Mechanism of Moisture Damage
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Moisture Damage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss the mechanism of moisture damage in bituminous mixes. Can anyone tell me what happens when water infiltrates a pavement?

Does it weaken the bond between the bitumen and the aggregate?

Exactly! When moisture enters, it disrupts this bond. This can result in pavement issues like stripping and potholes. Remember the acronym 'BRAP': Bond Rupture from Adhesion and Moisture Penetration.

What is stripping?

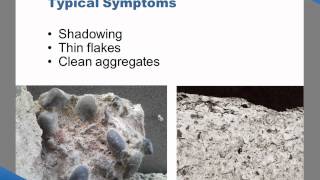
Stripping occurs when the asphalt binder detaches from aggregate due to moisture. It's a major concern because it can lead to raveling and loss of surface integrity.

So, is raveling the loss of the surface of the pavement?

Yes! Raveling can lead to further problems if not addressed. The key takeaway here is that moisture can severely compromise pavement performance.

In summary, moisture damage can lead to significant pavement distress like stripping, raveling, and potholes, reinforcing the need for proper design and testing.
Moisture Sensitivity Tests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore how we can evaluate moisture sensitivity in bituminous mixes. What tests can we use?

I've heard of the Tensile Strength Ratio (TSR) test?

Correct! The TSR test measures the retained strength of a mix after water exposure. It’s vital for assessing how well the mix will perform under wet conditions.

What other tests can help us assess stripping potential?

Excellent question! Besides TSR, we also have the Boiling Water Test and the Rolling Bottle Test. Both are useful for evaluating stripping susceptibility.

Why is it important to carry out such tests?

Testing ensures we select materials that adhere well to prevent moisture damage, enhancing pavement longevity. In summary, conducting moisture sensitivity tests like the TSR, Boiling Water, and Rolling Bottle is critical for guaranteeing pavement durability.
Mitigating Moisture Damage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss how to mitigate moisture damage in bituminous mixes. Why do you think we need to plan for that?

To prolong the life of the pavement, right?

Exactly! One way to do this is by using anti-stripping agents. Can anyone name one?

Is hydrated lime one of those agents?

Yes! Hydrated lime enhances the bonding between the aggregate and binder, effectively reducing moisture susceptibility.

What about aggregate coating?

Great point! Improved aggregate coating and surface texture helps to ensure the asphalt binder adheres properly. Remember, good practices in the mix design can mitigate moisture damage effectively.

In summary, strategies for mitigating moisture damage in bituminous mixes include using anti-stripping agents, enhancing aggregate coatings, and proper mix design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The mechanism of moisture damage in bituminous mixes involves water infiltration disrupting the adhesive bond between bitumen and aggregate. This disruption can lead to stripping, raveling, and the formation of potholes, posing significant challenges for pavement integrity.
Detailed
Mechanism of Moisture Damage in Bituminous Mixes
Moisture damage is critical in maintaining the performance of bituminous pavements. Water infiltration can significantly weaken the adhesive bond between the binder (bitumen) and aggregate particles. When this bond is compromised, various forms of moisture-related distress ensue, such as stripping, where the asphalt film separates from the aggregate; raveling, which is the loss of aggregate particles from the surface; and the formation of potholes, which represent severe localized failure.
Understanding the mechanisms of moisture damage is essential for pavement engineers to develop strategies for mitigating these effects, such as employing moisture sensitivity tests and utilizing anti-stripping agents or better mix designs. This section underscores the importance of using appropriate tests like the Tensile Strength Ratio (TSR) to assess potential stripping and ensure the long-term durability of flexible pavements.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Water Infiltration and Adhesive Bond Breakdown
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Water infiltration breaks the adhesive bond between binder and aggregate.
Detailed Explanation
Moisture damage begins when water seeps into the pavement structure. This water can penetrate through cracks or voids, reaching the interface where the bitumen (binder) meets the aggregates (stones). Normally, this bitumen binds the aggregates firmly together. However, the presence of water compromises this bond, weakening the adhesive properties. Over time, this leads to a significant reduction in the structural integrity of the bituminous mix, making the pavement vulnerable to failure.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a piece of tape holding two pieces of paper together. If you apply water to that tape, it might weaken the adhesive properties, causing the papers to separate. Similarly, when water infiltrates the bond between the binder and aggregates, the pavement loses its cohesive strength, leading to deterioration.
Consequences of Moisture Damage
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Can cause stripping, raveling, and potholes.
Detailed Explanation
As the adhesive bond between the binder and aggregate deteriorates, several forms of distress can occur. Stripping refers to the loss of bitumen from the aggregate surfaces, leading to bare aggregate and weaker pavement. Raveling happens when loose aggregates start to separate from the mix, creating a rough surface. This process can accelerate, eventually leading to the formation of potholes—depressions in the pavement that can drastically hinder vehicle movement and increase maintenance costs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sturdy road as a well-built sandwich. The bread (binder) holds all the tasty fillings (aggregates) together. If a condiment (water) seeps into the sandwich, it can make the bread soggy, causing the sandwich to fall apart. This is similar to how moisture damage affects pavement, leading to breaking up of the surface and creating problems like potholes.
Key Concepts
-
Moisture Damage: Refers to the weakening of the bond between bitumen and aggregate, caused by water infiltration.
-
Stripping: A specific form of moisture damage resulting in the separation of asphalt binder from aggregate.
-
Moisture Sensitivity Testing: Methods to evaluate the effects of moisture on the performance of bituminous mixtures.
Examples & Applications
In colder climates, water can infiltrate cracks in asphalt, freeze, and expand, leading to additional cracking and pothole formation.
Use of hydrated lime in asphalt mixes has been shown to improve bonding and reduce stripping, particularly in wet conditions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When moisture creeps into the mix, Be careful, it can cause some tricks; Stripping, raveling, and potholes too, Protect your pavement—it's up to you!
Stories
Once in a town, a new road was laid down. The rain came pouring, and the road felt the frown. Moisture seeped in, the bond it would break, Soon the pavement started to shake!
Memory Tools
Remember 'MRS' for moisture issues: M for Moisture, R for Raveling, S for Stripping.
Acronyms
BRAP
Bond Rupture from Adhesion and Moisture Penetration.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Moisture Damage
A weakening of the adhesive bond between bitumen and aggregate due to water infiltration, leading to pavement distress.
- Stripping
The detachment of asphalt binder from aggregate particles precipitated by moisture.
- Raveling
The loss of aggregate particles from the pavement surface, often as a result of moisture damage.
- Tensile Strength Ratio (TSR)
A test that evaluates the retained strength of a mix after being exposed to water.
- Boiling Water Test
A method for assessing moisture susceptibility in bituminous mixes by boiling the sample in water.
- Rolling Bottle Test
A laboratory test used to assess the stripping potential of asphalt-aggregate mixtures.
- Antistripping Agents
Additives used to improve the adhesion between asphalt binder and aggregates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
