Stiffness and Modulus of Bituminous Mixes
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Dynamic Modulus (|E|)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss dynamic modulus, which is essential for assessing the stiffness of bituminous mixes during cyclic loading. Does anyone know what affects the dynamic modulus?

Is it dependent on temperature and how fast the load is applied?

Exactly! Dynamic modulus is influenced by both temperature and loading frequency. This means that as conditions change, so does the stiffness of our mixes. Remember: **Dynamo** = **D**ynamic **M**odulus & **E**ffects of temperature and frequency.

How is it actually measured?

Good question! It's obtained from Simple Performance Tests. These tests help simulate real-life conditions for our mixes.

So, it's crucial for predicting performance, right?

Absolutely! Predicting how mixtures will perform under different loads is essential for effective pavement design.

In summary, the dynamic modulus is key for understanding how bituminous mixes behave, influenced by both temperature and loading frequency.
Resilient Modulus (MR)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into the resilient modulus, symbolized as MR. Who can tell me what resilient modulus measures?

Is it the recoverable strain in relation to applied stress?

Exactly! MR is the ratio of recoverable strain to the applied stress during repeated loading. This modulus is particularly crucial for understanding how pavement materials behave structurally.

Why is it so important in design?

Great question! It helps engineers design pavements that can withstand varying loads without permanent deformation. Remember, high MR means better resilience.

Can you give an example of where this is applied?

Sure! It's commonly used in structural design analyses to ensure that pavements endure repeated stresses without failure.

To summarize, the resilient modulus helps determine the dynamic response of pavement materials, making it pivotal in structural design.
Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s turn our focus to the Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus, or ITSM. What do we know about this modulus?

It helps measure stiffness when applying indirect tensile loading, right?

Exactly! The ITSM gives us an idea of how a bituminous mix behaves under tension. Its formula is quite interesting—can anyone recall it?

Is it something like peak load times sample thickness over...horizontal deformation times sample diameter squared?

Spot on! ITSM = \(\frac{\text{peak load} \times \text{sample thickness}}{\text{horizontal deformation} \times \text{sample diameter}^2}\). This relationship is crucial for evaluating tensile properties.

Why is understanding ITSM important?

Understanding ITSM is vital for predicting cracking and determining the overall durability of the mix. A higher ITSM typically signifies a stiffer mix, which can be advantageous.

