Time-Temperature Superposition Principle
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Basics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about a crucial principle in asphalt engineering known as the Time-Temperature Superposition Principle. This principle allows us to use short-term test data to predict how bituminous mixes behave over much longer periods.

Why can't we just conduct long-term tests directly instead?

Great question! Long-term tests can be impractical and time-consuming. By using this principle, we can extrapolate from short tests, saving both time and resources!
Applications in Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Engineers leverage this principle extensively in pavement design. For instance, through short-term tests we can establish a master curve, which represents the modulus over different temperatures and loading times.

Can you explain what a master curve is?

Absolutely! A master curve provides a comprehensive view of material behavior that can be applied across varying conditions. It visualizes how temperature influences material properties.

How do we typically generate this master curve?

We often start by conducting Dynamic Shear Rheometer tests. Collecting data at various temperatures allows us to model the behavior efficiently.
The Science Behind the Principle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The principle harnesses rheological properties. As temperature increases, materials often behave differently, which we can quantify through time-temperature correlations.

What happens to the mix at higher temperatures?

At higher temperatures, the mixes become more viscous and may lose some structural integrity over time, leading to challenges such as rutting during summer conditions.

Does this affect the longevity of pavements?

Yes! By understanding this relationship, we can optimize mix designs to ensure better longevity and performance under varying environmental conditions.
Real-World Implications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Understanding this principle is essential for anticipating how roads will evolve over time. For instance, we can predict how asphalt may deform or crack based on seasonal temperature changes.

How does this affect our maintenance strategies?

Great link! By using predictions based on this principle, we can make informed decisions on when maintenance should occur, effectively extending the service life of pavements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This principle simplifies the analysis of bituminous materials by enabling engineers to predict long-term performance based on short-term rheological data. It is instrumental in estimating the impact of temperature variations on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures.
Detailed
Time-Temperature Superposition Principle
The Time-Temperature Superposition Principle is a fundamental concept in the study of bituminous mixes. This principle asserts that the complex behavior of these materials can be extrapolated over longer periods by using data obtained from shorter duration tests. By modifying the effects of temperature and time, it provides engineers with a reliable approach to predict how bituminous materials will perform under various conditions. The principle is crucial as it simplifies testing and aids in designing pavements that properly account for seasonal temperature variations and traffic loads.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Time-Temperature Superposition
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Enables the prediction of mix behavior over long durations using short-term tests.
Detailed Explanation
The Time-Temperature Superposition Principle is a concept that allows engineers and material scientists to predict how bituminous mixes will behave over extended periods (long durations) based on short-term tests. Essentially, this principle suggests that temperature and time can be treated as interchangeable, allowing us to simulate the long-term performance of materials by observing their response to short-term conditions. This is particularly useful because testing a material for an extended period can be time-consuming and impractical.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you want to know how a piece of fruit, like an apple, will taste after being stored for a long time. Instead of waiting weeks to see how it ages, you could take a small piece and observe how it reacts when put in different temperatures for a short time. If you notice that colder temperatures keep it fresher, you can predict that the whole apple will also stay fresh longer if it’s kept cold. This is similar to how the Time-Temperature Superposition works, using short-term observations to understand long-term behaviors in materials.
Key Concepts
-
Time-Temperature Superposition Principle: A method to predict long-term asphalt behavior based on short-term tests.
-
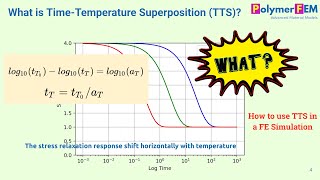
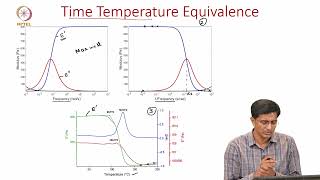
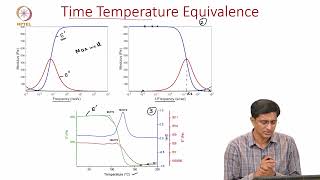
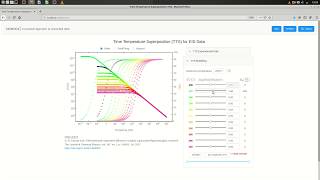
Master Curve: A plot showing the relationship between material properties and temperature/load.
-
Dynamic Shear Rheometer: A device for assessing material rheology crucial for understanding bituminous behavior.
Examples & Applications
Using the Time-Temperature Superposition Principle, engineers can predict how a road will behave under both summer and winter conditions by applying short-term viscosity test results to long-term stress scenarios.
When creating an asphalt mix for a highway expected to withstand high-temperature traffic, engineers may adjust the binder properties based on data generated from Dynamic Shear Rheometer tests.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the road gets hot, and time flies by, Use short tests to guess how long it'll lie.
Stories
Imagine a tire on a hot summer road. With the Time-Temperature Superposition Principle, engineers can predict how long it will last based on quick tests in cool conditions.
Memory Tools
Remember 'TIME' to think of Time-Temperature: T = Temperature, I = Immediate properties, M = Master curve, E = Extrapolation of data.
Acronyms
Use 'PREDICT' to recall
= Performance
= Results from short tests
= Extrapolate
= Data
= Impact of temperature
= Combined properties
= Time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- TimeTemperature Superposition Principle
A principle that allows predictions of material behavior over long durations using short-term test results by considering temperature and time effects.
- Master Curve
A graphical representation combining the effects of temperature and loading on the material properties of bituminous mixes.
- Dynamic Shear Rheometer
An instrument used to measure the rheological properties of materials by applying controlled shear stress.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
