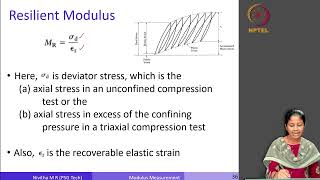
Dynamic Modulus (|E|)*
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Dynamic Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the concept of dynamic modulus, also known as |E|. Can anyone tell me what we mean by stiffness in the context of materials?

Isn't stiffness about how resistant a material is to deformation?

Exactly! Stiffness refers to that resistance to deformation. Now, when we talk about dynamic modulus, we're looking at this resistance specifically under cyclic loading conditions. Can someone think of an example where this might be relevant?

Maybe when cars drive over roads? The road has to bend and then come back?

Great example, Student_2! The dynamic modulus helps us understand how bituminous mixes behave under the repeated stresses caused by vehicle loads. It's also affected by temperature and the frequency of loading. Let's break that down.

So, does that mean in different temperatures, the dynamic modulus changes?

Right! As temperatures change, the material's ability to recover from deformation also changes. This is important in pavement design. Remember the acronym STIR: Stiffness, Temperature, Influence, Recovery. It summarizes these key aspects.

What tests do we use to find out the dynamic modulus?

Excellent question! We obtain the dynamic modulus from Simple Performance Tests. These are designed to simulate real-world conditions. So remember R.A.T. - Recovery After Test – which highlights the purpose of these tests!

To summarize, we learned that the dynamic modulus is essential for understanding bituminous mix behavior under loading, varies with temperature, and is obtained through specific performance tests.
Importance of Dynamic Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last session, we touched on dynamic modulus. Let's now discuss why it’s crucial for pavement engineering. Can anyone think of how a pavement might fail?

Over time or with heavy loads, right? Like when roads get cracks!

Absolutely! Cracks can develop from inadequate stiffness. The dynamic modulus helps us predict how long a pavement might last under certain conditions. What do you think could happen if we underestimate this value?

I guess it would lead to early failure, wouldn't it?

Exactly! Underestimating could lead to unexpected repairs and costs. Let’s remember the term P.A.C.E: Predict, Assess, Correct, and Evaluate - a strategy for using dynamic modulus in design.

How does temperature measure into this?

Good question, Student_3. Temperature affects material properties and, hence, the dynamic modulus. Colder temperatures may lead to stiffer pavements, while hotter conditions can make them more flexible. Remember T.A.L.C. – Temperature Affects Loading Capacity!

In summary, the dynamic modulus is vital in predicting pavement performance. It helps us ensure pavements last longer, reducing costs and improving safety.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Dynamic modulus is a crucial indicator of the stiffness of bituminous mixes when subjected to cyclic loading. This modulus varies with temperature and loading frequency and is primarily obtained from Simple Performance Tests. Understanding dynamic modulus is essential in evaluating the mechanical behavior of asphalt pavements and predicting their performance under traffic conditions.
Detailed
Dynamic Modulus (|E|)
Dynamic modulus is a key parameter in assessing the stiffness of bituminous mixes under cyclic loading conditions, which are common in real-world pavement scenarios. This modulus indicates how well the mix can resist deformation under applied loads and is significantly influenced by both temperature and loading frequency. The dynamic modulus can be obtained through specialized tests known as Simple Performance Tests (SPT).
Understanding the dynamic modulus helps engineers predict how bituminous materials respond to various stressors, thereby playing a vital role in pavement design and structural integrity assessments. This evaluation aids in ensuring that roads can handle expected traffic loads without premature failure.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Dynamic Modulus
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Indicates the stiffness of bituminous mixes under cyclic loading.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic modulus, represented as |E|, is a measure of how stiff or rigid a bituminous mix is when it experiences repeated loading. Stiffness is an important mechanical property because it determines how the material will respond to forces applied to it, especially in conditions of traffic and environmental changes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of dynamic modulus like the flexibility of a rubber band. When you pull on it, its stiffness determines how much it stretches and how quickly it returns to its original shape. Similarly, a higher dynamic modulus means that the bituminous mix will deform less under load, maintaining its shape better while under stress from vehicle traffic.
Influencing Factors of Dynamic Modulus
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Depends on temperature and loading frequency.
Detailed Explanation
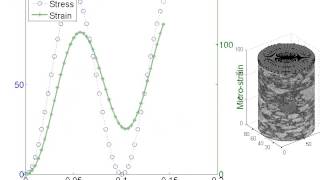
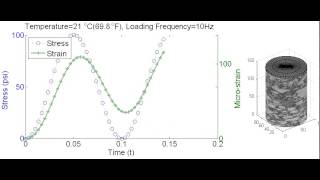
The dynamic modulus is not a constant value; it changes based on temperature and how frequently loads are applied. At higher temperatures, the bituminous material becomes softer and less stiff, leading to a lower dynamic modulus. Conversely, under low temperatures, the material is stiffer, resulting in a higher dynamic modulus. Additionally, loading frequency affects the dynamic modulus; under rapid loading (like that experienced during vehicle acceleration), the material may show different stiffness than under slower loading conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine cooking spaghetti. If you add them to boiling water (high temperature), they become soft and flexible, but if you try to cook them in cold water (low temperature), they remain firm and stiff. Just like pasta, bituminous mixes behave differently based on temperature and how fast you 'load' them with weight, like a truck driving over them.
Methods of Measuring Dynamic Modulus
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Obtained from Simple Performance Tests (SPT).
Detailed Explanation
The dynamic modulus of bituminous mixes is typically measured using a type of test called the Simple Performance Test (SPT). This test applies a cyclic load to the material and records its response. By measuring how much the sample deforms, engineers can calculate the dynamic modulus. This quantitative measure helps engineers understand how the mix will perform in real-world conditions, ensuring that pavement designs can withstand traffic over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the SPT like testing a sponge. If you press it repeatedly with your fingers, how much it squishes down and how quickly it returns to its original shape tells you how 'stiff' the sponge is. This is similar to how the SPT measures the dynamic modulus of a bituminous mix, evaluating its behavior under cyclic loading.
Key Concepts
-
Dynamic Modulus (|E|): A key measure indicating stiffness under cyclic loading.
-
Temperature Dependency: Dynamic modulus varies with temperature.
-
Simple Performance Tests: Tests used to determine dynamic modulus.
-
Cyclic Loading: Repetitive loading conditions experienced by pavements.
Examples & Applications
A pavement designed for hot climates may have a lower dynamic modulus to allow for flexibility under high temperatures, preventing cracking.
Dynamic modulus values help engineers choose appropriate materials for different environments, enhancing road durability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For stiffness to unfold, |E| is gold, helps pavement withstand what it’s told.
Stories
Imagine a road that bends and sways with passing cars, using its dynamic strength, it endures the harshest bars.
Memory Tools
STIR: Stiffness, Temperature, Influence, Recovery - remember the factors that affect dynamic modulus.
Acronyms
P.A.C.E
Predict
Assess
Correct
Evaluate - the four steps for using dynamic modulus in design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dynamic Modulus (|E|)
A measure of stiffness of bituminous mixes under cyclic loading, influenced by temperature and loading frequency.
- Simple Performance Test (SPT)
A test method used to determine the performance characteristics of bituminous mixes, including dynamic modulus.
- Stiffness
The resistance of a material to deformation.
- Cyclic Loading
Repeated application of load over time, characteristic of vehicle traffic on pavements.
- Temperature Dependency
The variation of material properties, including dynamic modulus, with changes in temperature.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