In conclusion, ITSM is a key factor in assessing the tensile performance of bituminous mixes, guiding us in effective pavement design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section covers the stiffness of bituminous mixes, which is crucial for understanding their behavior under loads. It explains dynamic modulus, resilient modulus, and indirect tensile stiffness modulus, highlighting their significance in pavement design. Also, it connects the stiffness of bituminous materials to factors like temperature and loading frequency.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Stiffness is the measure of a bituminous mix's ability to resist deformation when subjected to loads. This section specifically examines three critical types of modulus:
- Dynamic Modulus (|E|): It indicates the stiffness of bituminous mixes during cyclic loading and varies with factors like temperature and loading frequency. This modulus is essential for predicting material response and is determined through Simple Performance Tests (SPT).
-
Resilient Modulus (MR): Defined as the ratio of recoverable strain to the applied stress under repeated loading. This modulus is vital for pavement structural design as it reflects the material's elasticity and resilience under loading conditions.
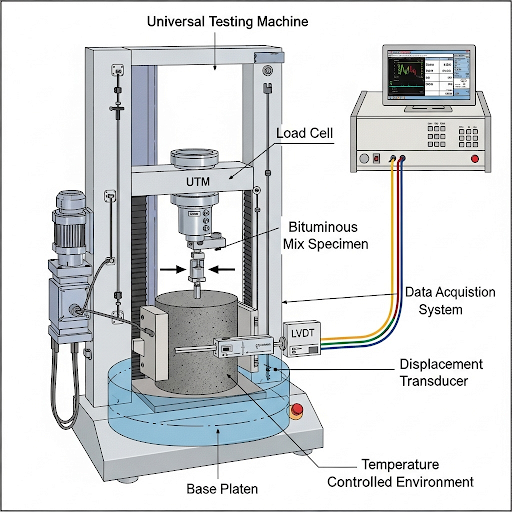
- Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM): This modulus assists in gauging stiffness under indirect tensile loading conditions. The formula for ITSM is:
\[\text{ITSM} = \frac{\text{peak load} \times \text{sample thickness}}{\text{horizontal deformation} \times \text{sample diameter}^2}\]
Together, these moduli provide insight into the mechanical behavior of bituminous mixes, influencing the design and maintenance of flexible pavements.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Stiffness Definition
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Stiffness is the ability of the bituminous mix to resist deformation under applied loads.
Detailed Explanation
Stiffness is a measure of how much a material deforms when a load is applied to it. In the context of bituminous mixes used in pavements, stiffness indicates how well the pavement can maintain its shape when vehicles pass over it. A stiffer mix will resist deformation better than a less stiff one, leading to improved durability and longevity of the pavement.
Examples & Analogies
Think of stiffness like the support of a mattress. A firm mattress resists body weight effectively and maintains its shape, providing good support, just as a stiff bituminous mix supports traffic loads without deforming significantly.
Dynamic Modulus (|E|)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Indicates the stiffness of bituminous mixes under cyclic loading.
• Depends on temperature and loading frequency.
• Obtained from Simple Performance Tests (SPT).
Detailed Explanation
The dynamic modulus represents how stiff a bituminous mix is when it is subject to changing loads, like those caused by moving vehicles. This stiffness is not constant; it changes based on the temperature of the mix and how fast the load is applied. Simple Performance Tests are used to measure this dynamic modulus and help engineers design pavements that will perform well under expected traffic conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine stretching a rubber band. If you pull it slowly, it stretches easily; if you pull it quickly, it feels stiffer. Similarly, the dynamic modulus captures how the mix responds to slow and fast loading conditions at different temperatures.
Resilient Modulus (MR)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Ratio of recoverable strain to applied stress under repeated loading.
• Commonly used in pavement structural design.
Detailed Explanation
The resilient modulus is a parameter that measures how well a bituminous mix can return to its original shape after it has been deformed by stress, such as the weight of vehicles. It shows the relationship between stress applied to the mix and the strain (deformation) it undergoes. This measure is crucial in structural design because it helps engineers determine how mixes will behave under repeated traffic loads.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. When you squeeze it (apply stress), it compresses (deforms). When you release it, it bounces back to its original shape (recoverable strain). The resilient modulus is like measuring how effectively that sponge returns to shape after each squeeze.
Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Used to determine stiffness under indirect tensile loading.
• ITSM = peak load × sample thickness / (horizontal deformation × sample diameter²).
Detailed Explanation
The Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus is used to assess the stiffness of a bituminous mix when it experiences tensile (stretching) forces indirectly. It provides a formula to calculate stiffness based on how much the sample deforms when a load is applied. This measurement is particularly useful for understanding how well the mix can withstand forces that pull it apart.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine stretching a piece of elastic fabric. When you pull on it from both ends, it stretches. If you measure how much it stretches compared to how much force you're applying, you can gauge its stiffness. Similarly, the ITSM provides a way to measure stiffness under indirect tensile conditions.
Key Concepts
-
Dynamic Modulus: A measure of stiffness of bituminous materials under dynamic loading conditions.
-
Resilient Modulus: Key metric for evaluating the elasticity and recoverability of bituminous mixes.
-
Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus: Measures stiffness under indirect tension, influential in assessing mix durability.
-
Stiffness: The capacity of materials to resist deformation when stressed.
Examples & Applications
An asphalt pavement designed for heavy traffic will utilize a higher resilient modulus to ensure durability under constant load.
Dynamic modulus test results for different temperature conditions will help predict how the asphalt behaves in hot versus cold climates.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To measure stiffness, we must see, the dynamic modulus is key, under load that's cyclic and free.
Stories
Imagine building a road where heavy trucks roll every day. The dynamic modulus ensures it won't sway, while the resilient modulus keeps cracks at bay.
Memory Tools
For remembering the types of modulus: 'D R I', dynamic, resilient, indirect tensile.
Acronyms
Remember 'DRI' for the three moduli
Dynamic
Resilient
Indirect Tensile.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dynamic Modulus (|E|)
A measure of stiffness of bituminous mixes under cyclic loading, influenced by temperature and loading frequency.
- Resilient Modulus (MR)
The ratio of recoverable strain to applied stress under repeated loading, important for pavement design.
- Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
A calculation to determine stiffness under indirect tensile loading, using peak load and deformation of a sample.
- Stiffness
The ability of a material to resist deformation under applied loads.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
