Stress Relaxation and Creep
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Stress Relaxation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss stress relaxation. Can anyone tell me what happens to a material when it is held at a constant strain?

I think the stress will decrease over time.

Correct! In stress relaxation, a constant strain indeed leads to decreasing stress. This is pivotal for materials like bituminous mixes in flexible pavements. Can anyone think of why this is important?

Because as stress decreases, it can affect the pavement's durability?

Exactly! This reduction in stress over time assists in maintaining the integrity of the pavement under long-term loads.

So, stress relaxation is a key factor in designing pavements to last longer?

Absolutely! Remember the acronym 'SReD' for Stress Relaxation decreases over time!
Introduction to Creep
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's switch gears and discuss creep. Who can tell me what occurs when a material is subjected to a constant stress?

The material will keep deforming, right?

Correct! Creep occurs when a constant stress causes an increase in strain over time. Why do you think this is critical for pavement materials?

Because it can lead to permanent deformation in the pavement, making it unsafe?

Exactly right! Creep can lead to issues like rutting in pavements. So, let's use the mnemonic 'Creep Keep' - it keeps on deforming!
Creep Compliance and Relaxation Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed stress relaxation and creep. Let's talk about how we measure these phenomena. Can anyone tell me how we can quantify creep and relaxation?

Is it through some kind of compliance or modulus functions?

Yes, precisely! Creep compliance measures how a material deforms under stress, while the relaxation modulus shows how stress decreases under constant strain. Why are these important in engineering?

It helps us understand how long the pavements will last under traffic loads?

Exactly! Knowing these functions allows engineers to optimize mix designs. Let’s remember 'Creepy Relaxation' to connect these functions to their behaviors!
Significance in Pavement Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To sum up, how can stress relaxation and creep affect pavement design?

It helps in predicting performance and ensuring durability?

Great! Engineers can use these concepts to address potential failures. What would be a real-world implication of not considering these factors?

The pavement could fail prematurely, leading to safety issues and costs?

Absolutely! Thus, understanding stress relaxation and creep is crucial. Remember the phrase 'Plan for Relaxation and Creep, For a Pavement that will Keep!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
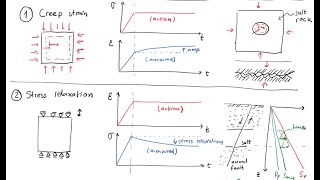
The section discusses stress relaxation, where constant strain leads to decreasing stress over time, and creep, where constant stress leads to increasing strain over time. These phenomena reflect the time-dependent characteristics of bituminous mixes, essential for understanding their durability under various conditions.
Detailed
Stress Relaxation and Creep
Stress relaxation refers to the phenomenon where a material, when subjected to a constant strain, experiences an exponential decrease in stress over time. This behavior is critical for bituminous mixes, especially in flexible pavements subjected to varying temperatures and loads. In contrast, creep describes the progressive increase in strain experienced by a material that is subjected to a constant stress over time. Both stress relaxation and creep are significant as they are analyzed through the parameters of creep compliance and relaxation modulus functions, which are essential in defining the long-term performance of pavements under traffic loads. Understanding these behaviors is vital for pavement engineers to predict potential distresses and optimize mix design for longevity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Stress Relaxation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Stress Relaxation: A constant strain results in decreasing stress over time.
Detailed Explanation
Stress relaxation describes a scenario where a material is held at a fixed deformation or strain. While the deformation is constant, the internal stress within the material gradually decreases over time. This phenomenon happens because the material can 'relax' some of the internal forces that were created when the deformation was first applied. In practical terms, if you imagine stretching a rubber band and holding it in that stretched position, over time, the tension in the rubber band may reduce even though it remains stretched.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the analogy of an elastic band being stretched. When you stretch the elastic band and hold it in place, if you check the tension in it after a few minutes, you'll notice that it feels looser than when you first stretched it. This is because some of the energy has dissipated, similar to the way materials in pavements may behave under constant strain.
Creep
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Creep: A constant stress causes increasing strain over time.
Detailed Explanation
Creep is the phenomenon where a material experiences continuous deformation or strain when subjected to a constant load or stress over an extended period. Unlike stress relaxation, where stress decreases while strain remains constant, creep involves a gradual increase in strain as the material yields under the sustained load. This is particularly evident in bituminous mixes used in pavements, where the weight of vehicles can lead to progressive deformation over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge being pressed down under a heavy object. Initially, the sponge compresses under the weight, but if the weight stays there for a long time, the sponge continues to flatten slightly more and more. This is similar to what happens in pavement structures where they may slowly deform under constant traffic loads, leading to issues like rutting.
Creep Compliance and Relaxation Modulus
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• These behaviors are analyzed using creep compliance and relaxation modulus functions.
Detailed Explanation
To understand and quantify the concepts of stress relaxation and creep, engineers use two important functions: creep compliance and relaxation modulus. Creep compliance indicates how much a material will deform over time under a constant stress, while relaxation modulus measures how much stress decreases over time under constant strain. These functions provide critical insights into the material’s performance, enabling engineers to predict how bituminous mixes will respond to loads and environmental factors throughout the lifespan of a pavement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge being pressed under a weight. If you tap the weight at regular intervals, creep compliance is like measuring how much the sponge squishes down further each time. On the other hand, if you stretched a rubber band and held it there, the relaxation modulus is like observing how much the tension decreases in the band even though you keep it stretched. These measurements help engineers design better pavements that can withstand constant loads without failing.
Key Concepts
-
Stress Relaxation: A phenomenon where stress decreases under constant strain over time.
-
Creep: A material's time-dependent strain increase under constant stress.
-
Creep Compliance: A function measuring the deformation in response to constant stress.
-
Relaxation Modulus: A function representing the decrease in stress with constant strain.
Examples & Applications
An asphalt pavement subjected to heavy traffic may experience stress relaxation, allowing it to adapt somewhat to the loads without instantaneous failure.
A road surface that is continually exposed to static heavy trucks might show creep over time, leading to an uneven surface.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For stress relaxation, don't be vexed, stress will relax—just check the effects!
Stories
Imagine an elastic band stretched tight. Over time, it relaxes, losing tension. That’s like stress relaxation!
Memory Tools
Remember 'SReC' - Stress Relaxation decreases and Creep increases, to memorize the core concepts.
Acronyms
Use 'RCC' - Relaxation decreases, Creep increases, Compliance is measured, to remember key behaviors.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Stress Relaxation
The decrease in stress over time when a material is held at a constant strain.
- Creep
The increase in strain over time when a material is subjected to a constant stress.
- Creep Compliance
A measure of how a material deforms under a constant applied stress.
- Relaxation Modulus
A measure of how the stress in a material decreases under constant strain over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
