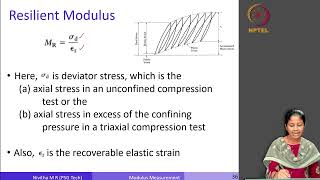
Resilient Modulus (MR)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Resilient Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today, we're diving into the Resilient Modulus, often abbreviated as MR. Can anyone tell me what you think the term 'modulus' generally refers to in materials science?

I think it relates to stiffness or rigidity in materials.

Exactly! Now, when we talk about the Resilient Modulus in bituminous mixes, we're specifically discussing a measure of how these materials recover their shape after being deformed under stress. Who can tell me why this might be important in pavement design?

It determines how well the pavement can handle repeated traffic loads without becoming permanently deformed.

Right again! MR provides insight into the longevity and performance of pavements under real-life conditions.
Application of Resilient Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what MR is, let’s discuss its role in pavement structural design. MR values guide engineers in selecting appropriate material combinations. Can anyone suggest why we might need different MR values for different pavements?

Different locations have different traffic loads and environmental conditions.

Exactly! It varies greatly based on factors like climate, load frequency, and material properties. What do you think could happen if we use a material with an incorrect MR?

It might lead to quicker wear and tear or even failure of the pavement.

Very good! Ensuring the right MR is essential for safe and durable roads.
Calculating Resilient Modulus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's cover how we actually measure this Resilient Modulus. Who can tell me what basic equation defines MR?

It's the ratio of recoverable strain to applied stress, right?

Correct! This relationship helps us quantify MR during testing. What types of tests do you think could be used to establish MR values?

I remember hearing about dynamic testing and maybe triaxial tests?

Absolutely! Dynamic tests simulate actual loading conditions to determine MR accurately. Remember, understanding these tests is critical for effective pavement design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Resilient Modulus (MR) quantifies the ability of bituminous mixes to recover from deformation after repeated loads. This property is pivotal in assessing pavement performance, influencing design decisions and ensuring longevity and effectiveness under varying conditions.
Detailed
Resilient Modulus (MR)
The Resilient Modulus (MR) denotes the elastic response of a bituminous mix when subjected to repeated loading, defined mathematically as the ratio of recoverable strain to the applied stress. It serves as a fundamental parameter in pavement structural design, informing engineers about the performance and durability of bituminous mixes under real-world conditions. The significance of MR lies in its ability to predict how materials will behave under the influence of traffic loads and environmental factors, guiding optimal mix design and ensuring safety and longevity of roadways. Understanding MR can facilitate better management of pavement performance and maintenance, making it critical for modern civil engineering.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Resilient Modulus (MR)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Ratio of recoverable strain to applied stress under repeated loading.
Detailed Explanation
The resilient modulus (MR) is defined as the ratio between the recoverable strain and the applied stress when a material is subjected to repeated loading. This means that when you apply a load to a bituminous mix, it will deform. Some of this deformation (strain) can be recovered once the load is removed, which is crucial for understanding how flexible pavements behave under conditions like traffic loads. The MR provides an important measure of the stiffness and elasticity of the pavement material.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the MR like a sponge. When you press down on a sponge (applying load), it squeezes and deforms (strain), but when you let go, it quickly returns to its original shape. The amount of deformation that can be recovered compared to how much you pressed down on it gives you an idea of its elasticity.
Importance of Resilient Modulus in Design
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Commonly used in pavement structural design.
Detailed Explanation
The resilient modulus is a critical parameter used in the design of pavement structures. Engineers use MR to predict how pavements will respond to the stresses induced by traffic loads. A higher MR indicates a stiffer material that can better resist deformation, while a lower MR suggests the material is more prone to permanent deformation under traffic. Understanding MR helps in choosing suitable materials and designing pavements that are safe, durable, and cost-effective.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a bridge. If you know how much weight the bridge can support (analogous to MR), you can decide how thick and sturdy the materials need to be to ensure it lasts for many years without sagging or breaking under the load of vehicles.
Key Concepts
-
Resilient Modulus (MR): The ratio that helps in understanding the recoverable strain of bituminous mixes.
-
Importance of MR: Critical for pavement design and longevity.
-
Measurement Methods: Various tests like dynamic tests help in determining MR.
Examples & Applications
Example of a flexible pavement using bituminous mixes where MR is crucial in ensuring the surface remains intact under high traffic.
In regions with extreme temperatures, determining MR helps in choosing the right pavement materials to prevent deformation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To keep the streets smooth and bright, MR makes the pavement right.
Stories
Imagine a tire rolling over a soft surface. If the material can bounce back, that's MR in action helping the pavement survive.
Memory Tools
MR = 'M' for Modulus and 'R' for Recovery—think of it as returning back to its form!
Acronyms
REMEMBER
MR - Means Recovery Modulus
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Resilient Modulus (MR)
The ratio of recoverable strain to applied stress under repeated loading for bituminous mixtures.
- Bituminous Mix
A composite material used in pavement layers, primarily made of bitumen and aggregates.
- Stress
Force applied per unit area within materials.
- Strain
Deformation per unit length resulting from stress.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
