for carbon and 7+7 for nitrogen).
Examples & Analogies
Consider isobars like different forms of the same family. Just as siblings may have different characteristics (protons) but still belong to the same family (same mass), isobars represent different elements that share a nucleon count.
Understanding Isotopes
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
On the other hand, atoms with identical atomic number but different atomic mass number are known as isotopes.
Detailed Explanation
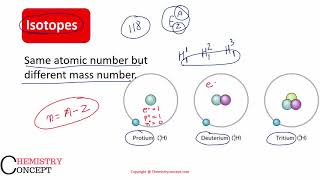
Isotopes are forms of the same element that have the same number of protons (atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers. For instance, consider hydrogen: \(^{1}H\) (protium, with one proton, zero neutrons) and \(^{2}H\) (deuterium, with one proton and one neutron) are isotopes of hydrogen. They have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons, but different mass numbers due to the variation in neutrons.
Examples & Analogies
Think of isotopes like flavors of ice cream in the same category (like chocolate). Though they taste slightly different (due to the difference in neutrons), they still share the core flavor of chocolate (the same atomic number).
Characteristics of Isotopes
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For example, considering the hydrogen atom again, 99.985% of hydrogen atoms contain only one proton. This isotope is called protium (\(^{1}H\)). The rest of the percentage of hydrogen atoms contains two other isotopes: deuterium (\(^{2}H\)) and tritium (\(^{3}H\)).
Detailed Explanation
Most hydrogen atoms in nature are found in the form of protium, which has just one proton and no neutrons. Deuterium has one neutron along with one proton, making it heavier, and tritium has two neutrons and one proton, making it even heavier. Despite these differences, all isotopes of hydrogen share similar chemical properties because they all have one proton and thus behave similarly in chemical reactions, but they vary in mass and stability.
Examples & Analogies
Isotopes can be likened to different versions of a movie: all versions tell the same story (the same element), but some versions have extra scenes or features (different neutrons) that set them apart—like the director's cut or the theatrical version.
Chemical Properties of Isotopes
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Lastly, an important point to mention regarding isotopes is that the chemical properties of atoms are controlled by the number of electrons, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus.
Detailed Explanation
The chemical behavior of an element is determined primarily by its electrons, especially the valence electrons. Since isotopes have the same number of protons, they also have the same number of electrons. Therefore, isotopes generally exhibit similar chemical properties despite the differences in neutron numbers that affect mass and nuclear stability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider isotopes as different students with the same educational background (same atomic structure). Even though one student may be larger than the other (due to different neutrons), they can still share the same skills and abilities in class activities (chemical properties).
Key Concepts
-
Isobars: Atoms with same mass number, different atomic numbers.
-
Isotopes: Atoms with same atomic number, different mass numbers.
Examples & Applications
Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) and Nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N) are examples of isobars. They share the same mass number but represent different elements.
Isotopes of hydrogen include protium (¹H), deuterium (²H), and tritium (³H), with varying neutron counts.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Isobars are atomic pairs, same mass they share, different elements, quite rare!
Stories
Imagine two houses on the same street (mass number), different colors (different atomic numbers) — they vibe differently even though they share the same address (mass number)! That's isobars!
Memory Tools
I for Isobars share mass, but differ in atoms — 'I' for 'Identity' varies!
Acronyms
I.S.O. - Isotopes Same Order (of protons!), Isobars Share Objectivity (in mass number).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Isobar
Atoms that have the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
- Isotope
Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
