Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ITSM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we are going to discuss the Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus, commonly referred to as ITSM. Can anyone tell me why stiffness is important for bituminous mixes in pavements?

I think it helps in understanding how well the pavement can handle loads and resist deformation, right?

Exactly! Stiffness is crucial as it relates to the pavement's durability and load-bearing capacity. Now, do you know how we calculate ITSM?

Is it connected to stress and deformation?

Yes, it is! ITSM is calculated using the formula: Peak Load multiplied by Sample Thickness, divided by the product of Horizontal Deformation and Sample Diameter squared. Remember it as 'PH/HD²' for easier recall! Let's proceed with how the factors in the formula influence its value.
ITSM Calculation and Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To get more familiar, when we perform the ITSM test, what does the peak load represent?

I believe it's the maximum load that the sample can withstand before deforming?

Correct! Now, consider what happens if we increase the sample's thickness. How might this affect ITSM?

If thickness increases, won’t ITSM also increase since we multiply by thickness in the formula?

Spot on! Higher thickness leads to increased ITSM, indicating greater stiffness. It’s essential to ensure that pavements respond adequately under traffic loads. Who can summarize why ITSM matters for pavement design?

It helps evaluate how bituminous mixes will perform and resist deformation, which ultimately affects pavement life!
Real-world Application of ITSM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s think about the practical aspect of ITSM. How do you think engineers use this modulus in real-world applications?

I guess they must use it when designing new roads or repairing existing ones to decide what materials to use?

Absolutely! Understanding the ITSM helps engineers select appropriate materials and predict pavement behavior over time. Can you think of any consequences if ITSM values are miscalculated?

If it's too low, it might lead to pavement failure or cracking?

Exactly, and that can cause serious safety issues and higher maintenance costs. Great job, everyone! Remember, ITSM is critical for assessing how well bituminous mixes will perform under stress.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) is a vital measure used to assess the stiffness of bituminous mixes subjected to indirect tensile loading. The ITSM is calculated using the peak load applied to a sample and the resulting horizontal deformation, providing important insight into the material's performance characteristics under structural loads, which directly impacts pavement durability and service life.
Detailed
Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
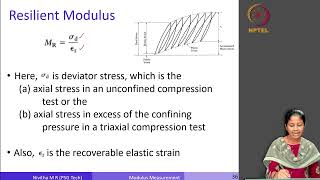
The Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) is a critical parameter used in the evaluation of the mechanical properties of bituminous mixes. It serves to determine the stiffness of a material when subjected to indirect tensile loading—a condition that closely mimics the stresses experienced by pavements during service. The ITSM is calculated using the following formula:
ITSM = (Peak Load × Sample Thickness) / (Horizontal Deformation × Sample Diameter²)
This formula highlights how the ITSM is influenced by three key variables: the magnitude of the applied load, the thickness of the sample, and the amount of horizontal deformation observed during testing. Understanding the ITSM helps engineers predict the behavior of bituminous mixes under road conditions, and it plays a crucial role in designing pavements that can withstand traffic loads and environmental factors, thereby extending the service life of roadways.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Used to determine stiffness under indirect tensile loading.
Detailed Explanation
The Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM) is a measure used to evaluate the stiffness of bituminous mixes specifically when they are subjected to indirect tensile loading. Indirect tensile testing provides information about how well the material can withstand tensile forces that act perpendicular to the direction of loading. This is important because it reflects the material's ability to perform under real-world conditions, where tensile stresses can lead to cracking.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a stretchy rubber band. When you pull it, it stretches but can also return to its original shape if not pulled too hard. In this analogy, the ITSM tells us how 'stiff' the rubber band is and how well it can handle stretching without breaking, which relates to how bituminous mixes perform under the stresses of traffic.
ITSM Calculation Formula
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• ITSM = peak load × sample thickness / (horizontal deformation × sample diameter²).
Detailed Explanation
To calculate the Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM), a specific formula is used that incorporates several key parameters: the peak load applied during the test, the thickness of the sample, the horizontal deformation that occurs during loading, and the diameter of the sample. This formula helps quantify how much the material deforms under a certain load relative to its dimensions. The stiffer the material, the higher the ITSM value, indicating its resistance to deformation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of squeezing a sponge. If you apply a certain force (the peak load), the sponge (the sample) changes shape (horizontal deformation). If the sponge is thick and sturdy, it will resist deformation well, leading to a higher 'stiffness' value according to the ITSM formula. The calculations mimic how we assess how well materials hold up under pressure.
Key Concepts
-
Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM): A measure for stiffness under indirect tensile loading in bituminous mixes.
-
Calculation Formula: ITSM = Peak Load × Sample Thickness / (Horizontal Deformation × Sample Diameter²).
-
Importance of ITSM: Indicates how well pavements can withstand loads and the potential for deformation and cracking.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: A bituminous mix with a peak load of 2000 N, a thickness of 50 mm, horizontal deformation of 2 mm, and a diameter of 150 mm; calculate ITSM.
Example 2: If a pavement shows a low ITSM value, what implications might this have for its expected lifespan and performance under traffic.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
ITSM helps to measure, stiffness is a treasure, under load it must endure, for pavements to stay secure.
Stories
Imagine a road testing day where samples of pavement stand tall under mighty loads. With ITSM, we see their strength—like a knight that must endure the blows of heavy steeds.
Memory Tools
To remember the formula for ITSM, think 'Push The Diameter to the Side', where Push is Peak Load, Thickness is Time, and Diameter is Down.
Acronyms
Remember ITSM as 'I Test Stiffness in Materials'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
A measure used to determine the stiffness of bituminous mixes under indirect tensile loading.
- Peak Load
The maximum load applied to a material in a test.
- Horizontal Deformation
The change in width or horizontal dimension of a sample when it is subjected to loading.
- Sample Thickness
The vertical height of the material sample used in the stiffness test.
- Sample Diameter
The horizontal measurement across the cylindrical test sample in the ITSM test.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
