Stress-Strain Behavior of Bituminous Mixes
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Elastic, Viscous, and Viscoelastic Behavior
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing the stress-strain behavior of bituminous mixes. First, can anyone explain what elastic behavior is in this context?

Elastic behavior is when the material returns to its original shape after the load is removed.

Exactly! This occurs at low temperatures and high loading rates. Now, what about viscous behavior? Who wants to define that?

Viscous behavior happens at high temperatures, right? The mix deforms permanently under a load.

Correct! Viscous materials like fluids retain their shape under constant stress. Now, let’s talk about viscoelastic behavior. Why do we consider it important?

Viscoelastic behavior shows time-dependent strain recovery, which is more realistic for bituminous materials.

Great summary! Remember the acronym EIV for Elastic, Inelastic, and Viscous behaviors. It encapsulates our three main behavior types!
Stress Relaxation and Creep
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to stress relaxation. Can anyone tell me what this means?

Stress relaxation occurs when a constant strain leads to decreasing stress over time.

Right! And how is this different from creep, Student_4?

Creep is when a constant stress results in increasing strain over time.

Exactly! These behaviors are crucial for understanding how pavements will perform under various loads. Now, let’s remember: S for Stress Relaxation and C for Creep!
Importance of Stress-Strain Behavior
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, why is it vital to understand the stress-strain behavior of bituminous mixes?

It helps predict how these materials will respond to traffic loads and environmental changes.

Great point! Predicting performance ensures road safety and longevity. What factors do you think influence these behaviors?

Temperature and loading rates definitely seem to play a role.

Right again! Understanding the interplay of these factors helps engineers design better flexible pavements. Summary: The knowledge of stress-strain behavior is crucial for infrastructure resilience!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
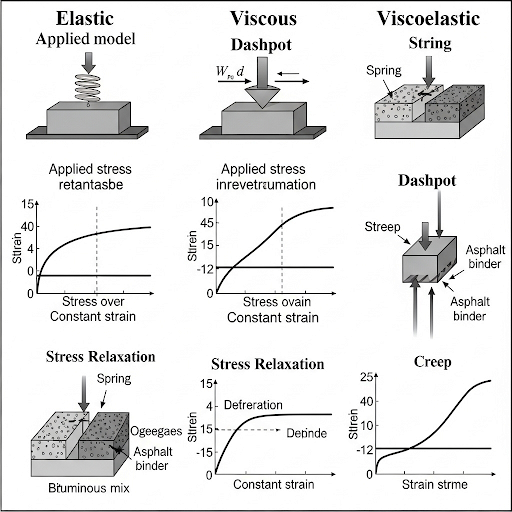
Bituminous mixes exhibit varying stress-strain behavior influenced by temperature, loading rate, and mix composition. The section outlines elastic, viscous, and viscoelastic behaviors, alongside stress relaxation and creep phenomena, emphasizing their significance in the mechanical behavior of flexible pavements.
Detailed
Stress-Strain Behavior of Bituminous Mixes
Bituminous mixes are essential for pavement structures, displaying a complex stress-strain behavior that can vary under different conditions. This section discusses:
1. Elastic, Viscous, and Viscoelastic Behavior
- Elastic Behavior: Observed at low temperatures and high loading rates; deformation is recoverable.
- Viscous Behavior: Seen at high temperatures or with slow loading; this results in permanent deformation.
- Viscoelastic Behavior: The mix exhibits time-dependent strain recovery under intermediate conditions, representing realistic material behavior.
2. Stress Relaxation and Creep
- Stress Relaxation: Under constant strain, the stress decreases over time.
- Creep: When a constant stress is applied, strain increases over time.
These behaviors are analyzed through creep compliance and relaxation modulus functions, critical for evaluating the performance of bituminous mixes under traffic loads.
Understanding these behaviors is vital for predicting the performance of flexible pavement structures, ensuring safety, durability, and service quality.
Youtube Videos










Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Stress-Strain Behavior
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bituminous mixes exhibit complex stress-strain behavior due to their heterogeneous and composite nature. The stress-strain response is influenced by temperature, loading rate, and the composition of the mix.
Detailed Explanation
The stress-strain behavior of bituminous mixes refers to how these materials respond when pressure or stress is applied. This behavior is complex because bituminous mixes are not uniform; they have various components that interact differently under force. Several factors influence this response, including temperature (a higher temperature can make the material softer), the speed at which the load is applied (fast loads can cause different reactions compared to slow loads), and the specific ingredients that make up the mix (different aggregates or binders can alter performance).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. When you squeeze it (applying stress), how it reacts depends on how quickly or slowly you are squeezing and how hot or cold it is. A dry, cold sponge will be firmer and resist squeezing more than a warm, wet sponge that gives way easily. Similarly, bituminous mixes react based on their environmental conditions and composition.
Elastic, Viscous, and Viscoelastic Behavior
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Elastic behavior: At low temperatures and high loading rates, bituminous mixes behave elastically. The deformation is recoverable.
• Viscous behavior: At high temperatures or slow loading, mixes behave like viscous fluids, and deformation is permanent.
• Viscoelastic behavior: Under intermediate conditions, the mix shows time-dependent strain recovery—this is the most realistic representation of bituminous material behavior.
Detailed Explanation
Bituminous mixes can exhibit three main behaviors depending on the conditions:
- Elastic behavior occurs when the mix is at low temperatures or subjected to high forces quickly. Here, if you were to relieve the stress, the mix would return to its original shape, much like a rubber band.
- Viscous behavior happens at high temperatures or with slow loading. The mixes behave like thick liquids, meaning when you stress them, they don’t return to their original form. Imagine warming honey; when you pour it, it flows and takes a shape, but it won't spring back when you stop pouring.
- Viscoelastic behavior is a mix of the two above and is the most common state for these materials under real conditions. They exhibit both recoverable and permanent deformations over time, depending on the exact conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Picture working with a piece of dough: when you press it lightly against the counter (akin to low stress), it easily bounces back (elastic behavior). If you try to stretch it very slowly while baking (high temperature), it will start deforming permanently (viscous behavior). If you stretch it briskly right after it has warmed, it will change shape, but then it can regain some of its form after a bit of time (viscoelastic behavior).
Understanding Stress Relaxation and Creep
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Stress Relaxation: A constant strain results in decreasing stress over time.
• Creep: A constant stress causes increasing strain over time.
• These behaviors are analyzed using creep compliance and relaxation modulus functions.
Detailed Explanation
Stress relaxation and creep are important phenomena to understand in bituminous mixes:
- Stress relaxation occurs when you hold a material in a stretched position (constant strain); over time, you will notice that the force you exert decreases even though you are not changing the amount you are stretching it. This means the material is adjusting to the stress it’s under.
- Creep is the opposite. When you apply a consistent weight (constant stress) to a material, over time, the material will continue to deform (strain) more and more. So, the longer you apply that weight, the greater the change in shape will be.
These behaviors are crucial for predicting how a pavement will perform over time under load.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a heavy bag of groceries. If you hang it from a hook (applying stress), at first it feels heavy, but after some time, the hook and the bag adjust slightly, and it may not feel as heavy anymore (stress relaxation). If you leave the groceries sitting on a counter, gradually, you may notice the counter sagging under the weight (creep).
Key Concepts
-
Elastic Behavior: Behavior where deformation is recoverable at low temperatures.
-
Viscous Behavior: Permanent deformation occurs at high temperatures under slow loading.
-
Viscoelastic Behavior: Represents realistic material behavior under intermediate conditions.
-
Creep: Increases strain over time under constant stress.
-
Stress Relaxation: Decreasing stress under constant strain over time.
Examples & Applications
Example of elastic behavior: When a rubber band returns to its original shape after being stretched.
Example of viscous behavior: Honey flows and retains its new shape when poured out of the jar.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Under stress we learn the best, Elastic bends but doesn't rest, Viscous flows, takes its test, Viscoelastic is the mix that’s blessed.
Stories
Imagine a rubber band on a cold day; as you stretch it, it snaps back. On a hot day, it stays stretched and doesn’t revert easily—this is how bituminous mixes behave differently based on temperature!
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym EIV: Elastic (recovers), Inelastic (permanent), and Viscous (flows like water) to keep behavior types straight.
Acronyms
To remember stress-strain behaviors, think of the word 'SCR'
Stress Relaxation decreases stress
Constant strain leads to stress changes
and Remember how materials behave.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Elastic Behavior
The property of a material that allows it to return to its original shape after deformation when the load is removed.
- Viscous Behavior
The behavior of materials that deform permanently under sustained loads, similar to liquids.
- Viscoelastic Behavior
A time-dependent deformation characteristic of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic properties.
- Creep
The gradual increase in strain of a material under constant stress over time.
- Stress Relaxation
The decrease in stress experienced by a material under constant strain over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
